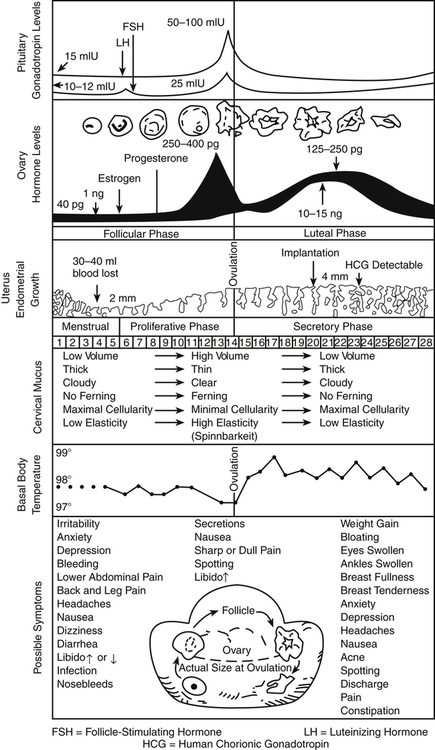
Chapter 54 In summary, the uterine lining proliferates in response to rising estrogen levels in the first half of the cycle. In the second half of the cycle, progesterone maintains a secretory endometrium. At the end of the menstrual cycle during which conception did not take place, progesterone and estrogen levels drop off, and the unsupported uterine lining sheds (Figure 54-1). The plasma half-life of progesterone is only 5 to 10 minutes, after which it is degraded to other steroids that have no progestational effect. Progesterone in its natural state cannot be used in oral form because of its rapid breakdown by the liver, so chemical modifications of synthetic progestins in hormonal contraceptives were made to deliberately slow down liver metabolism, making it possible to use the oral route (Table 54-1). TABLE 54-1 Synthetic Progestins and Their Characteristics Norethindrone, the progestin originally used in OCs, was derived from ethisterone, an orally active form of testosterone. The removal of a 19-carbon molecule from ethisterone results in the formation of norethindrone and changes the major effect from that of an androgen to that of progesterone, but the androgenic component is never totally eliminated, and the potential for anabolic and androgenic effects remains. See Table 54-2 for biologic effects of progestins and estrogen. This is a dose–effect relationship: The lower the dose of progestins given, the lesser is the androgenic effect. At today’s very low doses of progestin in COCPs, clinical effects are usually negligible. As with estrogens, serious side effects, especially adverse serum lipid changes, have been associated with high doses of progestins; therefore, the lowest effective doses available should be used. Through the years, changes have been made in the chemical structure of progestins in the quest to produce new progestins that have more potent progestational activity with fewer androgenic side effects. Many different progestins are marketed in the United States for use in hormonal contraception. TABLE 54-2 Biologic Effects of Estrogens and Progestins Estrogens are important in the development and maintenance of the female reproductive tract. Estrogen has effects throughout the body that are most notable in the breasts, bones, liver, and urogenital structures. See Table 54-2 for estrogen effects on the body. Two estrogenic compounds are used in COCPs in the United States: EE and mestranol. Mestranol is considered pharmacologically weaker because it must first be converted to EE. Therefore, unconjugated EE is the active estrogen in the blood in both mestranol and EE. All of the low-dose pills are low-estrogen pills. They contain ≤35 mcg of estrogen pills (EE). Mestranol is available in only a few pills in a 50-mcg dose, which is roughly equivalent to 35 mcg EE. A relatively safe dose of EE is ≤35 mcg. Pills that include 50-mcg EE are reserved for women on medications that induce liver enzymes that degrade estrogen, requiring higher initial doses, and they are rarely used. It is more common practice to use other methods with women who require higher-dose pills. High-dose EE should be given under special circumstances and generally is not used in primary care. In this chapter, COCPs are assumed to contain ≤35 mcg of EE (Table 54-3). TABLE 54-3
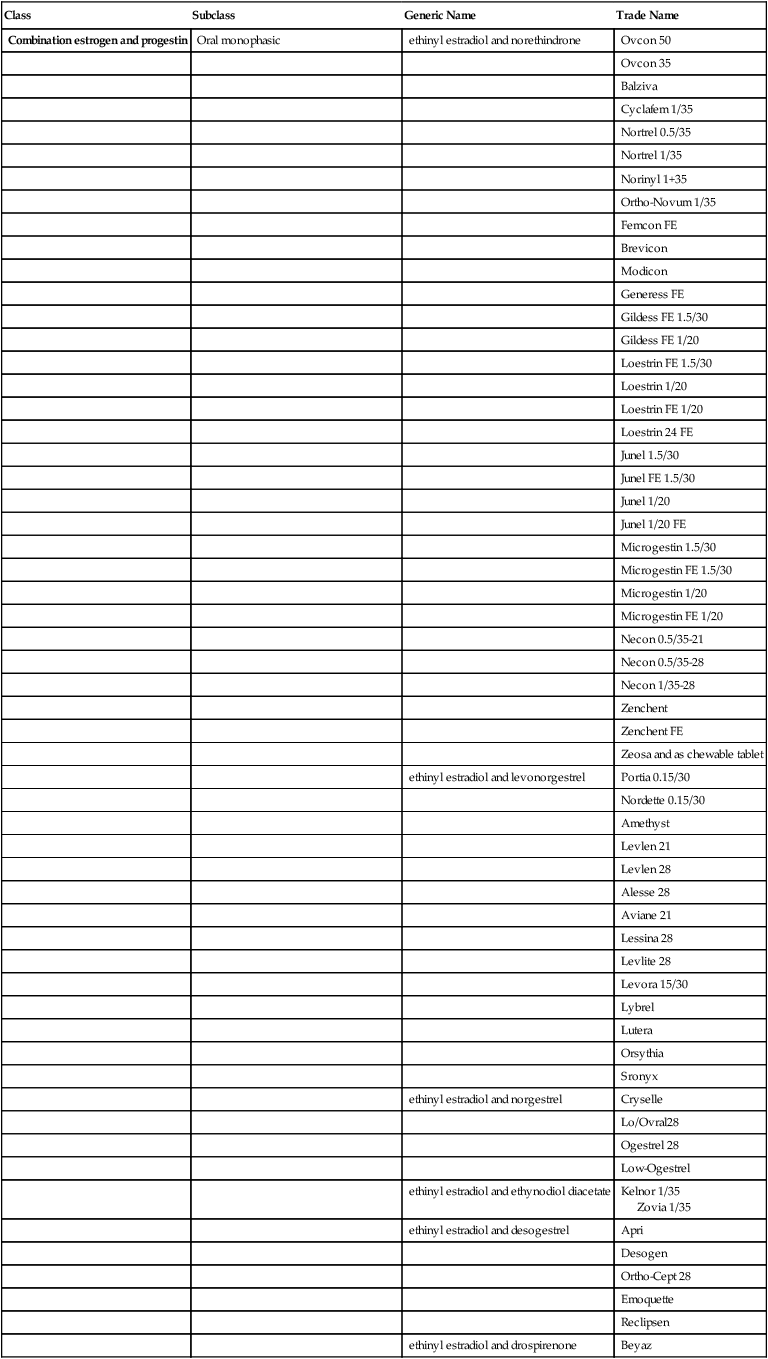
Contraceptives
Class
Subclass
Generic Name
Trade Name
Combination estrogen and progestin
Oral monophasic
ethinyl estradiol and norethindrone
Ovcon 50
Ovcon 35
Balziva
Cyclafem 1/35
Nortrel 0.5/35
Nortrel 1/35
Norinyl 1+35
Ortho-Novum 1/35
Femcon FE
Brevicon
Modicon
Generess FE
Gildess FE 1.5/30
Gildess FE 1/20
Loestrin FE 1.5/30
Loestrin 1/20
Loestrin FE 1/20
Loestrin 24 FE
Junel 1.5/30
Junel FE 1.5/30
Junel 1/20
Junel 1/20 FE
Microgestin 1.5/30
Microgestin FE 1.5/30
Microgestin 1/20
Microgestin FE 1/20
Necon 0.5/35-21
Necon 0.5/35-28
Necon 1/35-28
Zenchent
Zenchent FE
Zeosa and as chewable tablet
ethinyl estradiol and levonorgestrel
Portia 0.15/30
Nordette 0.15/30
Amethyst
Levlen 21
Levlen 28
Alesse 28
Aviane 21
Lessina 28
Levlite 28
Levora 15/30
Lybrel
Lutera
Orsythia
Sronyx
ethinyl estradiol and norgestrel
Cryselle
Lo/Ovral28
Ogestrel 28
Low-Ogestrel
ethinyl estradiol and ethynodiol diacetate
Kelnor 1/35
Zovia 1/35
ethinyl estradiol and desogestrel
Apri
Desogen
Ortho-Cept 28
Emoquette
Reclipsen
ethinyl estradiol and drospirenone
Beyaz
Sayfral
Yasmin 28
Yaz
Gianvi
Loryna
Ocella
Syeda
Zarah
ethinyl estradiol and norgestimate
Ortho-Cyclen
MonoNessa
Sprintec
mestranol and norethindrone
Norinyl 1+50
Ortho-Novum 1/50
Necon 1/50
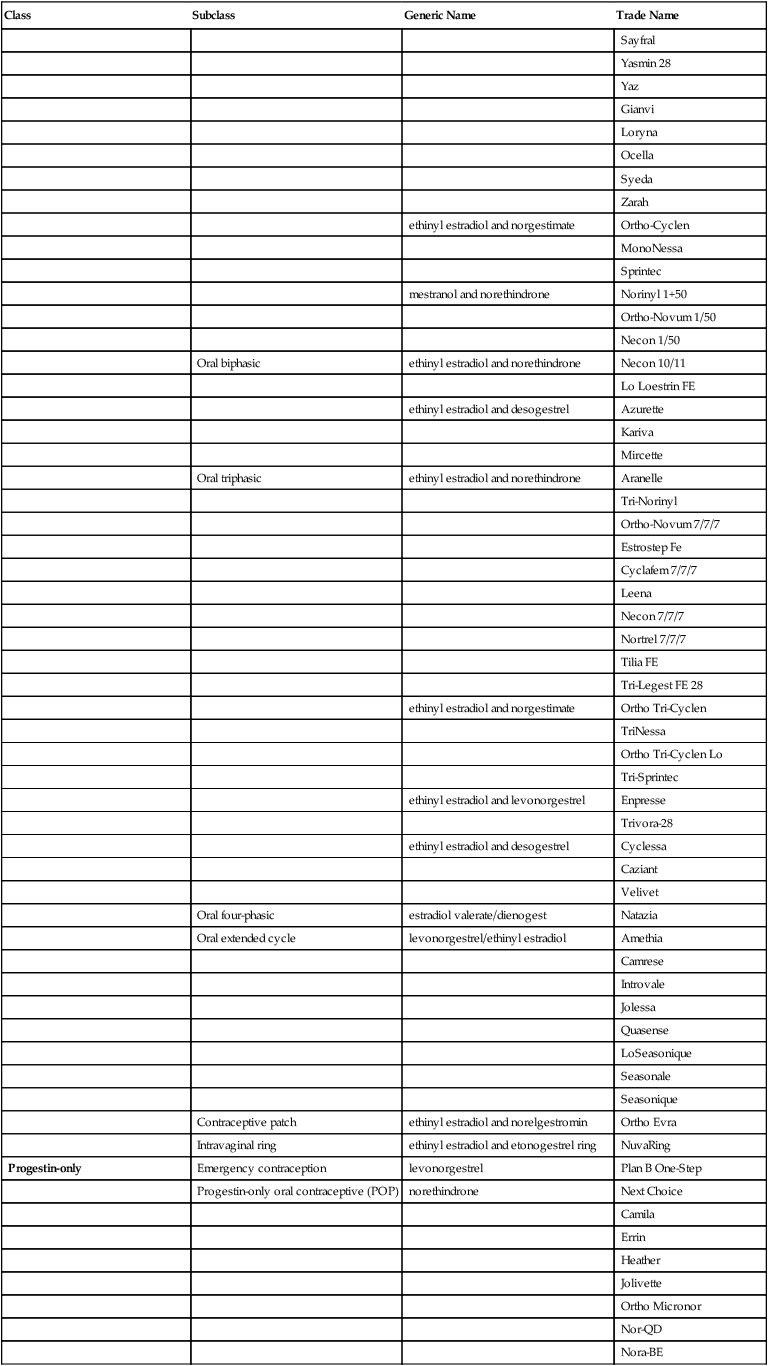
Oral biphasic
ethinyl estradiol and norethindrone
Necon 10/11
Lo Loestrin FE
ethinyl estradiol and desogestrel
Azurette
Kariva
Mircette
Oral triphasic
ethinyl estradiol and norethindrone
Aranelle
Tri-Norinyl
Ortho-Novum 7/7/7
Estrostep Fe
Cyclafem 7/7/7
Leena
Necon 7/7/7
Nortrel 7/7/7
Tilia FE
Tri-Legest FE 28
ethinyl estradiol and norgestimate
Ortho Tri-Cyclen
TriNessa
Ortho Tri-Cyclen Lo
Tri-Sprintec
ethinyl estradiol and levonorgestrel
Enpresse
Trivora-28
ethinyl estradiol and desogestrel
Cyclessa
Caziant
Velivet
Oral four-phasic
estradiol valerate/dienogest
Natazia
Oral extended cycle
levonorgestrel/ethinyl estradiol
Amethia
Camrese
Introvale
Jolessa
Quasense
LoSeasonique
Seasonale
Seasonique
Contraceptive patch
ethinyl estradiol and norelgestromin
Ortho Evra
Intravaginal ring
ethinyl estradiol and etonogestrel ring
NuvaRing
Progestin-only
Emergency contraception
levonorgestrel
Plan B One-Step
Progestin-only oral contraceptive (POP)
norethindrone
Next Choice
Camila
Errin
Heather
Jolivette
Ortho Micronor
Nor-QD
Nora-BE
Progestin-only injection
medroxyprogesterone
Depo-Provera IM and SQ
Progestin subdermal implants
etonogestrel
Implanon
Intrauterine device
levonorgestrel
Mirena ![]()
Progestin receptor modulators
Emergency contraception
ulipristal
Ella
Nonhormonal
Intrauterine device
ParaGard
Therapeutic Overview
Anatomy and Physiology
The Menstrual Cycle
Endometrial Changes
Hormone Physiology
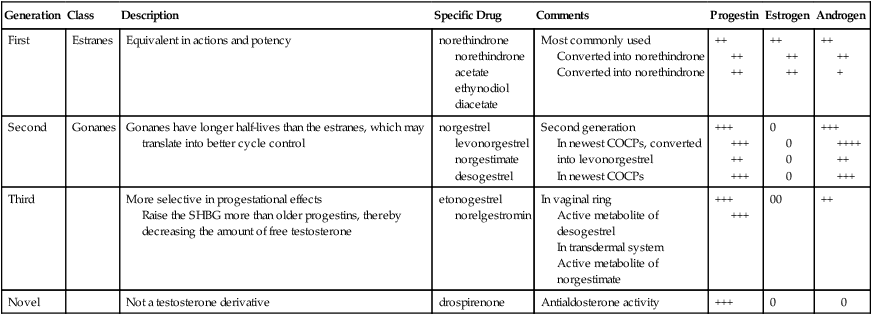
Progestins
Generation
Class
Description
Specific Drug
Comments
Progestin
Estrogen
Androgen
First
Estranes
Equivalent in actions and potency
norethindrone
norethindrone acetate
ethynodiol diacetate
Most commonly used
Converted into norethindrone
Converted into norethindrone
++
++
++
++
++
++
++
++
+
Second
Gonanes
Gonanes have longer half-lives than the estranes, which may translate into better cycle control
norgestrel
levonorgestrel
norgestimate
desogestrel
Second generation
In newest COCPs, converted into levonorgestrel
In newest COCPs
+++
+++
++
+++
0
0
0
0
+++
++++
++
+++
Third
More selective in progestational effects
Raise the SHBG more than older progestins, thereby decreasing the amount of free testosterone
etonogestrel
norelgestromin
In vaginal ring
Active metabolite of desogestrel
In transdermal system
Active metabolite of norgestimate
+++
+++
00
++
Novel
Not a testosterone derivative
drospirenone
Antialdosterone activity
+++
0
0
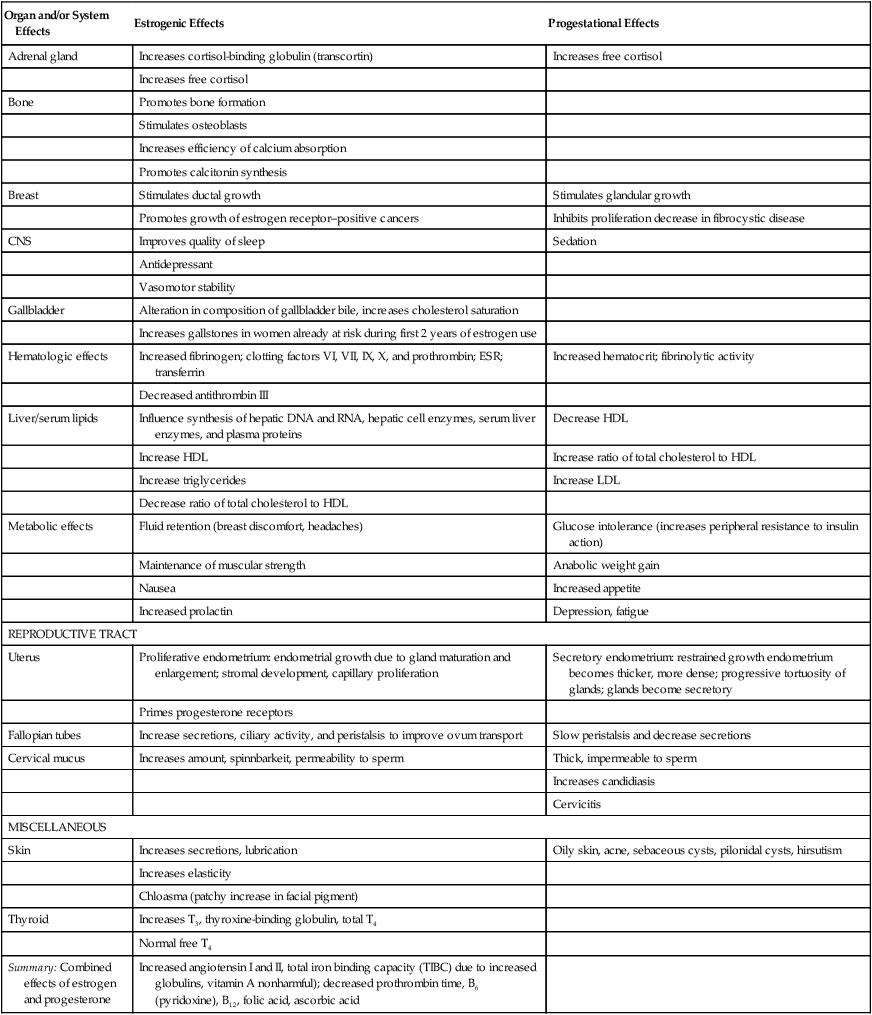
Organ and/or System Effects
Estrogenic Effects
Progestational Effects
Adrenal gland
Increases cortisol-binding globulin (transcortin)
Increases free cortisol
Increases free cortisol
Bone
Promotes bone formation
Stimulates osteoblasts
Increases efficiency of calcium absorption
Promotes calcitonin synthesis
Breast
Stimulates ductal growth
Stimulates glandular growth
Promotes growth of estrogen receptor–positive cancers
Inhibits proliferation decrease in fibrocystic disease
CNS
Improves quality of sleep
Sedation
Antidepressant
Vasomotor stability
Gallbladder
Alteration in composition of gallbladder bile, increases cholesterol saturation
Increases gallstones in women already at risk during first 2 years of estrogen use
Hematologic effects
Increased fibrinogen; clotting factors VI, VII, IX, X, and prothrombin; ESR; transferrin
Increased hematocrit; fibrinolytic activity
Decreased antithrombin III
Liver/serum lipids
Influence synthesis of hepatic DNA and RNA, hepatic cell enzymes, serum liver enzymes, and plasma proteins
Decrease HDL
Increase HDL
Increase ratio of total cholesterol to HDL
Increase triglycerides
Increase LDL
Decrease ratio of total cholesterol to HDL
Metabolic effects
Fluid retention (breast discomfort, headaches)
Glucose intolerance (increases peripheral resistance to insulin action)
Maintenance of muscular strength
Anabolic weight gain
Nausea
Increased appetite
Increased prolactin
Depression, fatigue
REPRODUCTIVE TRACT
Uterus
Proliferative endometrium: endometrial growth due to gland maturation and enlargement; stromal development, capillary proliferation
Secretory endometrium: restrained growth endometrium becomes thicker, more dense; progressive tortuosity of glands; glands become secretory
Primes progesterone receptors
Fallopian tubes
Increase secretions, ciliary activity, and peristalsis to improve ovum transport
Slow peristalsis and decrease secretions
Cervical mucus
Increases amount, spinnbarkeit, permeability to sperm
Thick, impermeable to sperm
Increases candidiasis
Cervicitis
MISCELLANEOUS
Skin
Increases secretions, lubrication
Oily skin, acne, sebaceous cysts, pilonidal cysts, hirsutism
Increases elasticity
Chloasma (patchy increase in facial pigment)
Thyroid
Increases T3, thyroxine-binding globulin, total T4
Normal free T4
Summary: Combined effects of estrogen and progesterone
Increased angiotensin I and II, total iron binding capacity (TIBC) due to increased globulins, vitamin A nonharmful); decreased prothrombin time, B6 (pyridoxine), B12, folic acid, ascorbic acid
Estrogens
Generic Name
Trade Name
Estrogen, mcg
Progestin, mg
COMBINATION
Monophasic
ethinyl estradiol and norethindrone
Ovcon 50
50
1
Cyclafem 1/35
35
1
Necon 1/35
35
1
Nortrel 1/35
35
1
Norinyl 1+35
35
1
Ortho-Novum 1/35
3535
1
Brevicon
35
0.5
Modicon
35
0.5
Necon 0.5/35
35
0.5
Nortrel 0.5/35
3535
0.5
BalzivaFemcon FE
35
0.4
Ovcon 35
35
0.4
Zenchent
35
0.4
Zenchent Fe
30
0.4
Zeosa
30
0.4
Gildess FE 1.5/30
30
1.5
Junel 1.5/30
30
1.5
Junel FE 1.5/30
30
1.5
Loestrin 1.5/30
35
1.5
Loestrin FE 1.5/30
20
1.5
Microgestin 1.5/30
20
0.8
Microgestin Fe 1.5/30
20
1
Generess FE
20
1
Gildess FE 1/20
10
1
Junel 1/20
1
Junel 1/20 FE
1
Loestrin 1/20
Loestrin FE 1/20
Microgestin 1/20
Microgestin Fe 1/20
ethinyl estradiol and levonorgestrel
Portia, Nordette, Levlen 21, Levlen 28, Levora
30
0.15
Alesse 21
30
0.15
Aviane 21
20
0.1
Lessina 28
20
0.1
Levlite 28
20
0.1
Lutera
20
0.1
Orsythia
20
0.1
Sronyx
20
0.1
Amethyst
20
0.1
Lybrel
20
0.09
20
0.09
ethinyl estradiol and norgestrel
Ogestrel 28
50
0.5
Cryselle
30
0.3
Lo/Ovral 28
30
0.3
Low-Ogestrel 28
30
0.3
ethinyl estradiol and ethynodiol diacetate
Kelnor 1/35
35
1
Zovia
35
1
1
ethinyl estradiol and desogestrel
Apri
30
0.15
Desogen
30
0.15
Emoquette
30
0.15
Ortho-Cept
30
0.15
Reclipsen
30
0.15
ethinyl estradiol and drospirenone
Ocella
30
3
Safyral
30
3; 451 mcg folate
Syeda
30
3
Yasmin 28
30
3
Zarah
30
3
Beyaz
20
3; 451 mcg folate
Gianvi
20
3
Loryna
20
3
Yaz
20
3
ethinyl estradiol and norgestimate
MonoNessa
35
0.25
Ortho-Cyclen
35
0.25
Sprintec
35
0.25
mestranol and norethindrone
Necon 1/50
50
1
Norinyl 1+50
50
1
Ortho-Novum 1/50
50
1
Biphasic
ethinyl estradiol and norethindrone
Necon 10/11
35
0.5 × 10 day then
Lo Loestrin FE
10
1 × 11 day
1 × 24 day then
0 × 2 day
ethinyl estradiol and desogestrel
Azurette, Kariva, Mircette
20 × 21 day then
0.15 × 21 day then
10 × 5 day
0 × 5 day
Triphasic
ethinyl estradiol and norethindrone
Aranelle, Leena, Tri-Norinyl
35
0.5 × 7 day then
Cyclafem 7/7/7, Necon 7/7/7, Nortrel 7/7/7, Ortho-Novum 7/7/7, Estrostep Fe, Tilia FE, Tri-Legest FE
35
1 × 9 day then
20 × 5 day then
0.5 × 5 day
30 × 7 day then
0.5 × 7 day then
35 × 9 day
0.75 × 7 day then
1 × 7 day
1
ethinyl estradiol and norgestimate
OrthoTri-Cyclen, TriNessa, Tri-Sprintec
35
0.18 × 7 day then
OrthoTri-Cyclen Lo
25
0.215 × 7 day then
0.25 × 7 day
0.18 × 7 day then
0.215 × 7 day then
0.25 × 7 day
ethinyl estradiol and levonorgestrel
Enpresse, Trivora-28
30 × 6 day then
0.05 × 6 day then
40 × 5 day then
0.075 × 5 day then
30 × 10 day
0.125 × 10 day
ethinyl estradiol and desogestrel
Caziant, Cyclessa, Velivet
25
0.1 × 7 day then
0.125 × 7 day then
0.15 × 7 day
Four-phasic
Estradiol valerate and dienogest
Natazia
0 mg × 2 day then
3 × 2 day then
2 mg × 5 day then
2 × 5 day then
2 mg × 17 day then
3 × 17 day then
2 mg × 2 day
0 × 2 day
Extended cycle
levonorgestrel/ethinyl estradiol
Seasonale, Introvale, Jolessa, Quasense
30 mcg × 91 day
0.15 × 91 day
30 × 84 day then
0.15 × 84 day then
Seasonique, Camrese
10 × 7 day
0 × 7 day
LoSeasonique
20 × 84 day then
0.1 × 84 day then
10 × 7 day
0 × 7 day
EMERGENCY CONTRACEPTION
levonorgestrel
Plan B One-Step
0
1.5 mg once. Take ASAP after unprotected intercourse; maximum efficacy w/in 72 hours, moderate efficacy w/in 120 hours.
Next Choice
0
0.75 mg × 1 dose 12 hours apart ASAP after unprotected intercourse; maximum efficacy within 72 hours, moderate efficacy within 120 hours; Alt: 2 tabs po × 1
Progestin receptor modulators
Ulipristal
30 mg once; ASAP within 120 hours of unprotected intercourse
PROGESTIN ONLY
norethindrone
Camila
0
0.35
Errin
0
0.35
Heather
0
0.35
Jolivette
0
0.35
OrthoMicronor
0
0.35
Nor-QD
0
0.35
Nora-BE
0
0.35
TRANSDERMAL SYSTEM
ethinyl estradiol and norelgestromin
Ortho-Evra
20/24 hr
0.15/24 hr q wk × 3, then no patch × 1 wk
20 mcg/day
VAGINAL
ethinyl estradiol and etonogestrel ring
NuvaRing
15/24 hr
0.12/24 hr for 3 wk, then off 1 wk, self-inserted
15 mcg/day
INTRAUTERINE
Nonhormonal IUD
ParaGard
q10yr
levonorgestrel IUD
Mirena
52 mg q5yr
INJECTION
medroxyprogesterone
Depo-Provera
150 mg q12wk (IM) or 104 mg SQ q12wk
PROGESTIN SUBDERMAL IMPLANT
etonogestrel
Implanon, Nexplanon (radiopaque)
68-mg implant, one implant subdermally q3y ![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Contraceptives
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue