1. Identify and explain the key morphologic and biochemical characteristics for Eikenella corrodens. 2. Describe the normal habitat for Eikenella spp. and situations that provide optimal conditions for the opportunistic bacteria to become a pathogen. 3. Define the acronym HACEK; what organisms does this acronym refer to, and what medical conditions are associated with these organisms? 4. Define the general characteristics for Eikenella corrodens, Methylobacterium spp., Weeksella virosa, and Bergeyella zoohelcum, and explain how the organisms are distinguished from one another. 5. Describe the Gram stain characteristics for each type of bacteria listed in objective 4. 6. Identify the normal habitat for Methylobacterium and explain why the organism is frequently isolated from water distribution systems. 7. Explain how the pink colonies produced in culture by Methylobacterium spp. are differentiated from other species of bacteria capable of producing pink colonies. 8. Describe the culture techniques used to isolate Eikenella corrodens and Methyolobacterium spp. 9. Correlate patient signs, symptoms, and laboratory results to identify the most probable etiologic agent associated with the data. The organisms listed in Table 29-1 are not commonly associated with human infections, but they are occasionally encountered in clinical specimens. Eikenella corrodens is normal flora of the human oral cavity. The organism is a facultative anaerobe, nonmotile, gram-negative rod. Among the organisms considered in this chapter, it is the organism most frequently isolated and is usually found in mixed infections resulting from human bites or clenched-fist wounds. The organism can be isolated from dental plaque and has been implicated in periodontitis, osteomyelitis, bite wound infections, bacteremia, and endocarditis. It is an opportunistic pathogen predominantly in immunocompromised patients, causing abscesses and infections, and may lead to death. Patients with diabetes are often at risk for Eikenella infections as a result of the daily microtrauma to their skin via glucose monitoring, insulin injections, and the potential for introduction of the organism from oral secretions by licking or biting their skin. The organism is often the cause of soft tissue infections in intravenous drug abusers who lick the injection site. TABLE 29-1 Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Spectrum of Disease This organism also is the “E,” for Eikenella, in the HACEK group of bacteria known to cause subacute bacterial endocarditis (see Chapter 68 for more information regarding endocarditis and bloodstream infections). HACEK is an acronym used to represent the slow-growing gram-negative bacilli associated with endocarditis. The additional members of the HACEK group of bacteria include Aggregatibacter aphrophilus, Actinobacillus actinomycetemcometans, Cardiobacterium hominis, and Kingella kingae. The rarity with which these organisms are encountered in the clinical laboratory and the lack of validated in vitro susceptibility testing methods do not provide enough data to recommend definitive treatment guidelines (Table 29-2). Although ß-lactamase production has been described in E. corrodens, this species is usually susceptible to penicillin and other ß-lactam antimicrobials. Penicillin-resistant strains of E. corrodens have been identified. TABLE 29-2 Antimicrobial Therapy and Susceptibility Testing
Eikenella and Similar Organisms
Epidemiology, Spectrum of Disease, and Antimicrobial Therapy
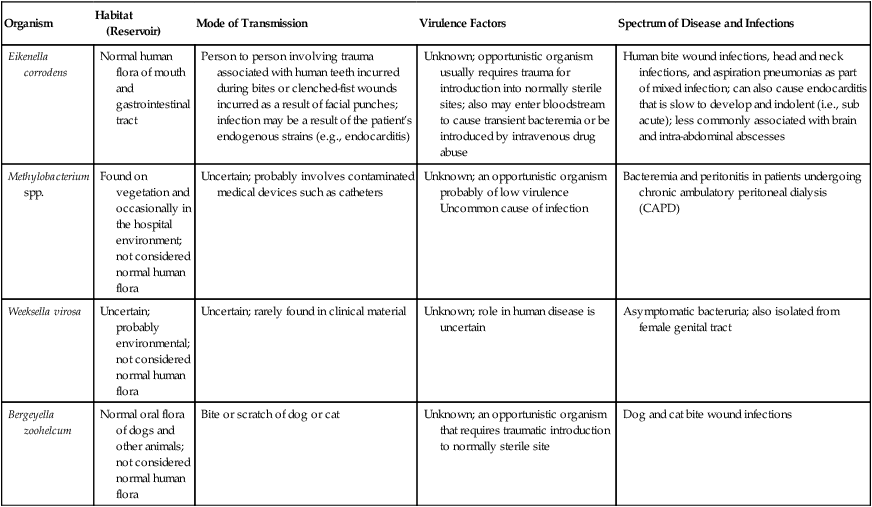
Organism
Habitat (Reservoir)
Mode of Transmission
Virulence Factors
Spectrum of Disease and Infections
Eikenella corrodens
Normal human flora of mouth and gastrointestinal tract
Person to person involving trauma associated with human teeth incurred during bites or clenched-fist wounds incurred as a result of facial punches; infection may be a result of the patient’s endogenous strains (e.g., endocarditis)
Unknown; opportunistic organism usually requires trauma for introduction into normally sterile sites; also may enter bloodstream to cause transient bacteremia or be introduced by intravenous drug abuse
Human bite wound infections, head and neck infections, and aspiration pneumonias as part of mixed infection; can also cause endocarditis that is slow to develop and indolent (i.e., sub acute); less commonly associated with brain and intra-abdominal abscesses
Methylobacterium spp.
Found on vegetation and occasionally in the hospital environment; not considered normal human flora
Uncertain; probably involves contaminated medical devices such as catheters
Unknown; an opportunistic organism probably of low virulence
Uncommon cause of infection
Bacteremia and peritonitis in patients undergoing chronic ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD)
Weeksella virosa
Uncertain; probably environmental; not considered normal human flora
Uncertain; rarely found in clinical material
Unknown; role in human disease is uncertain
Asymptomatic bacteruria; also isolated from female genital tract
Bergeyella zoohelcum
Normal oral flora of dogs and other animals; not considered normal human flora
Bite or scratch of dog or cat
Unknown; an opportunistic organism that requires traumatic introduction to normally sterile site
Dog and cat bite wound infections
Organism
Potential Resistance to Therapeutic Options
Therapeutic Options
Validated Testing Methods*
Eikenella corrodens
Often susceptible to penicillins, quinolones, cephalosporins, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
May produce beta-lactamases; usually resistant to clindamycin, metronidazole, and aminoglycosides
See CLSI document M45, section on “HACEK” organisms
Methylobacterium spp.
No guidelines
Unknown
Not available
Weeksella virosa and Bergeyella zoohelcum
No guidelines; potentially active agents include beta-lactams and quinolones
Susceptibility to tetracycline, aminoglycosides, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
Not available ![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Eikenella and Similar Organisms
