Cellular Neurothekeoma
Cyril Fisher, MD, DSc, FRCPath
Key Facts
Terminology
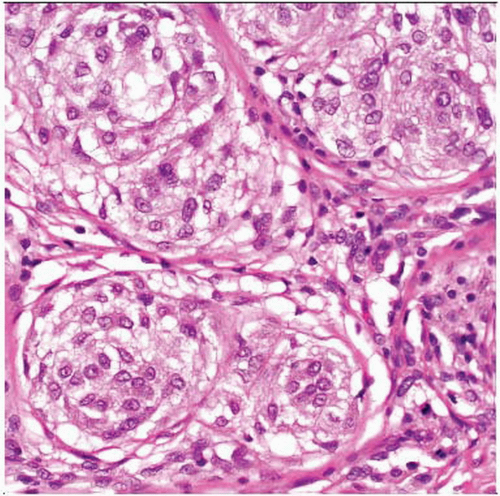
Multinodular dermal tumor composed of nests of rounded cells separated by delicate fibrous septa
Differs from dermal nerve sheath myxoma (a.k.a. neurothekeoma)
Clinical Issues
Young adults, most 15-25 years
Head and neck and upper extremity most common sites
Elevated dermal nodule
Reported cases have behaved in benign fashion
Microscopic Pathology
˜ 50% confined to dermis
48% involve superficial subcutis
Nests of rounded cells
Occasional spindling of cells, especially in myxoid areas
Myxoid change in 20%
Nuclear atypia in 25%
Mitoses: ≤ 3 per 10 high-power fields
Osteoclast-like cells in 30%
Occasional plexiform pattern
Top Differential Diagnoses
Dermal nerve sheath myxoma
Circumscribed, S100 positive
Plexiform fibrohistiocytic tumor
Based at dermal-subcutaneous junction
Also has multinucleated cells and fibroblasts
Fibroblastic variant with fascicles in subcutis
Melanocytic nevus
S100 protein positive
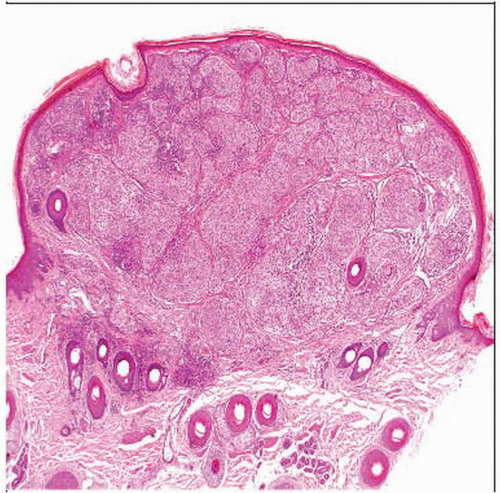 Hematoxylin & eosin of a transverse section of whole tumor shows the smooth, dome-shaped outline. The lesion is confined to the dermis. The epidermis is thinned except at the lateral margins. |
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Multinodular dermal tumor composed of nests of rounded cells separated by delicate fibrous septa
Differs from dermal nerve sheath myxoma (a.k.a. neurothekeoma)
Cell type unknown; considered fibrohistiocytic
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Rare
Age
Young adults, most 15-25 years
Gender
M = F
Ethnicity
No predilection
Site
Head and neck and upper extremity most common
Presentation
Slow growing
Elevated dermal nodule
Painless
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Simple excision
Prognosis
Reported cases have behaved in benign fashion
Occasional recurrence, especially if incompletely excised
Atypical histologic features have no prognostic significance
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Rounded or dome-shaped skin lesion
Pale or tan
Size
≤ 2 cm diameter
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
˜ 50% confined to dermis; 48% involve superficial subcutis
Nests of rounded cells
Uniform nuclei, scanty cytoplasm
Occasional spindling of cells, especially in myxoid areas
Nests separated by thin fibrous septa
Myxoid change in 20%
30% are mixed cellular and myxoid lesions
Nuclear atypia in 25%
Mitoses occasionally seen up to 3 per 10 HPF
Multinucleated cells in 40%
Osteoclast-like cells in 30%
Occasional plexiform pattern
Predominant Pattern/Injury Type
Nested
Predominant Cell/Compartment Type
Mesenchymal, fibrohistiocytic
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree