Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma
Francisco Vega, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
CHL can involve extranodal tissues
Most common: Spleen, lungs, liver, and bone marrow
Macroscopic Features
Variable patterns of splenic involvement
Multiple nodules, isolated or confluent (most common)
Solitary nodule
Miliary small nodules
Microscopic Pathology
All types of CHL may involve spleen
More frequent in mixed cellularity or lymphocyte-depleted types (up to 60%)
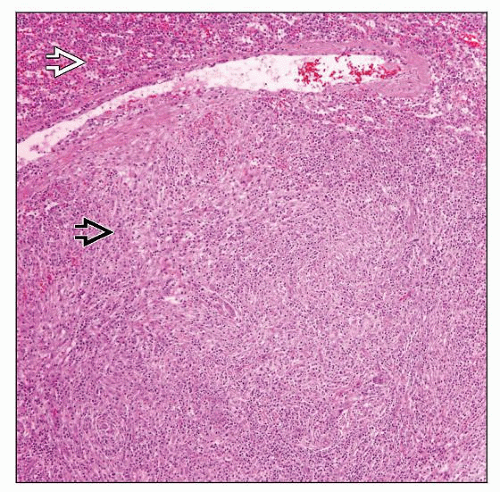
Periarterial lymphoid sheath and marginal zones are initial sites of involvement
Irrespective of type, fibrosis or sclerosis can be seen
Hodgkin/Reed Sternberg (HRS) cells &/or lacunar cells in inflammatory background
Ancillary Tests
CD30(+), CD15(+), CD45/LCA(−) in most cases
pax-5(+) with characteristic weaker expression than reactive B cells
CD20(−/+), CD79a(−/+)
Monoclonal IgH gene rearrangements usually detected by single cell PCR
Top Differential Diagnoses
Splenic marginal zone lymphoma
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Classical Hodgkin lymphoma (CHL)
Synonyms
Hodgkin disease
Definitions
Splenic involvement by CHL
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
> 80% of patients with CHL present with lymphadenopathy above diaphragm
Most common: Cervical, supraclavicular, and axillary lymph nodes
1/3 of patients present with B symptoms: Fever, night sweats, weight loss
CHL can involve extranodal tissues
Common: Spleen, lungs, liver, and bone marrow
Primary splenic CHL is extremely rare
Splenic involvement
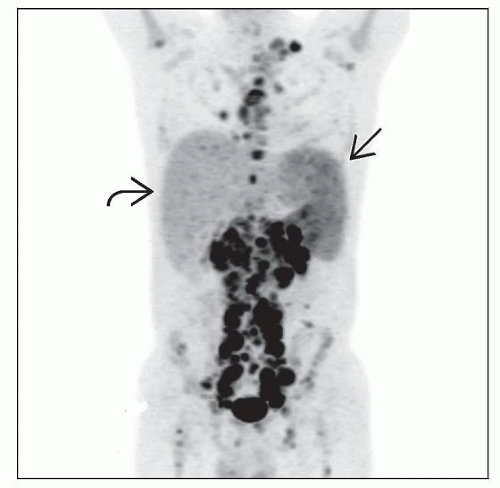
37% of patients have splenic involvement (mean from 17 published case series)
Splenic involvement is associated with bone marrow and liver involvement
Staging laparotomy in CHL patients was performed in past
Nowadays, staging laparotomy is no longer performed, mainly because
Routine use of chemotherapy is independent of stage (replacing wide-field radiotherapy)
Improvement of imaging studies
Positron emission tomography (PET) with fluorodeoxyglucose 18F (standard staging tool)
Treatment
Drugs
Chemotherapy
Adriamycin, bleomycin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine (ABVD) is standard regimen
Prognosis
CHL staging
According to Ann Arbor criteria modified at Cotswolds meeting
Extranodal disease is adverse prognostic factor for localized CHL according German Hodgkin Lymphoma Study Group (GHLSG)
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
Size
Spleen may be large or normal size
Variable patterns of splenic involvement
Multiple nodules, isolated or confluent (most common)
Solitary nodule
Miliary small nodules
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY Histologic Features
All types of CHL can involve spleen
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree