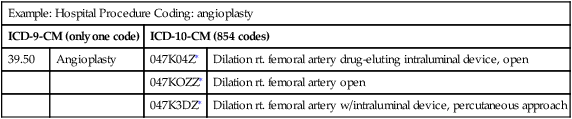
2
Diagnostic Coding
International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM)
After completing this chapter, readers should be able to:
 Have a rudimentary understanding of the new coding system ICD-10-CM.
Have a rudimentary understanding of the new coding system ICD-10-CM.
 Apply the basic steps studied in Chapter 1 for application with the new coding system.
Apply the basic steps studied in Chapter 1 for application with the new coding system.
 Be able to identify and code correct diagnosis based on documented specificity.
Be able to identify and code correct diagnosis based on documented specificity.
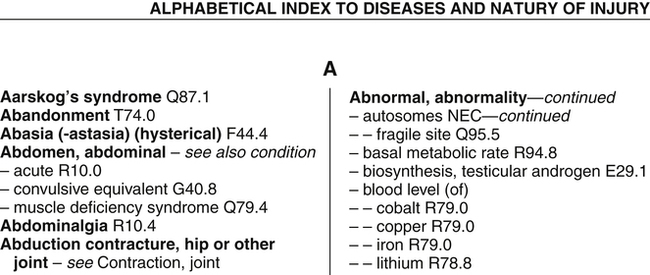
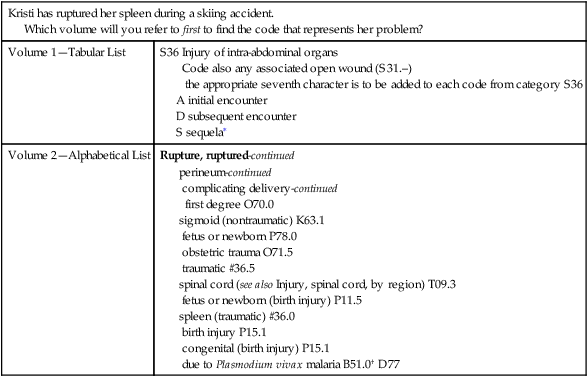
 Recognize and use the tables in the ICD-10-CM Index.
Recognize and use the tables in the ICD-10-CM Index.
 Understand the differences between ICD-9 and ICD-10 coding systems.
Understand the differences between ICD-9 and ICD-10 coding systems.
| Term | Definition |
| Manifestation code | A display or characteristic signs or symptoms of an illness. Also known as an asterisk (∗) code in some editions of ICD-10. |
| CDC | Centers for Disease Control. |
| Classification | Standard grouping of diseases by a set of principles. |
| CM | Clinical modification. |
| CMS | Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. |
| Default code | A code located in the Index that refers to a condition most commonly associated with the main term. An unspecified code where a higher level of specificity is not presented. |
| ICD-10-CM | International Classification of Disease, Tenth Edition, Clinical Modification. |
| ICD-10-PCS | International Classification of Disease, Tenth Edition, Procedural Coding System. |
| NEC | Not elsewhere classified: A category of codes to be used only when the coder lacks the information required to code the term to a more specific category. |
| Place holder | Usually a fifth digit character that is an “x” that must be used for correct code selection. |
| Sequela | Morbid condition following as a consequence of a disease. |
| Specificity | Applying the highest level of code based on the documentation of patient care. |
| Underlying cause | Typically a patient’s main condition. In some editions of ICD-10 these codes are also referred to as a dagger (†) code. |
| WHO | World Health Organization. |
What is ICD-10-CM?
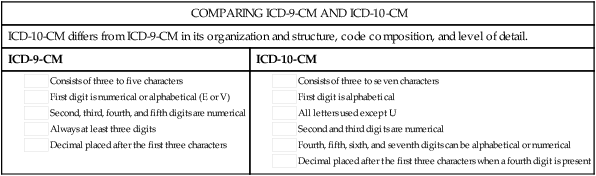
| COMPARING ICD-9-CM AND ICD-10-CM | |
| ICD-10-CM differs from ICD-9-CM in its organization and structure, code composition, and level of detail. | |
| ICD-9-CM | ICD-10-CM |
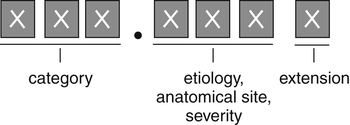
| Code structure of ICD-10-CM versus ICD-9-CM ICD-10-CM codes may consist of up to seven digits, with the seventh-digit extensions representing visit encounters or sequelae for injuries and external causes. | |
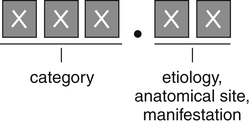
| ICD-9-CM Code Format | ICD-10-CM Code Format |
 |  |

Organizational Changes
 ICD-10-CM consists of 21 chapters.
ICD-10-CM consists of 21 chapters.
 Some chapters include the addition of a sixth character.
Some chapters include the addition of a sixth character.
 ICD-10-CM includes full code titles for all codes (no references back to common fourth and fifth digits).
ICD-10-CM includes full code titles for all codes (no references back to common fourth and fifth digits).
 V and E codes are no longer supplemental classifications.
V and E codes are no longer supplemental classifications.
 Sense organs have been separated from nervous system disorders.
Sense organs have been separated from nervous system disorders.
 Injuries are grouped by anatomical site rather than injury category.
Injuries are grouped by anatomical site rather than injury category.
 Postoperative complications have been moved to the procedure-specific body system chapter.
Postoperative complications have been moved to the procedure-specific body system chapter.
New Features
 Combination codes for conditions and common symptoms or manifestations
Combination codes for conditions and common symptoms or manifestations
 Combination codes for poisonings and external causes
Combination codes for poisonings and external causes
 Added extensions for episode of care
Added extensions for episode of care
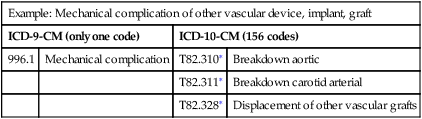
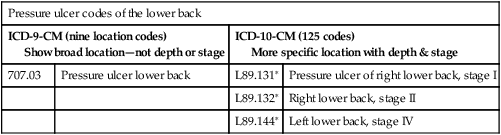
 Expanded codes (injury, diabetes, alcohol and substance abuse, postoperative complications)
Expanded codes (injury, diabetes, alcohol and substance abuse, postoperative complications)
 Inclusion of trimester in obstetrics codes and elimination of fifth digits for episode of care
Inclusion of trimester in obstetrics codes and elimination of fifth digits for episode of care
 Expanded detail relevant to ambulatory and managed care encounters
Expanded detail relevant to ambulatory and managed care encounters
 Changes in time frames specified in certain codes
Changes in time frames specified in certain codes
 External cause codes no longer a supplementary classification
External cause codes no longer a supplementary classification
ICD-10-CM also includes added standard definitions for two types of excludes notes.
Coding System Objectives
| ICD-10-CM | The diagnosis classification system developed by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for use in all U.S. health care treatment settings. Diagnosis coding under this system uses three to seven alphabetical and numerical digits and full code titles. The format or layout of the codes is much the same as ICD-9-CM. |
| ICD-10-PCS | The procedure classification system developed by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) for use in the United States for inpatient hospital settings and hospital billing only. This coding system uses seven alphabetical or numerical digits unlike the three or four numerical digits used in the ICD-9-CM system. |
Why the Need for Change?
 Does not provide the necessary detail to report medical conditions or the procedures and services performed in hospitalized patients
Does not provide the necessary detail to report medical conditions or the procedures and services performed in hospitalized patients
 Current coding system is 30 years old
Current coding system is 30 years old
 Contains outdated and obsolete terminology
Contains outdated and obsolete terminology
 Uses outdated codes that produce inaccurate, limited data
Uses outdated codes that produce inaccurate, limited data
 Is inconsistent with current medical practice
Is inconsistent with current medical practice
 Does not accurately describe the diagnoses and inpatient procedures for care provided in the 21st century
Does not accurately describe the diagnoses and inpatient procedures for care provided in the 21st century
| ICD-9-CM VS ICD-10-CM CHAPTER COMPARISONS | |||
| ICD-9-CM | ICD-10-CM | ||
| Chapter I | 001-139 | A00-B99 | Certain Infectious and Parasitic Diseases |
| Chapter II | 140-239 | C00-D49 | Neoplasms |
| Chapter III | 240-279 (Endocrine) | D50-D89 | Diseases of the Blood and Blood-Forming Organs and Certain Disorders Involving the Immune Mechanism |
| Chapter IV | 280-289 (Blood) | E00-E89 | Endocrine, Nutritional, and Metabolic Diseases |
| Chapter V | 290-319 | F01-F99 | Mental and Behavioral Disorders |
| Chapter VI | 320-389 | G00-G99 | Diseases of the Nervous System |
| Chapter VII | 390-459 (Circulatory) | H00-H59 | Diseases of the Eye and Adnexa |
| Chapter VIII | 460-519 (Respiratory) | H60-H95 | Diseases of the Ear and Mastoid Process |
| Chapter IX | 520-579 (Digestive) | I000-I99 | Diseases of the Circulatory System |
| Chapter X | 580-629 Genitourinary | J00-J99 | Diseases of the Respiratory System |
| Chapter XI | 630-677 (Pregnancy) | K00-K94 | Diseases of the Digestive system |
| Chapter XII | 680-709 (Skin) | L00-L99 | Diseases of the Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue |
| Chapter XIII | 710-739 (Musculoskeletal) | M00-M99 | Diseases of the Musculoskeletal System and Connective Tissue |
| Chapter XIV | 740-759 (Congenital) | N00-N99 | Diseases of the Genitourinary System |
| Chapter XV | 760-779 (Perinatal) | O00-O99 | Pregnancy, Childbirth, and the Puerperium Period |
| Chapter XVI | 780-799 (Signs) | P00-P96 | Certain Conditions Originating in the Perinatal Period |
| Chapter XVII | 800-999 (Injury) | Q00-Q99 | Congenital Malformations |
| Chapter XVIII | V01-V89 V-Codes (Health Status) | R00-R99 | Symptoms, Signs, and Abnormal Clinical and Laboratory Findings Not Elsewhere Classified |
| Chapter XIX | E000-E999 E-Codes (External Causes) | S00-T88 | Injury, Poisoning, and Certain Other Consequences of External Causes |
| Chapter XX | V00-Y99 | External Causes of Morbidity (Originally E Codes) | |
| Chapter XXI | Z00-Z99 | Factors Influencing Health Status and Contact with Health Services (Originally V Codes) | |
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree