Ependymoma
Elizabeth A. Montgomery, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
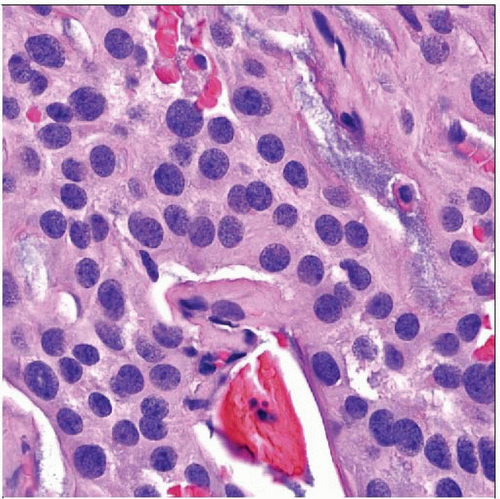
Cellular glial or epithelial-appearing neoplasm manifesting ependymal differentiation as either perivascular rosettes or true rosettes
Myxopapillary variant has pseudopapillary architecture and intercellular myxoid matrix
Synonyms: Extraspinal ependymoma, sacrococcygeal ependymoma
Microscopic Pathology
Range of cellularity
Hypocellular to “blue”
Nuclei round
Respect blood vessels
Anuclear zone around vessels composed of cell processes (pseudorosettes)
Perivascular rosettes often inconspicuous in extraspinal lesions
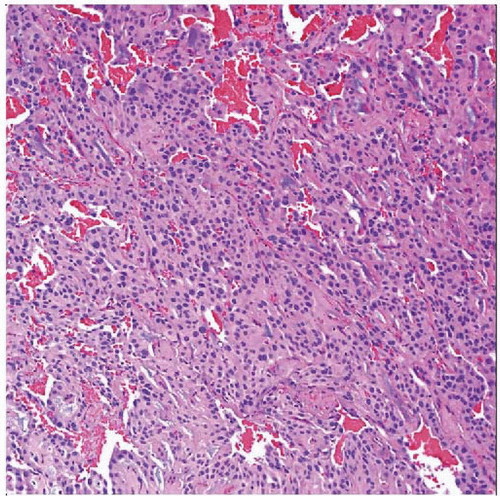 Extraspinal ependymoma appears identical to those lesions arising in the neuraxis (4th ventricle, spinal cord central canal). Note the prominent vascularity at low magnification. |
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Extraspinal ependymoma, sacrococcygeal ependymoma
Definitions
Cellular glial or epithelial-appearing neoplasm manifesting ependymal differentiation as either perivascular rosettes or true rosettes
Myxopapillary variant has pseudopapillary architecture and intercellular myxoid matrix
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Subcutaneous Sacrococcygeal Ependymomas
Believed to arise from coccygeal medullary vestige
Ependymal-lined cavity composed of remnant of caudal portion of neural tube
Presacral Ependymomas
Believed to arise from extradural remnants of filum terminale
Ependymomas of Ovary and Mediastinum
Germ cell origin postulated
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Rare
Age
Usually children and young adults
Wide range: Months to > 65 years
Gender