Fibroosseous Pseudotumor
David R. Lucas, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Benign reactive ossifying fibroblastic proliferation most often affecting skin and soft tissue in digits of hands and feet
Clinical Issues
Proximal phalanx of hand most common site
Fusiform swelling, often with erythema, pain, or ulceration
Rapid onset, weeks to months
Simple excision usually curative
Image Findings
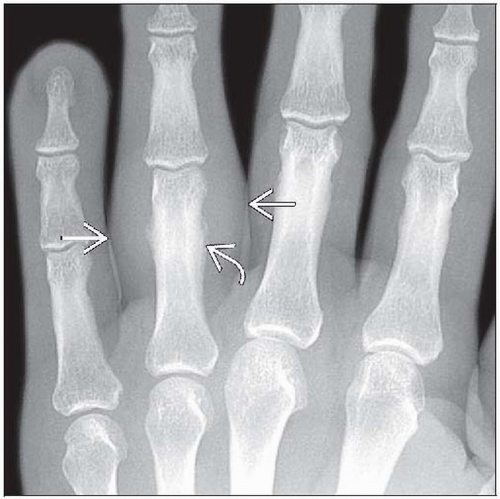
Early lesions characterized by ill-defined soft tissue density
Older lesions with intralesional calcification
Periosteal reaction common
Microscopic Pathology
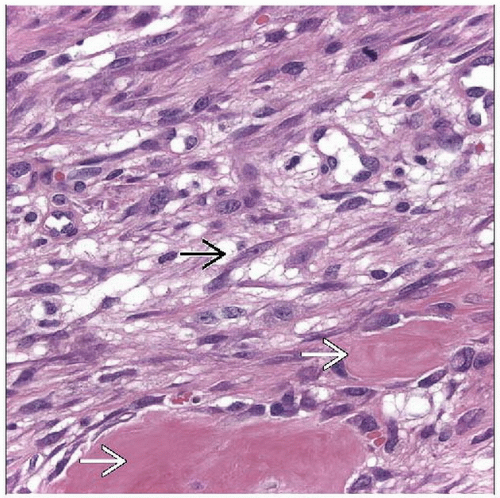
Fasciitis-like spindle cell proliferation with active ossification
Myofibroblastic spindle and stellate cells with vesicular nuclei and granular amphophilic cytoplasm
Ossification in various stages of maturation
Peripheral zonal osseous maturation present in 50%
Top Differential Diagnoses
Extraskeletal osteosarcoma
Myositis ossificans
Fracture callus
Bizarre parosteal osteochondromatous proliferation of hands and feet (Nora lesion)
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Fibroosseous pseudotumor (FP)
Synonyms
Florid reactive periostitis of tubular bones of hands and feet
Fasciitis ossificans
Panniculitis ossificans
Parosteal fasciitis
Pseudomalignant osseous tumor of soft tissues
Definitions
Benign reactive ossifying fibroblastic proliferation most often affecting skin and soft tissue in digits of hands and feet
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Reparative Reaction
Trauma
Repetitive injury
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Rare, exact incidence unknown
Age
5-75 years; median: ≈ 35 years
Gender
Slight female predominance
Site
Hands and feet
Proximal phalanx of hand most common site
Rarely occurs beyond acral extremities
Presentation
Fusiform swelling, often with erythema, pain, or ulceration
Rapid onset, weeks to months
Natural History
Benign, may be self-limited
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Simple excision usually curative
Prognosis
Excellent, rarely recurs
IMAGE FINDINGS
General Features
Early lesions characterized by ill-defined soft tissue density
Older lesions with intralesional calcification
Periosteal reaction common
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
Size
0.5-5.6 cm; median: ≈ 2 cm
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Fasciitis-like spindle cell proliferation with active ossification
Cellular areas alternate with less cellular fibromyxoid areas in lobular pattern
Myofibroblastic spindle and stellate cells with vesicular nuclei and amphophilic cytoplasm
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree