Ectopic Meningioma
Lester Thompson, MD
Cyril Fisher, MD, DSc, FRCPath
Key Facts
Terminology
Benign neoplasm of meningothelial cells
Clinical Issues
Approximately 0.2% of sinonasal tract and nasopharynx tumors
M:F= 1:1.2
Women older by over a decade
Good outcome: 10-year survival (80%)
Image Findings
Must exclude direct CNS extension
Microscopic Pathology
Infiltrative growth of neoplastic cells, including soft tissue and bone
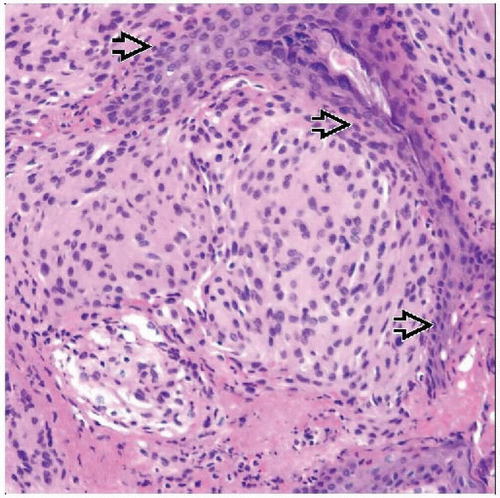
Meningothelial (syncytial) lobules of neoplastic cells without distinct borders
Whorled architecture, psammoma bodies
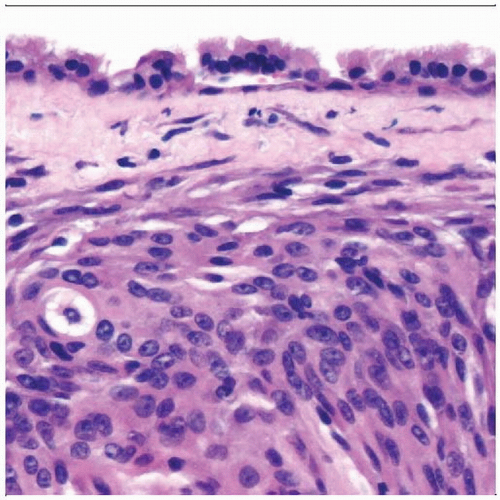 Hematoxylin & eosin shows intact respiratory mucosa overlying a syncytial-like neoplastic proliferation of meningothelial cells. The nuclei are uniform, and there are moderate amounts of cytoplasm. |
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Benign neoplasm of meningothelial cells within nasal cavity, sinonasal tract, nasopharynx, or lung
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Pathogenesis
Arachnoid cells from arachnoid granulations or pacchionian bodies lining sheaths of nerves and vessels through skull foramina
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Approximately 0.2% of sinonasal tract and nasopharynx tumors
20% of meningiomas have extracranial extension
Very rare examples occur outside head and neck
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree