Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma
Roberto N. Miranda, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
CLL/SLL is neoplasm of small B lymphocytes that typically involves peripheral blood (PB), bone marrow (BM), lymph nodes, and spleen
CLL is used for disease involving PB or BM (leukemic)
SLL is used for disease restricted to lymph nodes or other tissue sites (nonleukemic)
Clinical Issues
CLL is most common leukemia in western hemisphere
Splenic involvement by CLL/SLL is typically detected by radiologic imaging
At time of CLL/SLL diagnosis, splenic involvement often asymptomatic
Splenectomy can be performed to alleviate symptoms or refractory cytopenias
Microscopic Pathology
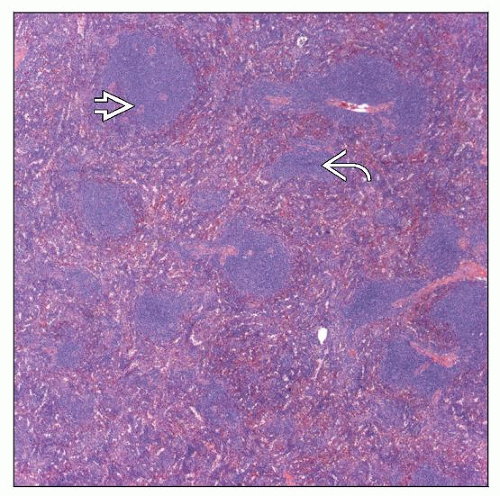
Expansion of white pulp forming uniform nodules
Red pulp involvement as small aggregates or diffuse in cords and sinuses
Lymphocytes are round to slightly irregular with clumped chromatin and scant cytoplasm
Proliferation centers (a.k.a. pseudofollicles) can be observed in spleen
Ancillary Tests
Surface Ig(dim [+]), CD19(+), CD20(dim [+])
CD5(+), CD23(+), Ki-67(low)
Unmutated Ig variable (V) genes predicts poorer prognosis
ZAP70 or CD38 expression correlates with unmutated IgV genes
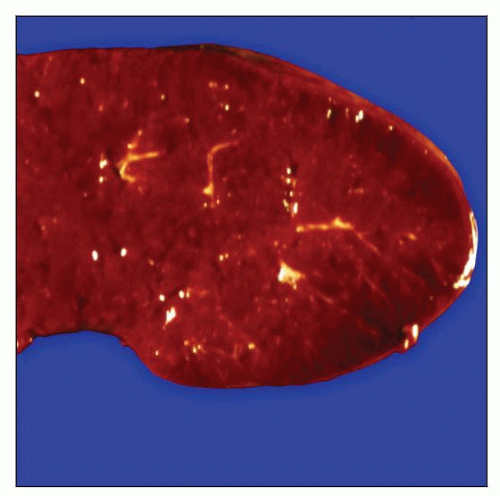 Gross specimen of spleen involved by chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL) shows diffuse enlargement with a miliary appearance of white pulp. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)/small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL)
Synonyms
CLL and SLL are used as synonyms but have slightly different meanings
CLL is used for disease involving peripheral blood or bone marrow (leukemic)
SLL is used for disease restricted to lymph nodes or other extramedullary sites (nonleukemic)
Definitions
CLL/SLL is a neoplasm of small B lymphocytes that typically involves blood, bone marrow, lymph nodes, and spleen
Neoplastic cells have characteristic immunophenotype
Surface immunoglobulin (Ig)(dim [+]), CD5(+), CD23(+)
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
CLL is most common type of leukemia in western hemisphere
Uncommon or rare in eastern hemisphere
CLL/SLL shows genetic and familial predisposition
˜ 5-10% of cases
Age
Median: 65 years (range: 43-82 years)
Gender
M:F ratio = 1.5:1
Site
Diagnosis of CLL/SLL usually established by examination of blood and bone marrow
Lymph node biopsy is performed in nonleukemic cases
Splenic involvement is typically detected by radiologic imaging studies
Splenectomy can be performed to alleviate symptoms or cytopenias
Biopsy of spleen is rare
Presentation
At time of CLL/SLL diagnosis, splenic involvement is often asymptomatic
30% present with autoimmune manifestations, such as hemolytic anemia
Laboratory Tests
Persistent peripheral blood monotypic B-cell lymphocytosis, ≥ 5 x 109/L
Natural History
Most patients have indolent clinical course
In general, patients with splenomegaly &/or cytopenias have high-stage disease and shorter survival
Subset of patients develop higher grade, clinically aggressive neoplasm (Richter syndrome)
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL)
Can arise in spleen
Often discrete mass with necrosis
Classical Hodgkin lymphoma
Can arise in spleen
Usually Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)(+)
Subset of patients develop prolymphocytoid transformation of CLL
Closely related to or variant of Richter syndrome
Increased (often > 55%) prolymphocytes in peripheral blood
Extensive involvement of bone marrow and usually marked splenomegaly
Chemotherapeutic CLL/SLL drug fludarabine is immunosuppressive
Patients are predisposed to infections
EBV is associated with atypical lymphoproliferative disorders in CLL/SLL patients
May resolve with antiviral therapy
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection/reactivation is common in CLL/SLL patients
HSV infection can clinically or histologically mimic transformation to large cell lymphoma
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Splenectomy performed usually for refractory cytopenias or local symptoms
Drugs
Fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR regimen)
This regimen was initiated at M.D. Anderson Cancer Center
Becoming popular for use when patients require chemotherapy
Many other chemotherapy regimens are used
Prognosis
Rai and Binet clinical staging systems are used to assess prognosis
50% 5-year overall survival
Great interest in biologic markers to assess prognosis
Markers correlated with worse prognosis
Unmutated immunoglobulin variable region (IgV) genes
CD38 or ZAP70 expression
Chromosomal abnormalities: del(11q22-23), del(17p)/p53, del(6q)
Markers associated with better prognosis
Del(13q14.3)
IMAGE FINDINGS
Radiographic Findings
Various modalities show splenomegaly
FDG PET scan usually negative
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Median weight: 1.4 kg (wide range: 0.2-7.1 kg)
Cut surface shows diffuse/miliary growth
Discrete tumor mass can occur in cases of large cell transformation
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
CLL/SLL preferentially involves white pulp
White pulp nodules are expanded
Rarely, involvement mimics marginal zone pattern
Red pulp involvement as small aggregates or diffuse replacement of cords and sinuses
Proliferation centers (a.k.a. pseudofollicles) can be observed in spleen
Presence correlates with more extensive involvement
CLL/SLL can surround reactive germinal centers without mantle zones
So-called “naked” germinal centers
Splenic hilar lymph nodes
Lymph nodes show features of nodal CLL/SLL
Partial or total architectural replacement
Patent sinuses in cases with partial involvement
Proliferation centers
Bone marrow is usually involved in patients with CLL/SLL in spleen
3 patterns: Diffuse, interstitial, or nodular
Nodular pattern uncommon if spleen is large
Richter syndrome
DLBCL is most common form of Richter syndrome
Sheets of large B cells that can replace both white and red pulp
Increased mitotic figures; ± necrosis
High proliferation rate (Ki-67 immunostaining)
˜ 50-60% of DLBCL are clonally related to underlying CLL/SLL
Classical Hodgkin lymphoma
Reed-Sternberg and Hodgkin cells; background inflammatory cells
Necrosis common; usually EBV(+)
Much less common than DLBCL
Cytologic Features
Tumor cells are predominantly small with round nuclear contours, clumped chromatin, and scant cytoplasm
Scattered prolymphocytes or paraimmunoblasts
In some cases, CLL/SLL cells can show plasmacytoid differentiation
Can be associated with serum paraprotein; usually low level
Subset of CLL cases show atypical cytologic features
More irregular nuclear contours or large cells increased
Association with trisomy 12
ANCILLARY TESTS
Immunohistochemistry
CD19(+), CD20(+), CD79a(+), pax-5(+)
CD5(+), CD23(+), Bcl-2(+)
Usually low proliferation rate: < 10% (Ki-67)
CD10(−), Bcl-6(−), Cyclin-D1(−)
ZAP70 expression
Surrogate for unmutated IgV genes
Discordance between ZAP70 and molecular analysis in ˜ 20% of cases
Can be assessed by immunohistochemistry or flow cytometry
Flow Cytometry
Surface Ig(dim [+]), CD19(+), CD20(dim [+])
IgM(+), IgD(+)
CD5(+), CD23(+), CD43(+)
˜ 5% of CLL/SLL cases are CD23(−)
CD3(−), CD10(−), CD22(−), CD79b(−), FMC7(−)
Atypical immunophenotypes occur in ˜ 10-20% of CLL/SLL
Bright surface Ig(+) or CD20(+), CD22(+), CD79b(+), or FMC7(+)
CD38 expression
Surrogate for unmutated IgV genes
Discordance between CD38 and molecular analysis in ˜ 20% of cases
Best assessed by flow cytometry
Cytogenetics
Usually performed on blood or bone marrow specimens
Abnormal karyotypes in ˜ 50% of cases
CLL/SLL cells grow poorly in culture
Trisomy 12 occurs in ˜ 20% of cases of CLL/SLL
Presence correlates with atypical morphologic or immunophenotypic features
Small subset (< 5%) of CLL/SLL cases have chromosomal translocations
Usually detected by FISH
In Situ Hybridization
FISH can detect cytogenetic abnormalities in ˜ 80% of cases
Panel has been designed to detect most common abnormalities
Probes for 13q14, 11q22, +12, 17p13, and 6q21
Target genes
Del(13q14.3): Possibly micro-RNA genes miR-16 and miR-15a
Del(11q22): Ataxia-telangiectasia mutated (ATM)
Trisomy 12: Unknown
Del(17p13): P53
Del(6q21): Unknown
Molecular Genetics
Monoclonal IgH gene rearrangements
No evidence of T-cell receptor gene rearrangements
Somatic hypermutation of IgV genes in ˜ 50% of cases
Correlate with better prognosis; CD38(−), ZAP70(−)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree