Chapter 24 Drugs Used in the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus and Errors of Glucose Metabolism
TABLE 24-1 Characteristics of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
| Characteristic | Type 1 | Type 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Age of onset | Usually <25 yr | Usually >40 yr |
| Acuteness of onset | Usually sudden | Usually gradual |
| Presenting features | Polyuria, polydipsia, polyphagia, acidosis | Often asymptomatic |
| Body habitus | Often thin | Usually overweight |
| Control of diabetes | Difficult | Easy |
| Ketoacidosis | Frequent | Seldom, unless under stress |
| Insulin requirement | Always | Often unnecessary |
| Control by oral agents | Never | Frequent |
| Control by diet alone | Never | Frequent |
| Complications | Frequent | Frequent |
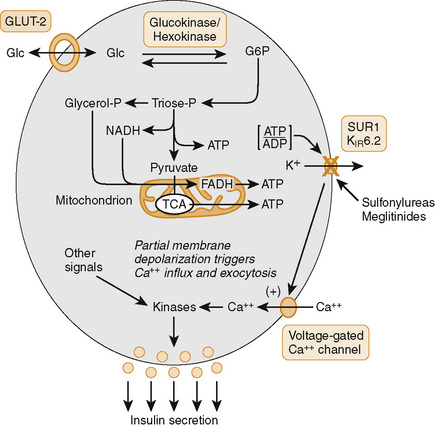
(From Wecker L, et al.: Brody’s Human Pharmacology, 5th ed. Philadelphia, Mosby, 2010, Figure 43-3.)
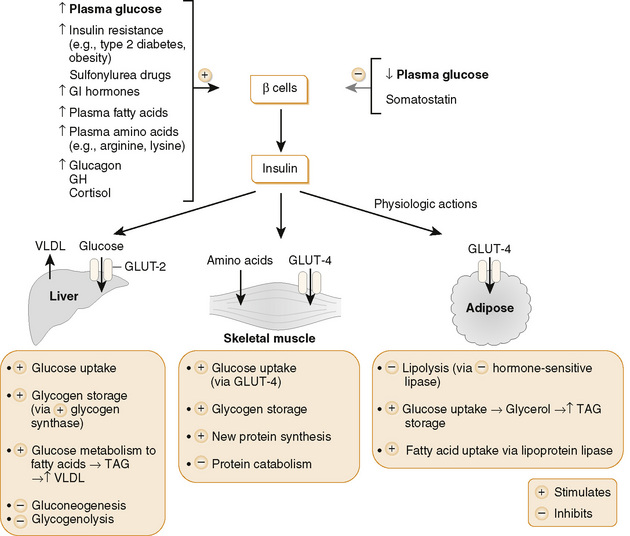
c. Major role of insulin is to maintain plasma glucose levels and, to a lesser extent, serum K+ levels
BOX 24-1 Drugs Used in the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree