Chapter 6 BLOOD, BONE MARROW, AND THE LYMPHOID SYSTEM
Introduction
 Some of the blood diseases, such as anemia or thrombosis, are extremely common and are encountered daily by medical specialists of any profile, including primary care physicians and general practitioners.
Some of the blood diseases, such as anemia or thrombosis, are extremely common and are encountered daily by medical specialists of any profile, including primary care physicians and general practitioners.
 Blood abnormalities are found by means of laboratory testing not only in persons who have hematologic diseases per se, but also those who have many other systemic or organ-centered diseases. For example, hematologic abnormalities, such as high white blood cell (WBC) count, are encountered in the course of many infections. In such cases the hematologic abnormalities are more a symptom of other diseases than diseases in their own right.
Blood abnormalities are found by means of laboratory testing not only in persons who have hematologic diseases per se, but also those who have many other systemic or organ-centered diseases. For example, hematologic abnormalities, such as high white blood cell (WBC) count, are encountered in the course of many infections. In such cases the hematologic abnormalities are more a symptom of other diseases than diseases in their own right.
 Hematologic tests are routinely performed on both healthy and sick people, and essentially all who are hospitalized or prepared for surgery.
Hematologic tests are routinely performed on both healthy and sick people, and essentially all who are hospitalized or prepared for surgery.
 Malignant tumors of the bone marrow and lymphoid organs are important causes of morbidity and mortality. Every year approximately 65,000 new cases of lymphoma and 25,000 cases of leukemia are diagnosed in the United States.
Malignant tumors of the bone marrow and lymphoid organs are important causes of morbidity and mortality. Every year approximately 65,000 new cases of lymphoma and 25,000 cases of leukemia are diagnosed in the United States.
 The incidence of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma increases with age from 2.4 cases per 100,000 persons in the 20- to 24-year age group to more than 100 cases per 100,000 persons in those older than 75 years.
The incidence of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma increases with age from 2.4 cases per 100,000 persons in the 20- to 24-year age group to more than 100 cases per 100,000 persons in those older than 75 years.
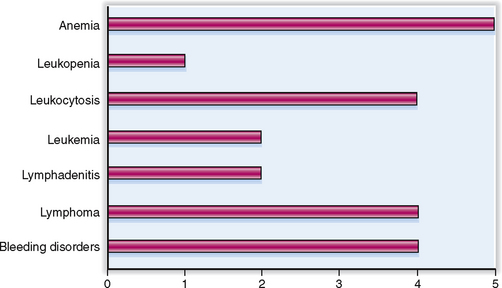
The relative clinical significance of various diseases involving the blood, bone marrow, and the lymphoid organs is presented graphically in Figure 6-1.
Anatomy and Physiology
Antibody Immunoglobulin produced by plasma cells in response to immunization with a specific antigen.
Basophil (basophilic leukocyte) Mononuclear white blood cell that contains abundant basophilic granules (stains blue with the Giemsa stain). Like mast cells, to which it is related, it participates in inflammatory reactions and atopic hypersensitivity reactions.
Bone marrow Central part of the bones, composed of trabecullar bone, fat cells or hematopoietic cells, and stroma. The hematopoietic bone marrow occupies the medullary part of most bones in neonates and infants, but in adults it is mostly limited to flat or short bones, such as the sternum, ilium, or vertebrae.
Clot (coagulum) Semisolid mass made up of a meshwork of polymerized fibrinogen (i.e., fibrin) and other coagulation proteins activated in the intrinsic or extrinsic coagulation pathway. In vivo formed clots also contain blood cells enmeshed in the strands of fibrin.
Cluster of differentiation (CD) antigens Cytoplasmic and cell surface molecules differentially expressed during the development and differentiation of various subsets of white blood cells and their bone marrow precursors. CD antigens are recognized immunohistochemically with monoclonal antibodies and named by consensus of an international committee. They carry numerical designations (e.g., CD4 as marker or helper T cells). CD antigens are also expressed on malignant cells and are important for the diagnosis of lymphomas and leukemias by immunohistochemistry and flow cytometry.
Coagulation factors Group of plasma proteins that participate in the coagulation cascade and the formation of the fibrin clot. Coagulation factors are numbered from 1 to 13, but most of them also have assigned names. Calcium is also a coagulation factor and is also known as factor IV. Protein coagulation factors are mostly synthesized by the liver. The activation of factors II, VII, IX, and X occurs only in the presence of the vitamin K-dependent carboxylase.
Coagulation pathway Physiologic process that leads to the formation of a fibrin clot. It can proceed through an intrinsic and an extrinsic pathway, which converge into a common terminal pathway.
Eosinophil (eosinophilic leukocyte) Nucleated cell that in its mature form has a bilobed nucleus and numerous eosinophilic cytoplasmic granules. It participates in the defense of the body against infections and plays a prominent role in allergic reactions and the body’s response to parasites.
Erythrocyte (red blood cell, RBC) Nuclear blood cell containing hemoglobin. RBCs are the most abundant cells in the blood, accounting for its red color. Their primary function is oxygen transport.
Erythrocyte precursor cells Nucleated ancestors of mature red blood cells that are derived in the bone marrow from erythroid progenitor cells in the erythroid burst-forming unit (BFU-E). As they differentiate sequentially, erythrocyte precursor cells can be recognized cytologically in bone marrow aspirates as pronormoblasts, normoblasts, and reticulocytes.
Erythropoietin Growth/differentiation factor produced primarily by kidneys, stimulating the growth and differentiation of erythrocyte precursor and progenitor cells.
Fibrinolysis A physiologic process that leads to a controlled dissolution of the fibrin component of the clot. It is principally mediated by plasmin, a zymogen derived from the plasma protein plasminogen under the influence of tissue plasminogen activator (TPA). Plasmin acting on fibrin forms fibrin degradation products (FDPs), which may be found in plasma or urine during fibrinolysis.
Hematopoietic growth factors Polypeptides that act on hematopoietic progenitor and precursor cells, promoting their proliferation or differentiation (or both). This group of polypeptides includes erythropoietin; thrombopoietin; granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF); macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF), interleukin-3; and related cytokines produced by stromal cells, macrophages, T lymphocytes, and many others.
Hemoglobin Main protein in erythrocytes enabling them to carry oxygen. Biochemically it is a heterodimeric tetramer composed of four globin polypeptide chains and four heme moieties linked to an iron. Several forms of hemoglobin are recognized on the basis of their globin composition. In adult red blood cells the most abundant is hemoglobin A, which is composed of two alpha and two beta globin chains (α2β2).
Lymphocyte Mononuclear white blood cell with a round nucleus and scant cytoplasm. Lymphocytes are subdivided into two major groups: T and B lymphocytes. They are derived from precursors located in the bone marrow, lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue. Lymphocytes participate in inflammatory reactions and are essential for immune reactions.
Megakaryocytes Multinucleated cells in the bone marrow acting as a precursor of platelets that form by budding of its cytoplasm.
Monocyte Mononuclear cell containing only a few cytoplasmic granules that are not visible under light microscopy. It participates in inflammatory reactions and can differentiate into tissue macrophages.
Multipotent bone marrow stem cell Developmentally pluripotent cell, which can differentiate into progenitor cells, giving rise to myeloid or lymphoid lineages.
Myeloblast Mononuclear poorly granulated precursor of neutrophils that has a relatively large nucleus.
Neutrophil (neutrophilic granulocyte or polymorphonuclear leukocyte (PMN) Motile phagocytic white blood cell (WBC) derived from precursors in the bone marrow. In its mature form it has a segmented nucleus and abundant cytoplasmic granules, which are neither acidophilic (as in eosinophils) nor basophilic (as in basophils). Neutrophils are the most numerous WBC, even though only 10% of neutrophils are found in circulating blood at any one time. Neutrophils can migrate through the vessel wall in response to chemotactic stimuli and participate in acute inflammatory reactions.
Neutrophil precursor cells Nucleated ancestors of mature neutrophils derived from the pluripotential stem cell, which gives rise to the myeloid stem cell. This multilineage precursor cell also gives rise to the precursors of monocytes, eosinophils, basophils, platelets, and erythrocytes. In the lineage giving rise to neutrophils it differentiates consecutively into myeloblasts, promyelocytes, metamyelocytes, and band neutrophils prior to becoming mature neutrophils.
Normoblast Bone marrow precursor of red blood cells, characterized by a bluish cytoplasm that contains small amounts of hemoglobin and a round, relatively large nucleus.
Plasma cell Immunoglobulin producing terminally differentiated cells derived from B lymphocytes. Typically found in tissues in chronic inflammation.
Platelet (thrombocyte) Small (2–4 μm) anuclear cell, derived from the fragmentation of the cytoplasm of bone marrow megakaryocytes. It contains many biologically active substances and participates in blood coagulation and inflammation.
White blood cells (WBCs) Nucleated blood cells including neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, monocytes, lymphocytes, and platelets. WBCs can be seen as a buffy coat on the interface between centrifuged red blood cells and plasma.
Clinical and Laboratory Findings and Procedures
Activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) Laboratory test based on measuring the time needed for the in vitro formation of a clot under conditions most favorable for estimating the intrinsic and common coagulation pathway.
Agranulocytosis (granulocytopenia) Reduced number of granulated WBCs (neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils) in peripheral blood. Typically it is caused by the reduced production of blood cells in the bone marrow and is a feature of aplastic anemia.
Anemia In laboratory medicine it is used as a designation for a reduced red blood cell mass. It is characterized by a reduced volume of RBCs (low hematocrit), a reduced RBC count, or a reduced concentration of hemoglobin.
Bleeding time Clinical test based on measuring the duration of bleeding that follows a needle prick. It is a rough measure of the integrity of the vessel wall and platelet function.
Bone marrow biopsy Sampling of tissue from the bone marrow with a needle. The tissue may be prepared for histologic examination, or the aspirated cells can be smeared and stained for microscopic examination (bone marrow smear).
Coagulopathy Any disturbance of coagulation characterized by either increased coagulability of blood (hypercoagulability or thrombophilia), or a bleeding tendency (hemorrhagic diathesis) related to inadequate clotting of blood. Coagulopathies can be acquired (e.g., vitamin C and K deficiencies) or congenital (e.g., hemophilia).
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC—consumption coagulopathy, or defibrination syndrome) Condition characterized by widespread clotting in the peripheral circulation. It is accompanied by the formation of microthrombi in arterioles, capillaries, and venules (microangiopathy), hemolytic anemia, and a tendency for uncontrolled bleeding due to the consumption of coagulation factors. It may be triggered by many diseases and is a common feature of shock.
Eosinophilia (hypereosinophilia) Increased number of eosinophilic leukocytes in blood or tissues. It is often induced by allergies or parasitic infections.
Fibrin degradation products (FDPs or fibrin split products) Cleaved fragments of fibrin formed through the enzymatic action of fibrolytic enzymes such as plasmin. Since FDPs are relatively small, they pass in urine and can be detected there in DIC.
Hematocrit Measure of the packed red blood cell volume, obtained by separating the red blood cells from plasma by centrifugation in a calibrated tube.
Hemolysis Lysis of red blood cells, which may occur in vivo in circulation or in tissues or in the test tube in vitro. A feature of various hemolytic anemias, lysis also occurs due to aging of RBCs or following bleeding. In vitro it may be induced by toxins, antibodies, or exposure to hypotonic fluid.
Leukocytosis Increased number of WBCs in the circulation. Most often it is a reaction to infection or other diseases, but it may also be a sign of leukemia.
Leukopenia Reduced number of WBCs, usually due to bone marrow failure or bone marrow suppression by some adverse influences, such as toxins or viruses.
Lymphadenopathy Enlargement of lymph nodes of unknown origin. Most often it represents lymph node hyperplasia in response to infection, due to a neoplastic process involving the lymph nodes (e.g., lymphoma or metastatic carcinoma).
Lymphocytosis Increased number of lymphocytes in the peripheral blood. It may be a reaction to infection or immune stimuli, but it is also a sign of lymphocytic leukemia.
Lymphopenia Reduced number of lymphocytes in the peripheral blood. Usually caused by viral infections, as in AIDS.
Monoclonal gammopathy Increased concentration of immunoglobulin gamma, presenting in serum electrophoresis as a sharp (“monoclonal”) peak. Typical of multiple myeloma, a neoplastic disorder characterized by monoclonal proliferation of malignant plasma cells that all secrete the same immunoglobulin. Monoclonal gammopathy is also found in monoclonal gammopathy of unknown significance (MNGUS), which may progress to multiple myeloma.
Peripheral blood smear Microscopic specimen prepared by spreading a thin film of peripheral blood on a glass slide and staining it with a metachromatic stain such as Giemsa stain. It used for microscopic examination of the morphology of RBCs and WBCs.
Prothrombin time Clinical test designed to measure the rate at which thrombin is formed in vitro under optimal conditions for estimating the function of factors II, V, VII, and X. It is thus used for assessing the extrinsic and common coagulation pathways. Clinical laboratories report it as standardized to external test values, such as the international normalized ratio (INR).
Thrombocythemia Increased number of platelets in peripheral blood, often a sign of myelodysplastic disorders or leukemia.
Thrombocytopenia Reduced number of platelets in peripheral blood. It may be caused by bone marrow failure or increased destruction of platelets in the spleen or during a coagulopathy, such as DIC.
Thrombosis Formation of clots inside the blood vessels or the heart. Thrombi form due to increased coagulability of the blood, damaged blood vessels, or abnormal circulation.
Hematopathology
Anemia Group of diseases characterized by a decreased number of circulating RBCs or hemoglobin content of blood. It can be classified pathogenetically as anemia due to defective RBC production in the bone marrow or increased blood loss and hemolysis.
Bleeding tendency Group of congenital or acquired disorders characterized by uncontrollable or recurrent bleeding usually from more than one site.
Hemophilia Congenital bleeding disorder characterized by a deficiency of factor VIII (hemophilia A) or factor IX (hemophilia B). Clinically it is characterized by uncontrollable bleeding following trauma or surgery.
Leukemia Group of clonal neoplastic disorders involving the stem cells and precursors of myeloid and lymphoid cells, in which the peripheral blood contains an increased number of neoplastic leukocytes. It can be classified as myelogenous or lymphocytic, and acute or chronic. Each of these groups comprises several distinct clinicopathologic subsets, which can be distinguished from one another by their unique cytogenetic, immunocytochemical, and molecular biologic features.
Lymphoma Malignancy involving the lymphoid system. It includes Hodgkin’s lymphoma and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, which in turn can be subclassified into several clinicopathologic entities. Each of these subtypes has unique histopathologic, immunocytochemical, cytogenetic, and often molecular biologic features, which must be taken into account when choosing proper chemotherapy.
Multiple myeloma Malignancy involving neoplastic proliferation of plasma cells, characterized by monoclonal gammopathy.
Myelodysplastic syndrome Group of clonal hematologic disorders affecting maturation of erythroid, myeloid, and megakaryocytic precursors, with consequent trilineage cytopenia (pancytopenia) in the peripheral blood. It may be hereditary (genetic), primary (idiopathic), or secondary (treatment-related). This group of disorders includes several variants of refractory anemia (e.g., with ring sideroblasts or with an excess of blasts) and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia.
Myeloproliferative disorders Group of neoplastic hematopoietic stem cell disorders characterized by clonal expansion of the bone marrow or ineffective hematopoiesis and the appearance of neoplastic cells and their descendants in the peripheral blood. This group of disorders includes clinicopathologic entities such as chronic myelogenous leukemia, polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, and agnogenic myeloid metaplasia (myelofibrosis).
Polycythemia vera Form of neoplastic clonal myeloproliferative disorder characterized by panmyelocytic hypercellularity of the bone marrow and an increased red blood cell mass. It must be distinguished from secondary polycythemia, in which the increased production of red blood cells is related to exogenous factors evoking oversecretion of erythropoietin.
Purpura Group of bleeding disorders characterized by widespread bleeding into the skin and internal organs. It results from diseases affecting the small blood vessels, platelets, or the entire coagulation system. It comprises a variety of diseases such as vascular, thrombotic, thrombocytopenic, or idiopathic purpura. Etiologically it may be classified as genetic, immune, drug-induced, viral, or idiopathic.
von Willebrand’s disease Genetic disease characterized by a bleeding tendency due to a congenital defect in the production of von Willebrand’s coagulation factor.
Normal Hematopoiesis
In the adults most blood cells are derived from the bone marrow.
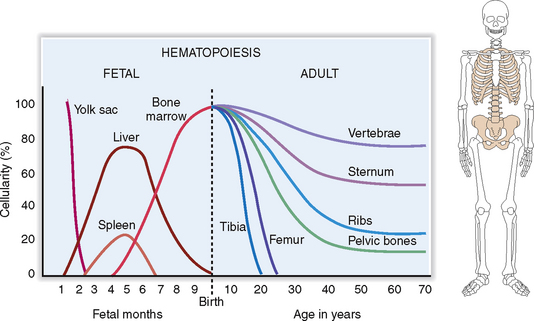
During prenatal life, the first signs of embryonic hematopoiesis are found in the yolk sac 4 weeks after conception. During the second trimester the liver and the spleen become the primary sites of fetal hematopoiesis, to be gradually relocated to the bone marrow inside the developing skeleton. In adults, the hematopoietic bone marrow is confined to the axial skeleton, including the sternum, ribs, vertebrae, and pelvic bones (Fig. 6-2).
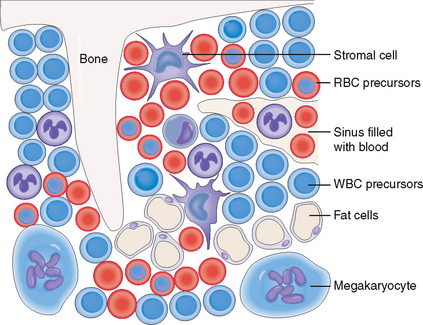
The hematopoietic bone marrow comprises hematopoietic cells and bone marrow stroma, which form the microenvironment essential for the growth and differentiation of the hematopoietic cells (Fig. 6-3). It also contains blood vessels, mostly in the form of sinusoids. These sinusoids have fenestrated walls so that the newly formed blood cells can easily enter the circulation. The bone marrow also contains thin bone trabeculae, which provide mechanical support and protection, and fat cells. With aging the hematopoietic elements decrease in number, and the fat cells become more numerous, replacing up to 70% of the total hematopoietic bone marrow in the elderly.
Blood cells develop from pluripotent hematopoietic stem cells under the influence of growth and differentiation factors.
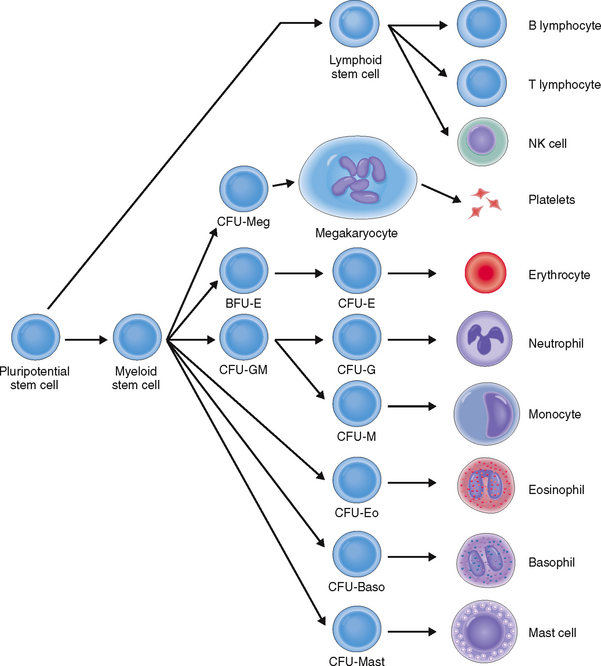
The formation of blood cells is a highly regulated process that occurs in several steps involving both cell multiplication and differentiation. Several cell lineages are formed, ultimately giving rise to mature RBCs, platelets, and several distinct types of WBCs: neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes (Fig. 6-4).
All hematopoietic cell lineages can be traced to a common ancestor—the pluripotent hematopoietic stem cell. Even though these cells account for less than 1% of all hematopoietic bone marrow cells, the adult bone marrow contains 25 to 500 million pluripotent stem cells. Some of these stem cells also enter into the circulating blood, from where they can be harvested for bone marrow transplantation. The pluripotent hematopoietic stem cells resemble small lymphocytes and can be identified only immunocytologically or by flow cytometry using labeled antibodies to their cell membrane marker—CD34.
The replication of stem cells and progenitor cells and the differentiation of precursor cells depend on the action of growth and differentiation factors produced by the stromal cells, macrophages, and T lymphocytes. Numerous growth and differentiation factors have been isolated and characterized; many of these have been synthesized using recombinant DNA technology and are used in clinical practice to stimulate and or regulate hematopoiesis. Erythropoietin acts on the precursors of RBCs, thrombopoietin stimulates platelet production, and granulocyte colony–stimulating factor (G-CSF) acts on the differentiation of neutrophil precursors. Interleukin 3 (IL-3) behaves as a nonlineage-specific growth factor, acting on both myeloid and lymphoid lineages. Note that the terminal stages of lymphocyte maturation and differentiation are antigen-dependent and can be significantly amplified during immune reactions.
Normal hematopoiesis requires an adequate supply of energy, nutrients, and vitamins.
 Proteins. Proteins are essential ingredients of food, and a protein-deficient diet adversely affects hematopoiesis. This is most prominent in persons who have unusual dietary habits, suffer from eating disorders, or have intestinal malabsorption syndromes. Increased demand for proteins during pregnancy or childhood also may affect hematopoiesis, especially if combined with other nutritional deficiencies, such as an iron or vitamin deficiency.
Proteins. Proteins are essential ingredients of food, and a protein-deficient diet adversely affects hematopoiesis. This is most prominent in persons who have unusual dietary habits, suffer from eating disorders, or have intestinal malabsorption syndromes. Increased demand for proteins during pregnancy or childhood also may affect hematopoiesis, especially if combined with other nutritional deficiencies, such as an iron or vitamin deficiency.
 Iron. A normal diet contains adequate amounts of iron, which is essential for the formation of hemoglobin (Hb). Inadequate intake or abnormal absorption in malabsorption syndromes, or an increased loss of RBCs (e.g., during heavy menstruation), may cause iron deficiency.
Iron. A normal diet contains adequate amounts of iron, which is essential for the formation of hemoglobin (Hb). Inadequate intake or abnormal absorption in malabsorption syndromes, or an increased loss of RBCs (e.g., during heavy menstruation), may cause iron deficiency.
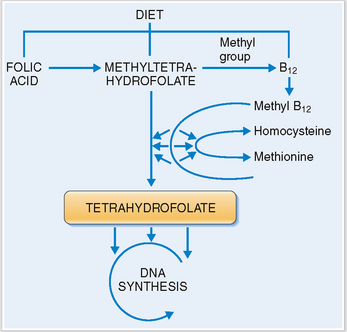
 Vitamin B12. This vitamin complex includes several cobalamines, which are normally present in meat and animal products. Vitamin B12 binds to the intrinsic factor secreted by gastric parietal cells and is absorbed in the small intestines. Dietary deficiency or abnormal absorption may adversely affect the synthesis of DNA during hematopoietic cell growth and maturation. Vitamin B12 is crucial for the formation of tetrahydrofolate, which plays the role of an essential coenzyme in the synthesis of DNA (Fig. 6-5). A lack of vitamin B12 typically results in megaloblastic anemia.
Vitamin B12. This vitamin complex includes several cobalamines, which are normally present in meat and animal products. Vitamin B12 binds to the intrinsic factor secreted by gastric parietal cells and is absorbed in the small intestines. Dietary deficiency or abnormal absorption may adversely affect the synthesis of DNA during hematopoietic cell growth and maturation. Vitamin B12 is crucial for the formation of tetrahydrofolate, which plays the role of an essential coenzyme in the synthesis of DNA (Fig. 6-5). A lack of vitamin B12 typically results in megaloblastic anemia.
 Folic acid. Normally present in green leafy vegetables, folic acid together with cobalamin is essential for normal DNA synthesis. Deficiency may result from inadequate intake, absorption, or utilization (i.e., as in patients treated with folic acid antagonists). Clinically it also manifests as megaloblastic anemia.
Folic acid. Normally present in green leafy vegetables, folic acid together with cobalamin is essential for normal DNA synthesis. Deficiency may result from inadequate intake, absorption, or utilization (i.e., as in patients treated with folic acid antagonists). Clinically it also manifests as megaloblastic anemia.
The life span of normal blood cells varies.
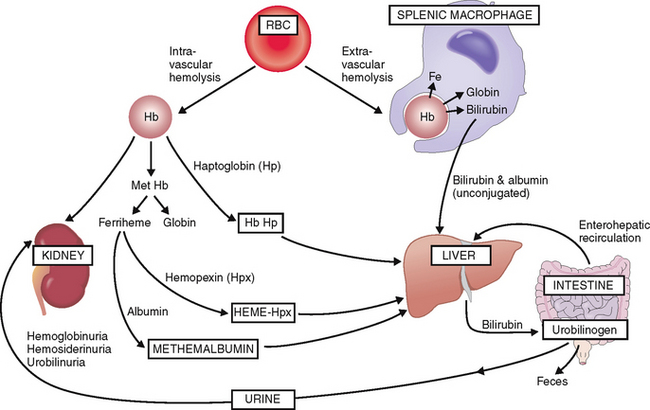
 Extravascular hemolysis. Lysis of RBCs in the splenic macrophages results in an efflux of bilirubin that is bound to albumin (“unconjugated bilirubin”) and transferred for further processing and excretion into the liver (Fig. 6-6). In the liver bilirubin is conjugated and made water-soluble and excreted into the intestine. Most of the intestinal bilirubin is recirculated and reused, but part of it is excreted in the urine as urobilinogen.
Extravascular hemolysis. Lysis of RBCs in the splenic macrophages results in an efflux of bilirubin that is bound to albumin (“unconjugated bilirubin”) and transferred for further processing and excretion into the liver (Fig. 6-6). In the liver bilirubin is conjugated and made water-soluble and excreted into the intestine. Most of the intestinal bilirubin is recirculated and reused, but part of it is excreted in the urine as urobilinogen.
 Intravascular hemolysis. Under normal circumstances intravascular hemolysis affects only a small percentage of RBCs, but under certain abnormal conditions it may take major proportions. The fragmented RBCs release free Hb, mostly in the form of Hb dimers, which bind to a plasma protein called haptoglobin. It serves as a carrier for free Hb dimers and transports them to the liver. A part of Hb is oxidized into methemoglobin, which is degraded into globin and oxidized heme (ferriheme). Ferriheme binds to hemopexin, which carries it to the liver. After hemopexin is exhausted, excess oxidized heme can also bind to albumin and thus form methemalbumin, which is also taken up by the liver. Hemoglobin dimers that are not bound to plasma proteins are excreted in the urine. Hence, intravascular hemolysis is accompanied by hemoglobinuria, hemosiderinuria, and urobilinuria.
Intravascular hemolysis. Under normal circumstances intravascular hemolysis affects only a small percentage of RBCs, but under certain abnormal conditions it may take major proportions. The fragmented RBCs release free Hb, mostly in the form of Hb dimers, which bind to a plasma protein called haptoglobin. It serves as a carrier for free Hb dimers and transports them to the liver. A part of Hb is oxidized into methemoglobin, which is degraded into globin and oxidized heme (ferriheme). Ferriheme binds to hemopexin, which carries it to the liver. After hemopexin is exhausted, excess oxidized heme can also bind to albumin and thus form methemalbumin, which is also taken up by the liver. Hemoglobin dimers that are not bound to plasma proteins are excreted in the urine. Hence, intravascular hemolysis is accompanied by hemoglobinuria, hemosiderinuria, and urobilinuria.
Iron released in extravascular or intravascular hemolysis is reused to synthesize Hb. Globin is also reused.
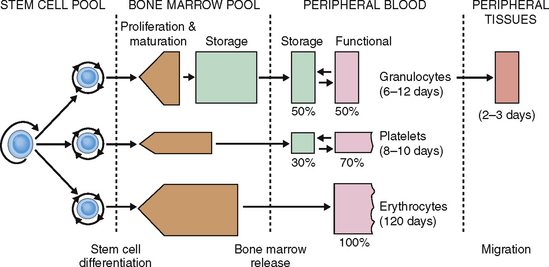
Neutrophils enter the circulation from the bone marrow pool maturation-storage compartment, which contains the equivalent of neutrophils in reserve for 4 to 8 days. The half-life of neutrophilic granulocytes in circulation is 6 to 12 days. Neutrophils enter the blood in the form of segmented neutrophils or band cells. In the circulation they form two distinct sets: the marginating pool (storage portion) and the circulating pool. Neutrophils also can enter into the tissue, where they live, on average, for 2 to 3 days (Fig. 6-7).
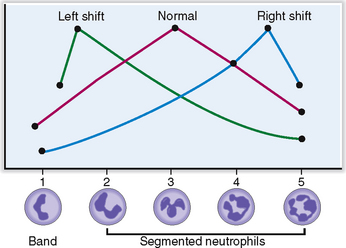
Approximately 6% of all circulating WBCs are nonsegmented (band cells), whereas all others undergo nuclear segmentation. As they age their nuclei become more segmented, and the oldest ones have five segments. This segmentation can be used to estimate the average age of neutrophils in the Arneth index, which is a curve based on the number of segments of neutrophilic nuclei (Fig. 6-8). Left shift indicates that fewer nuclei are segmented; that is, there is a prevalence of young PMNs, whereas right shift indicates that there are more aging PMNs.
Lymphocytes. These cells are long-lived, and their life span may be measured in months or years.
Normal Functions of Blood Cells
 Red blood cells—Oxygen transport. Red blood cells also serve as the primary transport vehicle for carbon dioxide, carrying it from the tissues into the lungs, where it is excreted. They also bind other gases and some other chemicals and act as part of the buffer system of the blood.
Red blood cells—Oxygen transport. Red blood cells also serve as the primary transport vehicle for carbon dioxide, carrying it from the tissues into the lungs, where it is excreted. They also bind other gases and some other chemicals and act as part of the buffer system of the blood.
 Granulocytes—Defense against infectious pathogens. Neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils form the primary line of defense against bacteria, and eosinophils act against parasites. All WBCs secrete cytokines and other biologically active substances that are important for the inflammatory reactions and also may contribute to the metabolic response to infections.
Granulocytes—Defense against infectious pathogens. Neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils form the primary line of defense against bacteria, and eosinophils act against parasites. All WBCs secrete cytokines and other biologically active substances that are important for the inflammatory reactions and also may contribute to the metabolic response to infections.
 Monocytes—Defense against pathogens and particulate matter. Monocytes are precursors of some tissue macrophages, and together they form the body’s phagocytic system. Tissue derivatives of monocytes act as antigen-presenting cells and participate in antigen uptake and presentation to lymphocytes; hence, they are an important part of the immune response. Macrophages produce cytokines and many other biologically active substances. They also participate in tissue repair, as in wound healing or healing of fractures.
Monocytes—Defense against pathogens and particulate matter. Monocytes are precursors of some tissue macrophages, and together they form the body’s phagocytic system. Tissue derivatives of monocytes act as antigen-presenting cells and participate in antigen uptake and presentation to lymphocytes; hence, they are an important part of the immune response. Macrophages produce cytokines and many other biologically active substances. They also participate in tissue repair, as in wound healing or healing of fractures.
 Lymphocytes—Immune response. B lymphocytes differentiate into antibody-secreting plasma cells, whereas the T lymphocytes participate in the cell-mediated immune reactions. These cells also participate in the defense against viral infections. Lymphocytes are a major source of cytokines, which regulate many body functions in health and disease.
Lymphocytes—Immune response. B lymphocytes differentiate into antibody-secreting plasma cells, whereas the T lymphocytes participate in the cell-mediated immune reactions. These cells also participate in the defense against viral infections. Lymphocytes are a major source of cytokines, which regulate many body functions in health and disease.
 Platelets—Coagulation. Platelets are essential components of blood clotting, but they also secrete mediators of inflammation and participate in many inflammatory and some immune reactions.
Platelets—Coagulation. Platelets are essential components of blood clotting, but they also secrete mediators of inflammation and participate in many inflammatory and some immune reactions.
The primary function of red blood cells is transport of oxygen.
Hemoglobin is a complex protein composed of globin and heme (Fig. 6-9). Globin is a tetramer composed of two α chains and two β chains or their equivalents γ and δ. The most abundant form of Hb is Hb A composed of two α and two β chains (α2β2). During fetal life the most predominant Hb is fetal hemoglobin (Hb F), which contains two α chains and two γ chains (α2γ2), but its level drops precipitously after birth, and by the age of 6 months it accounts for only 1% of the total Hb. Adult blood also contains Hb A2, which is composed of two α and two δ chains (α2δ2), accounting for less than 3.5% of total Hb. The concentration of Hb in the blood is lower in females than in males and also lower in adults than in newborns (Table 6-1).
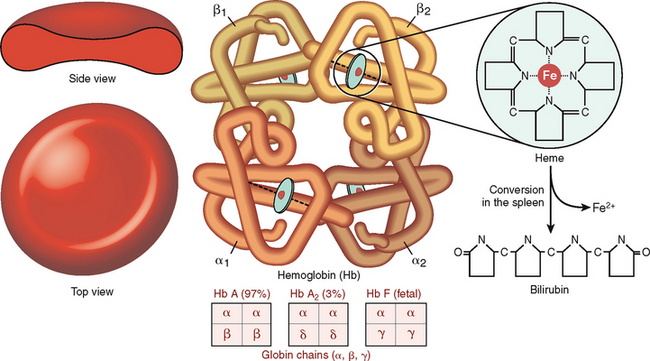
Figure 6-9 Hemoglobin structure.
(Reproduced with permission from Damjanov I: Pathology for Health Professions, 3rd ed. Philadelphia, Elsevier, 2005.)
Table 6-1 Normal Values of Hemoglobin (Hb) in Blood
| Newborns 16.5–21.5 g/dL (165–215 g/L) |
Affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen varies and depends on several factors.
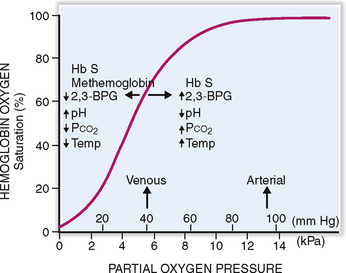
Hemoglobin has a high affinity for oxygen, but it also binds carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide. The affinity of Hb for oxygen depends on the pH of the blood, temperature, and concentration of 2,3-biphosphoglycerate (2,3-BPG), and the presence of variant hemoglobins that have a higher affinity for oxygen. The affinity for oxygen can be determined by measuring the oxygen pressure needed to achieve 50% saturation of Hb (P50) (Fig. 6-10). In a normal person at pH 7.35 this saturation can be achieved at a PO2 of 27 mm Hg. The oxygen saturation curve can be left-shifted, meaning that a P50 can be achieved at lower partial pressure by changing the following variables:
 Increasing the pH of blood into the alkaline range
Increasing the pH of blood into the alkaline range
 Decreasing the concentration of 2,3-BPG
Decreasing the concentration of 2,3-BPG
 Increasing the concentration of Hb variants that have high oxygen affinity, such as Hb F, or decreasing the amount of low-affinity Hb, such as Hb S in sickle cell anemia.
Increasing the concentration of Hb variants that have high oxygen affinity, such as Hb F, or decreasing the amount of low-affinity Hb, such as Hb S in sickle cell anemia.
Variant and abnormal hemoglobins influence oxygen binding and its release in tissues as follows:
 Fetal hemoglobin (Hb F) binds weakly with 2,3-BPG, thus shifting the curve to the left. In fetal or neonatal blood a P50 can be achieved at a PO2 of 19 to 21 mm Hg. This has an advantage before birth because it enables the fetus to “steal” oxygen from the mother. However, since the release of oxygen is also slower, in postnatal life the persistence of Hb F does not serve the affected person well.
Fetal hemoglobin (Hb F) binds weakly with 2,3-BPG, thus shifting the curve to the left. In fetal or neonatal blood a P50 can be achieved at a PO2 of 19 to 21 mm Hg. This has an advantage before birth because it enables the fetus to “steal” oxygen from the mother. However, since the release of oxygen is also slower, in postnatal life the persistence of Hb F does not serve the affected person well.
 Hemoglobin S (Hb S). In sickle cell anemia the RBCs containing Hb S tend to bind oxygen with high affinity, thus shifting the curve to the right.
Hemoglobin S (Hb S). In sickle cell anemia the RBCs containing Hb S tend to bind oxygen with high affinity, thus shifting the curve to the right.
 Methemoglobin. Instead of the ferrous iron (Fe2+) present in the normal Hb, methemoglobin contains ferric iron (Fe3+). Normal blood contains less than 1% of Hb in this form, which is produced due to spontaneous oxidation of Hb. Methemoglobin has an increased affinity for oxygen, and it cannot release it in tissues as efficiently as normal Hb. Increased amounts of methemoglobin, caused by drugs and toxins may result in cyanosis, especially in infants whose normal methemoglobin-reducing capacity has not been fully developed. It leads to a left shift of the oxygen dissociation curve.
Methemoglobin. Instead of the ferrous iron (Fe2+) present in the normal Hb, methemoglobin contains ferric iron (Fe3+). Normal blood contains less than 1% of Hb in this form, which is produced due to spontaneous oxidation of Hb. Methemoglobin has an increased affinity for oxygen, and it cannot release it in tissues as efficiently as normal Hb. Increased amounts of methemoglobin, caused by drugs and toxins may result in cyanosis, especially in infants whose normal methemoglobin-reducing capacity has not been fully developed. It leads to a left shift of the oxygen dissociation curve.
 Carboxyhemoglobin. Carbon monoxide (CO) is formed in small amounts in the healthy body. It binds to Hb, forming carboxyhemoglobin, which in normal persons accounts for 0.2 to 0.8% of total Hb in blood. In smokers it may be elevated from 4% to 15%. Since Hb has approximately 200 times higher affinity for CO than for oxygen, large amounts of carboxyhemoglobin are formed in CO poisoning, as after suicide by inhaling car exhaust gases or kitchen oven gas. Death results from CO preventing oxygenation of Hb, which ultimately leads to lethal hypoxia.
Carboxyhemoglobin. Carbon monoxide (CO) is formed in small amounts in the healthy body. It binds to Hb, forming carboxyhemoglobin, which in normal persons accounts for 0.2 to 0.8% of total Hb in blood. In smokers it may be elevated from 4% to 15%. Since Hb has approximately 200 times higher affinity for CO than for oxygen, large amounts of carboxyhemoglobin are formed in CO poisoning, as after suicide by inhaling car exhaust gases or kitchen oven gas. Death results from CO preventing oxygenation of Hb, which ultimately leads to lethal hypoxia.
Granulocytes participate in the defense against infection.
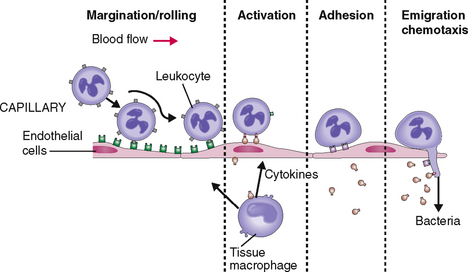
Granulocytes respond to infection by entering the circulation and moving toward the site of infection (Fig. 6-11). At the site of infection the neutrophils marginate, adhere to the endothelial cells of capillaries and venules, and undergo activation. In addition to surface changes and changes in motility, activated neutrophils secrete biologically active substances that act on other cells in the tissues, most notably endothelial cells, macrophages, and lymphocytes. In concert with the activated neutrophils these cells secrete cytokines and growth factors, such as interleukins, tumor necrosis factor (TNF), platelet-activating factor (PAF), and many others. These substances act on the bone marrow, stimulating it to release new neutrophils into circulation and to proliferate stem cells and the precursors of granulocytes. All these events lead to neutrophilia—an increase in the number of neutrophils in circulation.
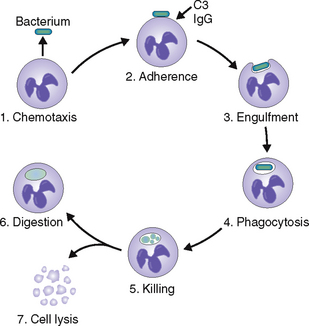
Neutrophils phagocytose and kill bacteria.
 High mobility. The PMNs are capable of amoeboid movement, allowing them to exit blood vessels and reach the site of infection much faster than any other cell.
High mobility. The PMNs are capable of amoeboid movement, allowing them to exit blood vessels and reach the site of infection much faster than any other cell.
 Sensitivity to chemotactic stimuli. PMNs respond to chemotactic substances generated by bacteria and injured tissue cells.
Sensitivity to chemotactic stimuli. PMNs respond to chemotactic substances generated by bacteria and injured tissue cells.
 Phagocytic capacity. PMNs readily form phagocytic vacuoles and are thus capable of ingesting bacteria and any other fragments found at the site of infection. Bacterial ingestion is facilitated by opsonins, such as complement fragment C3a and immunoglobulin G.
Phagocytic capacity. PMNs readily form phagocytic vacuoles and are thus capable of ingesting bacteria and any other fragments found at the site of infection. Bacterial ingestion is facilitated by opsonins, such as complement fragment C3a and immunoglobulin G.
 Bactericidal activity. PMNs can kill phagocytosed bacteria by oxygen-dependent and oxygen-independent enzymatic mechanisms (Fig. 6-12).
Bactericidal activity. PMNs can kill phagocytosed bacteria by oxygen-dependent and oxygen-independent enzymatic mechanisms (Fig. 6-12).
Loss of phagocytic cells, such as occurs in agranulocytosis caused by cytotoxic drugs and various disorders affecting the basic functions of the neutrophils, results in increased susceptibility to bacterial infections. These disorders can be congenital or acquired. The most important examples of deficient function of neutrophils are listed in Table 6-2.
Table 6-2 Congenital Disorders of Leukocyte Function
| DEFECTIVE MECHANISM | DISEASE |
| Defective adhesion | Leukocyte adhesion deficiency I and II |
| Decreased motility | Lazy leukocyte syndrome |
| Decreased phagocytosis | Chediak-Higashi syndrome |
| Decreased bacterial killing |
Lymphocytes are involved in the immune reactions.
 T cells mature by passing through the thymus, which typically occurs during fetal life and childhood. Inside the thymus the T cells differentiate into CD4+ T helper cells and CD8+ T cytotoxic cells. T cells are primarily involved in cell-mediated immune reactions, but they also regulate the functions of B cells.
T cells mature by passing through the thymus, which typically occurs during fetal life and childhood. Inside the thymus the T cells differentiate into CD4+ T helper cells and CD8+ T cytotoxic cells. T cells are primarily involved in cell-mediated immune reactions, but they also regulate the functions of B cells.
 B cells also differentiate stepwise and finally give rise to plasma cells—terminally differentiated cells involved in the production of immunoglobulins. Like T cells, the B cells interact with antigen-presenting cells, such as macrophages, Langerhans cells, or dendritic cells, but also among themselves.
B cells also differentiate stepwise and finally give rise to plasma cells—terminally differentiated cells involved in the production of immunoglobulins. Like T cells, the B cells interact with antigen-presenting cells, such as macrophages, Langerhans cells, or dendritic cells, but also among themselves.
 NK cells differ from T and B cells in that they do not have immunologic memory, but act without priming against tumor cells and virus-infected cells.
NK cells differ from T and B cells in that they do not have immunologic memory, but act without priming against tumor cells and virus-infected cells.
Platelets are involved in coagulation of the blood.
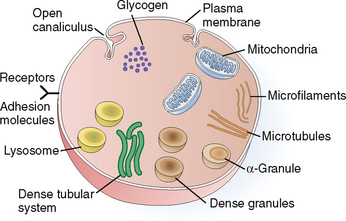
Platelets are small membrane-bounded particles measuring 2 to 4 μm. They do not have nuclei and are barely visible under light microscopy. The cytoplasm of platelets contains several components that are essential for their function (Fig. 6-13). Thus, it contains the following organelles:
 Mitochondria. These organelles generate energy, which is used to support all the essential functions of platelets. Glycogen stored in the cytoplasm serves as a source of energy.
Mitochondria. These organelles generate energy, which is used to support all the essential functions of platelets. Glycogen stored in the cytoplasm serves as a source of energy.
 Granules. The platelets contain several forms of granules. The most abundant are the alpha granules, which contain numerous proinflammatory and procoagulant and even anticoagulant proteins. Among other substances, alpha granules contain von Willebrand’s factor, fibrinogen, factor V, platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), and the anticoagulant protein S. Dense granules contain energy-rich compounds such as adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and vasoactive substances such as serotonin. Lysosomes are important for lytic functions.
Granules. The platelets contain several forms of granules. The most abundant are the alpha granules, which contain numerous proinflammatory and procoagulant and even anticoagulant proteins. Among other substances, alpha granules contain von Willebrand’s factor, fibrinogen, factor V, platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), and the anticoagulant protein S. Dense granules contain energy-rich compounds such as adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and vasoactive substances such as serotonin. Lysosomes are important for lytic functions.
 Cytoskeleton. The principal components of the cytoskeleton are the microtubules, composed of tubulin, and microfilaments, composed of actin and myosin. These fibrils are important for the maintenance of the shape of the platelets, their contraction, and the movement of other organelles and extrusion of granules.
Cytoskeleton. The principal components of the cytoskeleton are the microtubules, composed of tubulin, and microfilaments, composed of actin and myosin. These fibrils are important for the maintenance of the shape of the platelets, their contraction, and the movement of other organelles and extrusion of granules.
 Plasma membrane. This complex membrane is important for maintaining the integrity and the shape of platelets. It invaginates into the cytoplasm in the form of open canaliculi; it also contains numerous cell surface receptors and adhesion molecules. These complex glycoproteins are part of the cell membrane and are essential for the adhesion of platelets to surfaces and the initiation of the coagulation process. For example, the adhesion molecule GP IIb-IIIa binds to fibrinogen, and GP Ib binds to von Willebrand’s factor and collagen. Surface receptors also bind activators of platelets such as ADP or thromboxane A2 (TXA2).
Plasma membrane. This complex membrane is important for maintaining the integrity and the shape of platelets. It invaginates into the cytoplasm in the form of open canaliculi; it also contains numerous cell surface receptors and adhesion molecules. These complex glycoproteins are part of the cell membrane and are essential for the adhesion of platelets to surfaces and the initiation of the coagulation process. For example, the adhesion molecule GP IIb-IIIa binds to fibrinogen, and GP Ib binds to von Willebrand’s factor and collagen. Surface receptors also bind activators of platelets such as ADP or thromboxane A2 (TXA2).
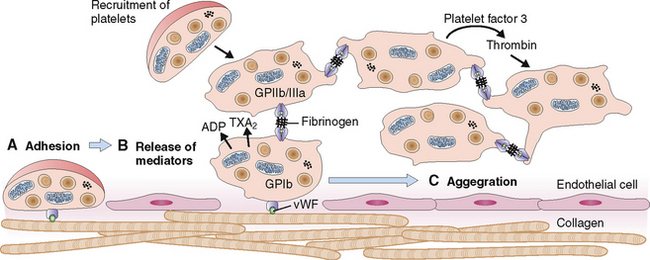
Circulating platelets readily adhere to damaged endothelial cells and fill the endothelial defects in disrupted or damaged blood vessels. The hemostatic platelet plug that forms under such conditions is a hallmark of primary hemostasis (Fig. 6-14). It leads to the activation of the coagulation cascade and formation of the fibrin clot known as secondary hemostasis (Fig. 6-15).
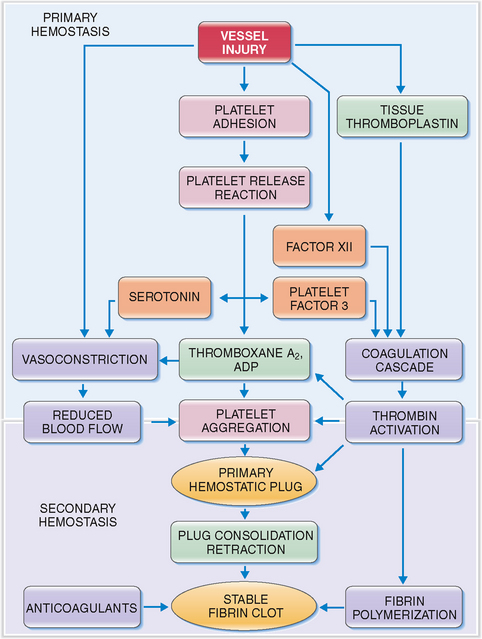
Figure 6-15 Primary and secondary hemostasis. As shown in Figure 6-14, vessel injury leads to the formation of the platelet adhesion, followed by the release of procoagulants and platelet aggregation. These events, leading to the formation of the primary hemostatic plug, are known as primary hemostasis. Substances released from platelets also cause vasoconstriction (thereby reducing blood flow to the damaged vessels) and activate the coagulation cascade and the formation of thrombin. Thrombin acts on platelets, promoting platelet aggregation, consolidation of the primary hemostatic plug, and its retraction. It also promotes polymerization of fibrin and thus contributes to the formation of a stable fibrin clot. These events are called secondary hemostasis. The fibrin clot is the substrate for several anticoagulants and fibrinolytic proteins, the most important of which is plasmin. ADP, adenosine diphosphate.
The typical features of defective primary and secondary hemostasis are compared in Table 6-3.
Table 6-3 Disturbances of Primary and Secondary Hemostasis
| PARAMETER | PRIMARY HEMOSTASIS | SECONDARY HEMOSTASIS |
| Cause | Vessel wall, platelets | Coagulation factors |
| Source of bleeding | Capillaries, venules | Arteries and arterioles |
| Mode of bleeding | Spontaneous | Trauma/surgery-related |
| Site of bleeding | Skin and mucosae | Intramuscular hematomas, hemarthrosis, surgical wounds |
| Screening tests | Platelet count | Prothrombin time |
| Bleeding time | Activated partial thromboplastin time |
Clinical and Laboratory Evaluation of Hematologic Diseases
Family and personal history may provide important diagnostic clues.
Family and personal history can point to some important risk factors that play a role in the pathogenesis of hematologic diseases. A few examples of such links and associations are given in Table 6-4.
Table 6-4 Risk Factors for Hematologic Diseases
| TYPE OF RISK FACTOR | SPECIFIC DISEASES–RISK FACTOR ASSOCIATIONS |
| Hereditary factors | |
| Nutritional factors | Folate or vitamin B12 deficient diet: Megaloblastic anemia |
| Gastrointestinal bleeding | Iron deficiency: Microcytic anemia |
| Cirrhosis | Bleeding tendency: Prolonged PTT or thrombocytopenia |
| Infections | |
| Medical and surgical procedures | |
| Drugs | |
| External mechanical factors |
DIC, disseminated intravascular coagulation; PTT, prothrombin time
Physical examination is important for evaluating hematologic disorders.
 Easy fatigability. Fatigue is a common symptom of anemia and is related to the reduced capacity of blood to carry oxygen. It may also manifest as shortness of breath, drowsiness, or inability to concentrate.
Easy fatigability. Fatigue is a common symptom of anemia and is related to the reduced capacity of blood to carry oxygen. It may also manifest as shortness of breath, drowsiness, or inability to concentrate.
 Pallor. A reduced concentration of Hb in anemia causes paleness of the mucosae best seen by examining the conjunctiva or oral mucosa. Previously when leukemia could not be treated, excess of WBCs in circulation also caused a white complexion.
Pallor. A reduced concentration of Hb in anemia causes paleness of the mucosae best seen by examining the conjunctiva or oral mucosa. Previously when leukemia could not be treated, excess of WBCs in circulation also caused a white complexion.
 Ruddy red face. In contrast to anemia, which causes pallor, polycythemia is typically associated with a ruddy red face. Sluggish flow of the hyperviscous blood in these patients also leads to prominent dilatation of the retinal blood vessels, which can be seen with the ophthalmoscope.
Ruddy red face. In contrast to anemia, which causes pallor, polycythemia is typically associated with a ruddy red face. Sluggish flow of the hyperviscous blood in these patients also leads to prominent dilatation of the retinal blood vessels, which can be seen with the ophthalmoscope.
 Jaundice. Hemolytic anemia is typically associated with jaundice. Excess bilirubin released from hemolyzed RBCs predisposes to the formation of gallstones.
Jaundice. Hemolytic anemia is typically associated with jaundice. Excess bilirubin released from hemolyzed RBCs predisposes to the formation of gallstones.
 Tachycardia. Anemia is associated with compensatory tachycardia and audible cardiac murmurs.
Tachycardia. Anemia is associated with compensatory tachycardia and audible cardiac murmurs.
 Oral mucosal changes. Deficiency of iron may cause angular cheilitis, whereas vitamin B12 and folate may produce a velvety red tongue typical of glossitis.
Oral mucosal changes. Deficiency of iron may cause angular cheilitis, whereas vitamin B12 and folate may produce a velvety red tongue typical of glossitis.
 Recurrent infection. Skin and nasopharyngeal infections occur at an increased rate in patients who have leukopenia, aplastic anemia, or functional disorders affecting leukocytes.
Recurrent infection. Skin and nasopharyngeal infections occur at an increased rate in patients who have leukopenia, aplastic anemia, or functional disorders affecting leukocytes.
 Excessive bleeding. Bleeding from the gums or nose or into the skin are signs of thrombocytopenia caused by bone marrow failure, which occurs in aplastic anemia or in various forms of leukemia. Hemophilia presents with post-traumatic bleeding, hemarthrosis, or prolonged bleeding after surgical interventions.
Excessive bleeding. Bleeding from the gums or nose or into the skin are signs of thrombocytopenia caused by bone marrow failure, which occurs in aplastic anemia or in various forms of leukemia. Hemophilia presents with post-traumatic bleeding, hemarthrosis, or prolonged bleeding after surgical interventions.
 Lymphadenopathy. Lymph node enlargement may be the first sign of lymphoma, but it could also be related to infections or autoimmune diseases. Clinically it is best to consider lymphadenopathy as either localized or generalized (Table 6-5).
Lymphadenopathy. Lymph node enlargement may be the first sign of lymphoma, but it could also be related to infections or autoimmune diseases. Clinically it is best to consider lymphadenopathy as either localized or generalized (Table 6-5).
 Splenomegaly. Enlargement of the spleen may be a sign of increased hemolysis in some forms of anemia, such as hereditary spherocytosis. Splenic enlargement is found in many forms of leukemia and lymphoma. Other causes of splenomegaly are listed in Table 6-6.
Splenomegaly. Enlargement of the spleen may be a sign of increased hemolysis in some forms of anemia, such as hereditary spherocytosis. Splenic enlargement is found in many forms of leukemia and lymphoma. Other causes of splenomegaly are listed in Table 6-6.
Table 6-5 Causes of Lymphadenopathy
| TYPE OF DISEASE | EXAMPLES |
| Acute infection | Strep throat, viral pharyngitis, syphilis, cat scratch disease |
| Chronic infection | Tuberculosis, histoplasmosis, chronic dermatitis |
| Autoimmune disease/unknown origin | SLE, sarcoidosis, erythema nodosum |
| Lymphoma | Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, Hodgkin’s lymphoma |
| Carcinoma | Metastatic carcinoma |
SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus.
Table 6-6 Causes of Splenomegaly
| TYPE OF DISEASE/MECHANISM | EXAMPLES |
| Hemolytic anemia | Spherocytosis, thalassemia |
| Leukemia/lymphoma | |
| Infections | Sepsis, endocarditis, malaria |
| Immune disorders | Rheumatoid arthritis, SLE, sarcoidosis |
| Storage diseases | Gaucher’s disease, Niemann-Pick disease |
| Portal hypertension | Cirrhosis, cardiac failure |
CLL, chronic lymphocytic leukemia; CML, chronic myelogenous leukemia; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus.
Laboratory studies are essential for the exact diagnosis of hematologic disorders.
We discuss only the most commonly performed tests, however, as they are used for evaluating RBC, WBC, and coagulation disorders. The most important hematologic values used in general clinical practice are listed in Tables 6-7 to 6-9.
Table 6-7 Normal Red Blood Cell Indices in Adults
| Hemoglobin | |
| Hematocrit | |
| Red blood cell (RBC) count | |
| Mean corpuscular hemoglobin | 27–33 pg/cell |
| Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration | 33–35% |
| Mean corpuscular volume | 80–96 m3 (fL) |
| Red cell distribution width | 11.5–14.5% |
| Reticulocyte count | 0.5–2.5% of all RBCs |
| Iron | Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|