Chapter 29 Chemotherapeutic Drugs
• Cancer is a disease in which the cellular control mechanisms that govern proliferation and differentiation are changed.
TABLE 29-1 Therapeutic Uses and Adverse Effects of Selected Drugs Used in Cancer Chemotherapy
| Drug | Use: Type(s) of Cancer* | Important Adverse Effect(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Aminoglutethimide | Breast, prostate | Adrenal suppression, dizziness, rash |
| Anastrozole | Breast | Hot flashes |
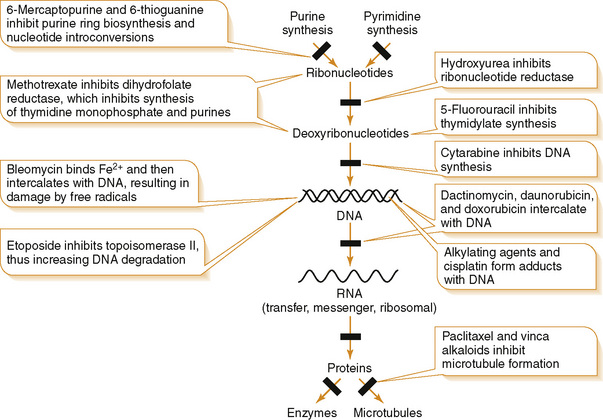
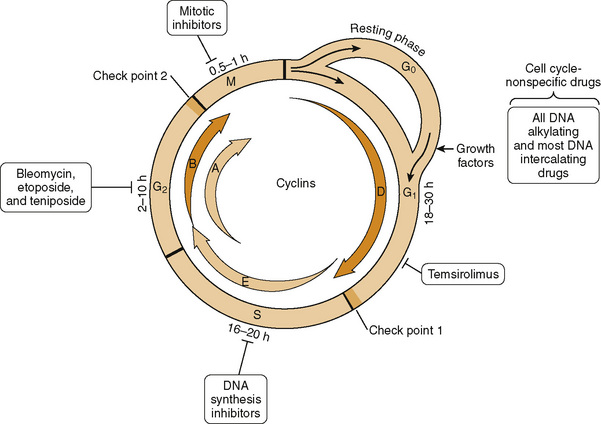
| Bleomycin | Testicular, ovarian, cervical, thyroid | Pulmonary fibrosis; very little bone marrow toxicity |
| Busulfan | CML, polycythemia vera | Interstitial pulmonary fibrosis |
| Carmustine/lomustine | Brain | Leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, hepatotoxicity |
| Cisplatin | Head and neck, lung, testicular, cervical, thyroid, ovarian | Ototoxicity, severe nephrotoxicity, mild bone marrow suppression |
| Cyclophosphamide | Leukemias/lymphomas | Hemorrhagic cystitis, alopecia |
| Cytarabine | Leukemias | Bone marrow suppression, CNS toxicity, immunosuppression |
| Dactinomycin | Wilms’ tumor | Hepatotoxicity |
| Daunorubicin/doxorubicin | Acute leukemia, Hodgkin’s disease, breast and lung | Cardiomyopathy (daunorubicin) |
| Etoposide | Lung, testicular | Bone marrow suppression |
| 5-Fluorouracil | Colon, stomach, prostate, breast | Bone marrow suppression, GI toxicity |
| Imatinib | CML, gastrointestinal stromal tumors | Fluid retention |
| Irinotecan | Colon | Bone marrow suppression |
| Leuprolide | Prostate, breast | Hot flashes |
| Melphalan | Multiple myeloma | Bone marrow suppression |
| 6-Mercaptopurine | Leukemias | Bone marrow suppression |
| Methotrexate | Wilms’ tumor, choriocarcinoma, leukemias | Bone marrow suppression, oral and GI tract ulceration, diarrhea, hepatotoxicity† |
| Paclitaxel | Breast, ovarian | Bone marrow suppression |
| Procarbazine | Hodgkin’s disease | Secondary malignancies, teratogenic |
| Tamoxifen | Breast | Hot flashes |
| Trastuzumab | Breast | Fever and chills |
| Vinblastine | Lymphomas | Bone marrow suppression |
| Vincristine | Acute lymphocytic leukemia | Neurotoxicity/peripheral neuropathy, low bone marrow suppression |
CML, chronic myelogenous leukemia; CNS, central nervous system; GI, gastrointestinal.
* Not a complete list; for most cancers, drug combinations are used.
† Adverse effects, especially toxicity, may be reversed with folic acid (“leucovorin rescue”).
(4) P-glycoprotein (Pgp, mdr1) can export multiple classes of anti-cancer drugs (multidrug resistance)

29-3 Bioactivation of cyclophosphamide.
(From Wecker L, et al.: Brody’s Human Pharmacology, 5th ed. Philadelphia, Mosby, 2010, Figure 54-6.)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree