Chapter 12 Antiarrhythmic Drugs
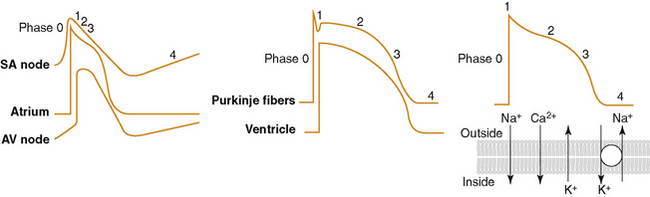
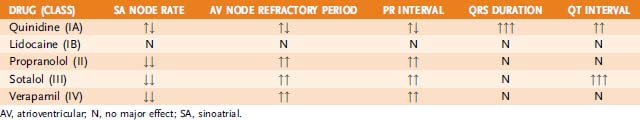
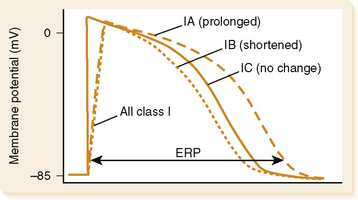
• Block open or activated sodium channels, also block potassium channel; thus prolong action potential and effective refractory period (ERP)
(a) Inhibition of sodium channels, extending ERP, thereby decreasing myocardial conduction velocity, excitability, and contractility
(b) Blockade of α-adrenergic receptors, producing vasodilation and leading to a reflex increase in the SA node rate
(d) Blockade of muscarinic receptors, thereby decreasing vagal tone, thus increasing heart rate and enhancing conduction through AV node
(a) Conversion to or maintenance of sinus rhythm in patients with atrial fibrillation, flutter, or ventricular tachycardia
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree