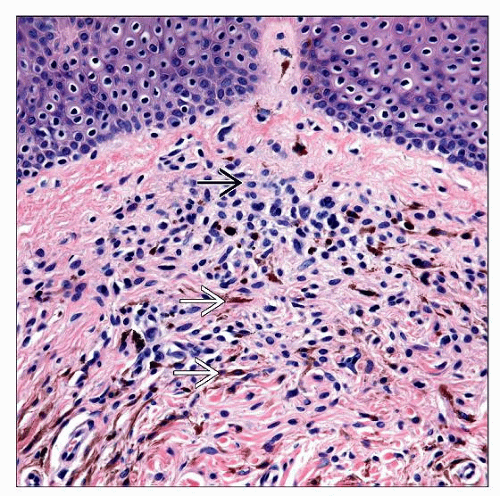
Combined Nevi
Christine J. Ko, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Presence of 2 or more distinct populations of melanocytes or
Presence of 2 or more types of melanocytic nevi
Clinical Issues
Generally in young adults, size < 6 mm
Pigment of lesion often very dark brown to black or blue-black
Site: May be more common on head and neck
Microscopic Pathology
Lesion overall orderly, symmetric, and well-circumscribed
Most commonly: Compound/intradermal melanocytic nevus plus blue nevus
Top Differential Diagnoses
Blue nevus (common and cellular types)
Deep penetrating nevus
Congenital melanocytic nevus
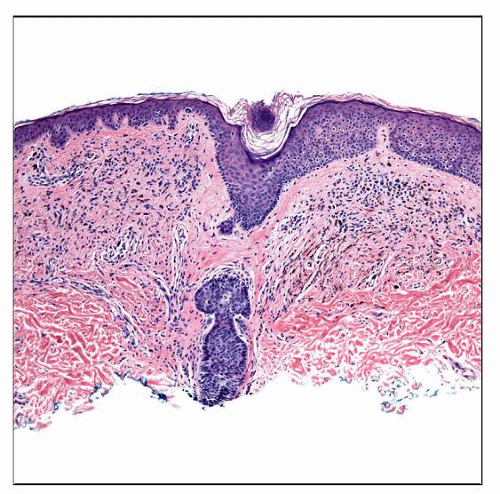 This is an example of a combined nevus of the most common type, i.e., composed of an “ordinary” intradermal melanocytic nevus and a blue nevus. The lesion is symmetric and orderly appearing. |
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Melanocytic nevus with phenotypic heterogeneity, clonal nevus, nevus with focal epithelioid component, combined Spitz nevus, inverted type A nevus
Definitions
Presence of 2 or more distinct populations of melanocytes (i.e., type A melanocytic nevus cells, and spindled dendritic cells) or
Presence of 2 or more types of melanocytic nevi (i.e., intradermal melanocytic, blue)
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
Generally in young adults
Any site, but may be more common on head and neck
Pigment of lesion often very dark brown to black or blue-black
Lesion may have small focus of blue to blue-black color in background of lighter pigment
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree