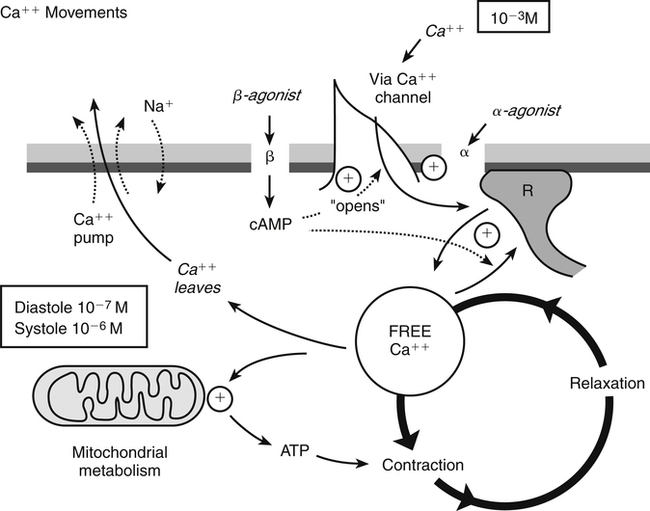
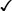Chapter 21 Although these compounds have diverse chemical structures, they all share a basic electrophysiologic property: they block the inward movement of calcium through the slow channels of the cell membranes of cardiac and smooth muscle cells. The drugs differ in their location of action (Tables 21-2 and 21-3). The three types of tissue cells acted on are as follows: TABLE 21-2 Major Differences Between the Subclasses of Calcium Channel Blockers TABLE 21-3 Effect of Calcium Channel Blockers on Myocardium 1. Cardiac muscle (myocardium) 2. Cardiac conduction system: SA and AV nodes 3. Vascular smooth muscle: coronary arteries and arterioles, peripheral arterioles In these tissues, CCBs decrease automaticity in the SA node and decrease conduction in the AV node. Automaticity means that a cell depolarizes spontaneously and initiates an action potential without an external stimulus. Automaticity is a normal characteristic of SA nodal cells. Depolarization (Phase 0) of the action potential is normally generated by the inward calcium ion current through slow channels. Thus, agents that can block the inward calcium ion current across the cell membrane of SA nodal tissue decrease the rate of depolarization and depress automaticity. The result is a variable decrease in heart rate (a negative chronotropic effect) (Figure 21-1). Similarly, an agent that decreases calcium ion influx across the cell membrane of the AV node slows AV nodal conduction (negative chronotropic effect) and prolongs AV refractory time. When AV conduction is prolonged, fewer atrial impulses reach the ventricles, thus slowing the rate of ventricular contractions.
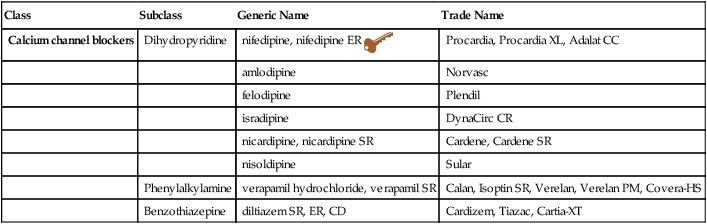
Calcium Channel Blockers
Class
Subclass
Generic Name
Trade Name
Calcium channel blockers
Dihydropyridine
nifedipine, nifedipine ER ![]()
Procardia, Procardia XL, Adalat CC
amlodipine
Norvasc
felodipine
Plendil
isradipine
DynaCirc CR
nicardipine, nicardipine SR
Cardene, Cardene SR
nisoldipine
Sular
Phenylalkylamine
verapamil hydrochloride, verapamil SR
Calan, Isoptin SR, Verelan, Verelan PM, Covera-HS
Benzothiazepine
diltiazem SR, ER, CD
Cardizem, Tiazac, Cartia-XT
Mechanism of Action
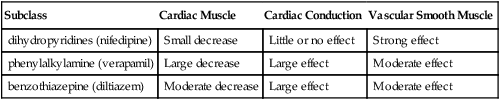
Subclass
Cardiac Muscle
Cardiac Conduction
Vascular Smooth Muscle
dihydropyridines (nifedipine)
Small decrease
Little or no effect
Strong effect
phenylalkylamine (verapamil)
Large decrease
Large effect
Moderate effect
benzothiazepine (diltiazem)
Moderate decrease
Large effect
Moderate effect
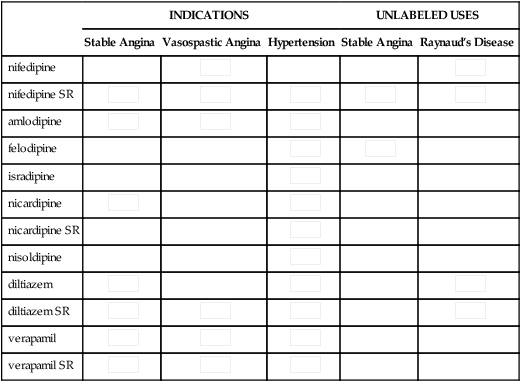
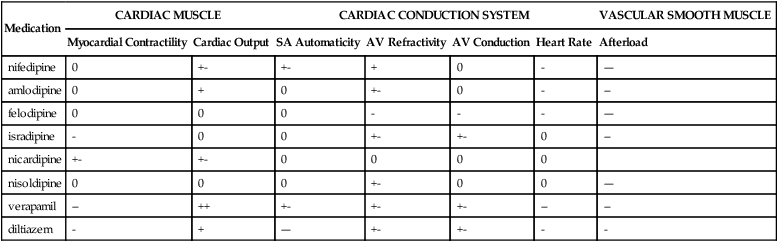
Medication
CARDIAC MUSCLE
CARDIAC CONDUCTION SYSTEM
VASCULAR SMOOTH MUSCLE
Myocardial Contractility
Cardiac Output
SA Automaticity
AV Refractivity
AV Conduction
Heart Rate
Afterload
nifedipine
0
+-
+-
+
0
–
—
amlodipine
0
+
0
+-
0
–
—
felodipine
0
0
0
–
–
–
—
isradipine
–
0
0
+-
+-
0
—
nicardipine
+-
+-
0
0
0
0
nisoldipine
0
0
0
+-
0
0
—
verapamil
—
++
+-
+-
+-
—
—
diltiazem
–
+
—
+-
+-
–
–
Cardiac Conduction System (SA and AV Nodes)
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree