Although capital letters are commonly used in this system, lower case letters are also seen to depict Roman numerals.
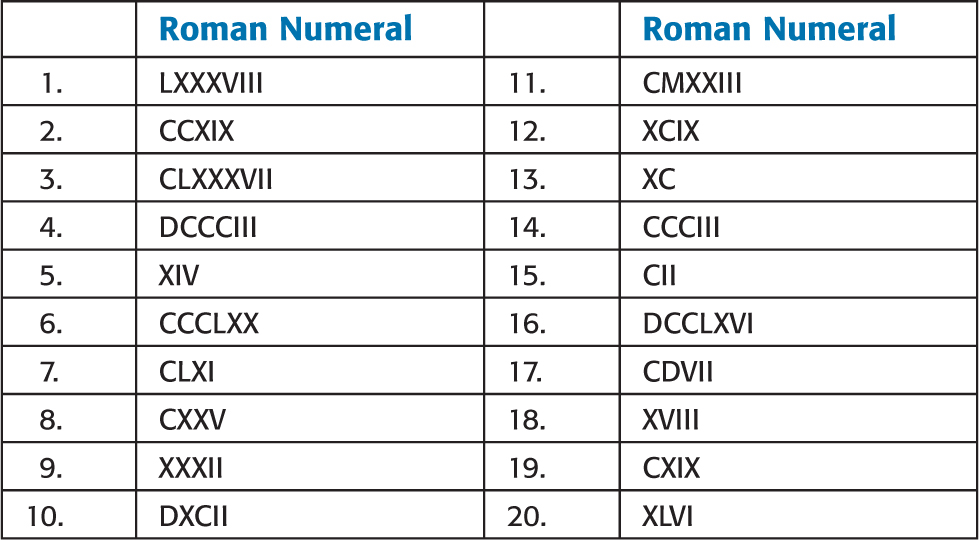
Practice Exercises
Convert the following Roman numerals to their Arabic equivalent
Whole Numbers, Fractions, and Decimals
Whole numbers are self explanatory. They are numbers like 11, 25, 337, 19, 3, etc. Fractions are parts of whole numbers expressed as a numerator and denominator. For example: ½, ¼, 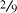 ,
, 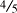 , etc. Fractions are used to depict amounts less than one.
, etc. Fractions are used to depict amounts less than one.
Decimals are another method of writing fractions. They are amounts less than one. The numerator is divided by the denominator yielding the decimal number. So, for example 1 divided by 2 (in ½) is 0.5; 1 divided by 4 (in ¼) is 0.25; and so on.
In pharmacy it is imperative that the placing of the decimal point is absolutely clear, otherwise tenfold errors can occur. Further complicating the problem is that some pharmacies only get NCR copies or faxed copies of prescriptions, making the zero or decimal point difficult to read.
To minimize interpretation errors, the convention in pharmacy is to avoid trailing zeros after the decimal point and to include leading zeros before the decimal point. In this manner it is unlikely that the value can be misunderstood. Examples: 3 not 3.0, 10 not 10.0, 0.3 not.3, 0.1 not.1.
Practice Exercises
Convert these fractions to decimals:
1. 3 ¾
2. 2 ½
3. 40/80
4. 1/100
5. 1/3
6. 27/90
7. 6/8
8. 6/5
9. 9/15
10. 12/8
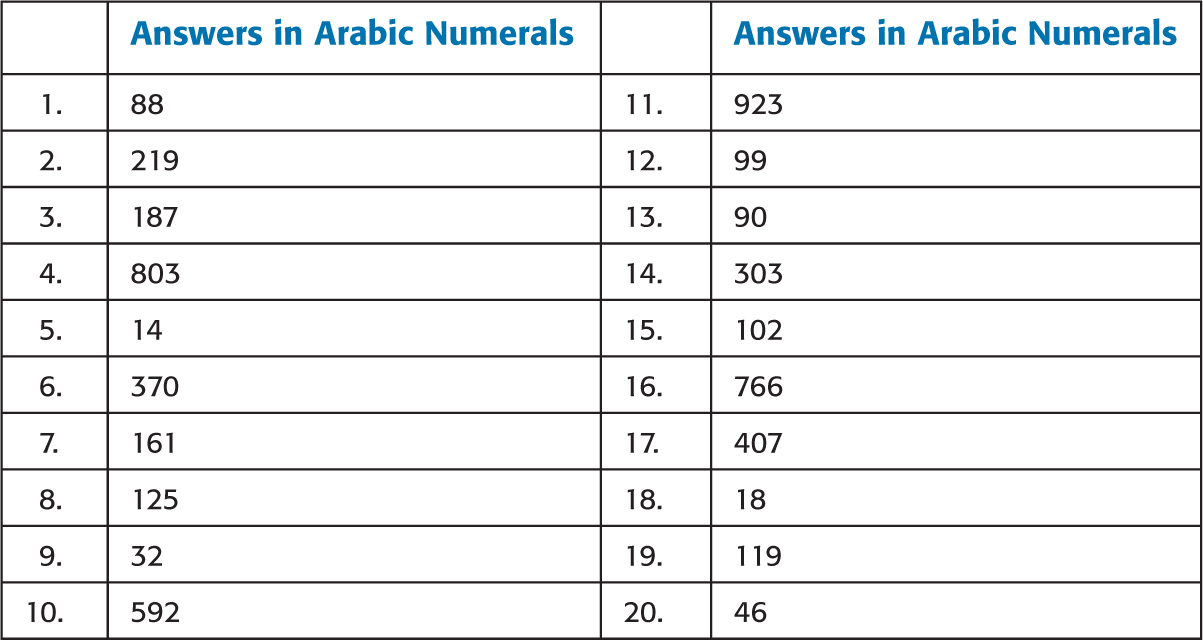
Answers
1. 3.75
2. 2.5
3. 0.5
4. 0.01
5. 0.33
6. 0.3
7. 0.75
8. 1.2
9. 0.6
10. 1.5
Remember, always write the decimal numbers with the leading zero as necessary.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>



