• Preventing disease and screening for pathology • Testing and evaluating suspicious lesions • Reducing side effects of conventional therapies • Improving tumor kill from conventional therapies • Improving environment that allowed malignancy • Supporting patient metabolically while starving tumor • Slowing or stopping abnormal cell division • Promoting normal cell differentiation and apoptosis • Reducing metastasis and angiogenesis • Enhancing cell-to-cell communication • Using natural antitumor agents • Blocking hormonal stimulation of tumors by normalizing hepatic clearance • Supporting healthy immune response • Supporting secondary prevention for patient after treatment • Dealing with death and dying for those who succumb • Encouraging prevention and screening for family members of patient The cell cycle is usually divided into the following four or five phases: • G0 phase: resting state, or gap phase. Many cells spend most of their time in this phase either at rest or performing assigned duties. Generally resistant to chemotherapy. • G1 phase: gap 1 phase, or interphase. Cells synthesize RNA and prepare for cell division. • S phase: synthesis phase. Cells duplicate DNA to create daughter cells. • G2 phase: gap 2 phase. DNA synthesis completed. Microtubules of mitotic spindles produced. • M phase: mitosis. Division of DNA and cellular proteins into two daughter cells. Return to G0 or resting phase. • Extent of spread of tumor and locations of metastatic lesions • Functional status of patient • TNM score includes size of tumor (T), number of involved lymph nodes (N), and presence or absence of distant metastasis (M). For example, breast cancer with primary tumor 2.5 cm, positive lymph nodes in ipsilateral axilla, and no metastasis would be T2, N1, M0. • Most are not useful as screening tests. Noncancerous tissue can also secrete higher amounts of these markers in conditions such as inflammation and infection. • Tumor may express different marker than typical for that tumor type. • Most useful: monitoring response to treatment or disease progression. Comparison of Karnofsky and ECOG scoring • Cure: treatment that allows patient to live as long as an age-matched cohort or die of other causes, even if some disease remains. • Remission: complete disappearance of all detectable tumors. Millions of tumor cells may remain. Remission is a better term than “cure.” • Complete response: complete disappearance of all evidence of disease for at least 2 measurement periods at least 4 weeks apart. • Partial response: decrease of at least 50% in diameter of all measurable lesions with no new lesions for at least 4 weeks. • Stable disease: less than 50% up to an increase of 25% in measurable lesions. • Progression: increase of more than 25% or appearance of new lesions. • Palliation: treatment not aimed at cure, simply reduction of symptoms or transient extension of life for brief period. • Reduce side effects of treatment • Maximize tumor kill from conventional therapies • Support normal cell division • Use antitumor herbs and nutrients (avoid waste of money on worthless products) • Support positive attitude and healthy lifestyle • Regular secondary cancer screening after completion of treatment
Cancer: Integrated Naturopathic Support
GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS
Cell Cycle
Complete Staging Description
Tumor Markers
Tumor Marker
Typical Tumor Types
CEA
Colorectal, breast, small cell lung
PSA
Prostate (some breast)
CA-15-3
Breast
CA 19-9
Pancreas, hepatic, biliary, gastric, colon
CA27-29
Breast
CA-125
Ovarian
Beta-HCG
Testis, trophoblastic neoplasia
Beta2 microglobulin
Multiple myeloma, lymphoma
Thyroglobulin
Thyroid
Performance Indexes
Karnofsky Score
Description
ECOG Score
100
Asymptomatic
0
90
Normal activity, minor disease signs
1
80
Some disease signs with exertion
1
70
Cares for self; unable to do active work
2
60
Requires occasional assistance; in bed less than 50% of day
2
50
Requires considerable assistance and medical care
3
40
Disabled; requires special assistance; in bed more than 50% of day
3
30
Severely disabled; hospital indicated
4
20
Quite ill; requires active supportive treatment; bedridden
4
10
Moribund
4
0
Deceased
5
Tumor Response Criteria and Terminology
THERAPEUTIC CONSIDERATIONS
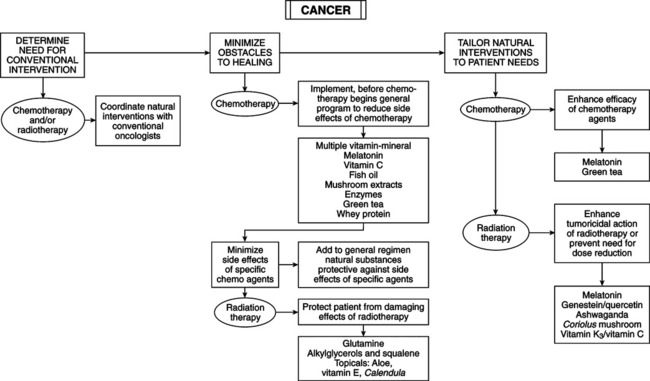
span id=”p126″ epub:type=”pagebreak” title=”126″/>Goals of Naturopathic Oncology Support
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Cancer: Integrated Naturopathic Support
