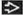Capillary, Venous, and Cavernous Hemangiomas
Amitabh Srivastava, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Benign vascular tumors composed of blood vessels lined by plump to flattened endothelial cells with no atypia
Etiology/Pathogenesis
May be congenital (infantile/juvenile hemangiomas)
Clinical Issues
Capillary hemangioma is commonest subtype of hemangioma
Juvenile hemangiomas occur in infancy
Capillary and cavernous hemangiomas in adults occur more commonly in women
Pyogenic granuloma occurs on skin and mucosal surfaces and is often ulcerated
Cavernous hemangiomas present as birthmarks
Venous hemangiomas are rare and present in adulthood
Juvenile capillary hemangiomas regress spontaneously with time
Microscopic Pathology
Nodules of small capillary-sized vessels in lobular pattern in capillary hemangioma
Large, cystically dilated vessels filled with blood in cavernous hemangioma
Large, thick-walled veins in venous hemangioma
Lining endothelium in all lesions does not typically show atypia
Thrombosis (± Masson tumor/change), hemorrhage, and calcifications may be present
Especially in venous and cavernous hemangiomas
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Pyogenic granuloma (PG)
Synonyms
Capillary hemangioma = lobular hemangioma
Definitions
Benign vascular tumors composed of blood vessels of various size lined by plump to flattened endothelial cells with no atypia
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Developmental Anomaly
Juvenile (infantile) capillary hemangiomas may be congenital
Venous hemangiomas may represent vascular malformations
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Age
Depends on subtype
Gender
Capillary and cavernous hemangiomas in adults occur more commonly in women
Site
Depends on subtype
Presentation
Painless mass
Red elevated papule(s)
Natural History
Juvenile capillary hemangiomas regress spontaneously with time
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Surgical excision is curative, but usually not necessary unless affecting vital structures
Drugs
Glucocorticoids or interferon-α therapy for large or symptomatic juvenile hemangiomas
Watchful waiting for juvenile hemangiomas that regress with time
Prognosis
Recurrences are rare; only occur in some incompletely excised lesions
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
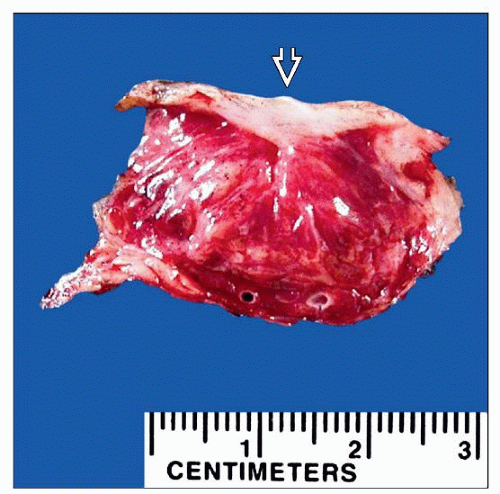
Elevated nodular red-purple lesions
Usually involve skin or subcutaneous tissue
Discoloration may not be obvious in deep-seated lesions
Recurrences may be sessile
Size
Variable size
Capillary (Lobular) Hemangioma
Most common type of hemangioma
Variants
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree