Patient Story
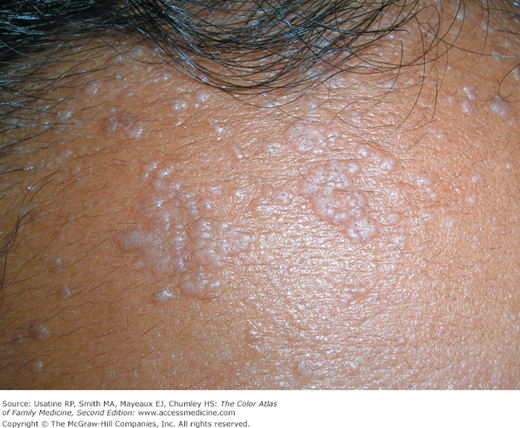
A 16-year-old girl presents with multiple flat lesions on her forehead (Figure 132-1). It started with just a few lesions but has spread over the past 3 months. She is diagnosed with flat warts and topical imiquimod is prescribed as the initial treatment.
Introduction
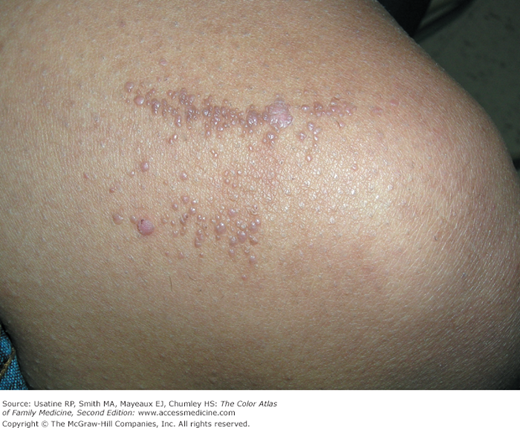
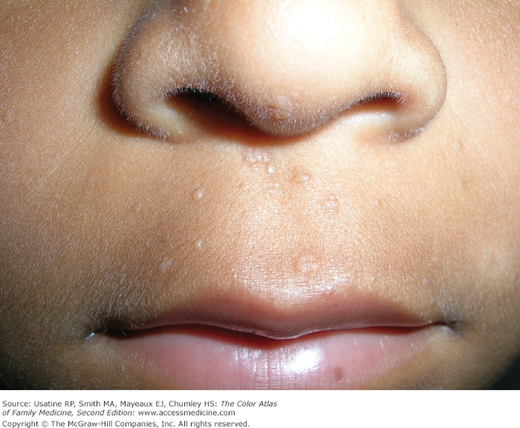
Flat warts are characterized as flat or slightly elevated flesh-colored papules. They may be smooth or slightly hyperkeratotic. They range in size from 1 to 5 mm or more, and numbers range from a few to hundreds of lesions, which may become grouped or confluent. They occur most commonly on the face, hands, and shins. They may appear in a linear distribution as a result of scratching, shaving, or trauma (Koebner phenomenon) (Figure 132-2).
Epidemiology
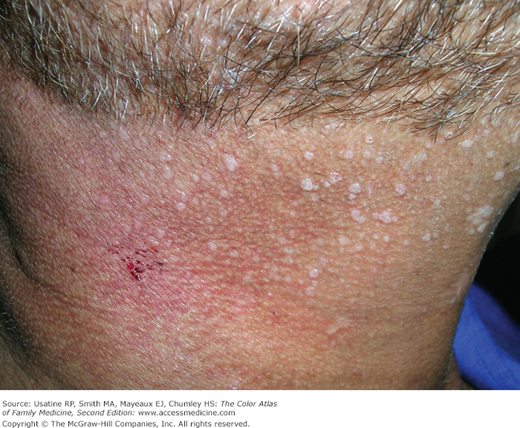
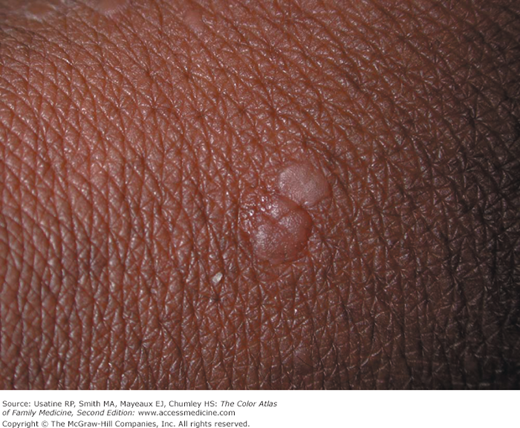
- Flat warts (verruca plana) are most commonly found in children and young adults (Figures 132-1, 132-2, 132-3, 132-4, and 132-5).
- Flat warts are the least common variety of wart, but are generally numerous on an individual.1
- Flat warts are usually caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) types 3, 10, 28, and 29.2
Etiology and Pathophysiology
- Like all warts, flat warts are caused by HPV.2
- Flat warts may spread in a linear pattern secondary to spread by scratching or trauma, such as shaving.
- Flat warts present a special treatment problem because they persist for a long time, they are generally located in cosmetically important areas, and they are resistant to therapy.
Risk Factors
- Shaving next to infected areas (Figures 132-2 and 132-3).
- HIV infection or other types of immunosuppression (Figure 132-3).
Diagnosis
- Multiple small, flat-topped papules that may be pink, light brown, or light yellow colored. They may be polygonal in shape (Figure 132-4).