Diagnostic component is spindle or epithelioid smooth muscle cells

Epithelioid smooth muscle cells are typically large, with round to oval nuclei, and eosinophilic to fibrillar or vacuolated cytoplasm
•
Features that predict malignant behavior are not well defined

Nuclear atypia and infiltrative margins can be seen in benign tumors
Ancillary Tests
•
Smooth muscle cells stain with antibodies to HMB-45, MART-1, but not keratin or Hep-Par1
Top Differential Diagnoses
•
Hepatocellular neoplasm, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma
•
Metastatic malignant tumor, either carcinoma or sarcoma
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Definitions
•
Rare, benign mesenchymal neoplasm composed of smooth muscle, adipose tissue, and vessels

Thought to arise from perivascular epithelioid cells (PEC); therefore, considered part of PEComa family of tumors
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
•
Incidence

Rare: Overall incidence unknown but only a few hundred cases reported

Some cases associated with tuberous sclerosis (6-10%), but less often than renal AML (20-40%)
–
More likely to be associated with tuberous sclerosis if multiple &/or associated with renal tumors
•
Age

Adults 17-86 years (mean: 43.5-50 years)
•
Sex

Marked female predominance
Presentation
•
Most patients are asymptomatic and present incidentally
•
Large tumors may cause symptoms related to mass effect or abdominal discomfort
Treatment
•
Surgical approaches

Excision
–
When diagnosis cannot be established on biopsy
–
Large lesions at risk for rupturing
•
Conservative approaches

If diagnosis can be confidently established, radiologic follow-up is recommended
Prognosis
•
Benign behavior in nearly all cases

Tumor recurrence is uncommon

Metastasis extremely rare
IMAGING
Ultrasonographic Findings
•
Most angiomyolipomas present as heterogeneous hyperechoic lesions, but can be hypoechoic
MR Findings
•
MR is most specific imaging modality for detecting lipomatous component
•
Most tumors are hypointense on T1WI and slightly hyperintense on T2WI
CT Findings
•
Usually hypodense on precontrast CT
MACROSCOPIC
General Features
 Epithelioid smooth muscle cells are typically large, with round to oval nuclei, and eosinophilic to fibrillar or vacuolated cytoplasm
Epithelioid smooth muscle cells are typically large, with round to oval nuclei, and eosinophilic to fibrillar or vacuolated cytoplasm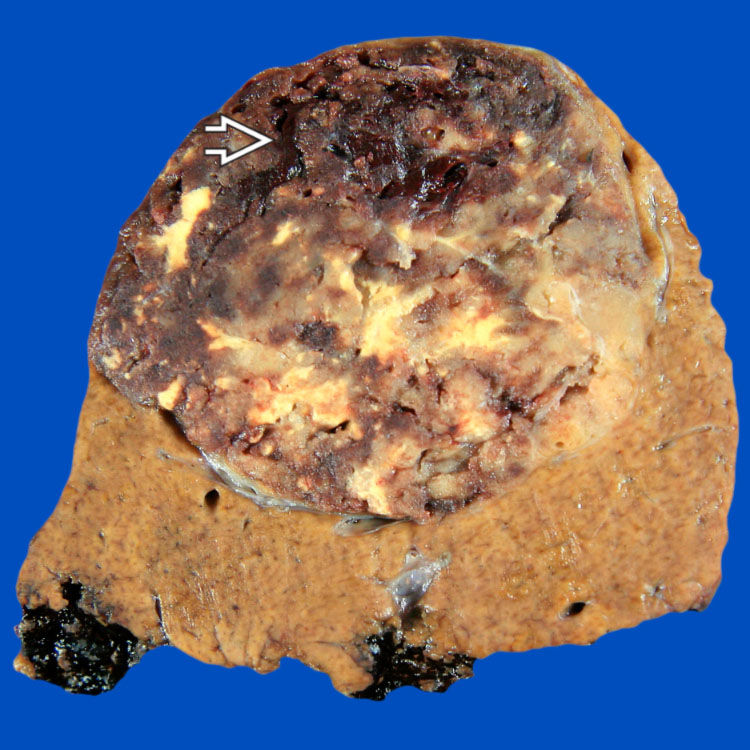
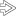 . Note that the background liver is not cirrhotic.
. Note that the background liver is not cirrhotic.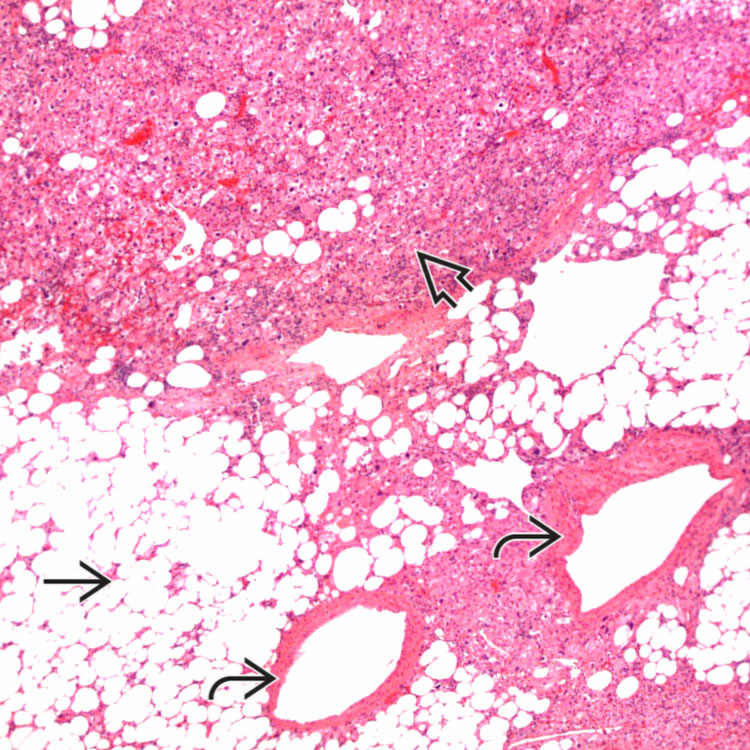
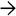 , vessels
, vessels 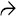 , and myoid cells
, and myoid cells 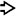 , which in this case are plump and spindled.
, which in this case are plump and spindled.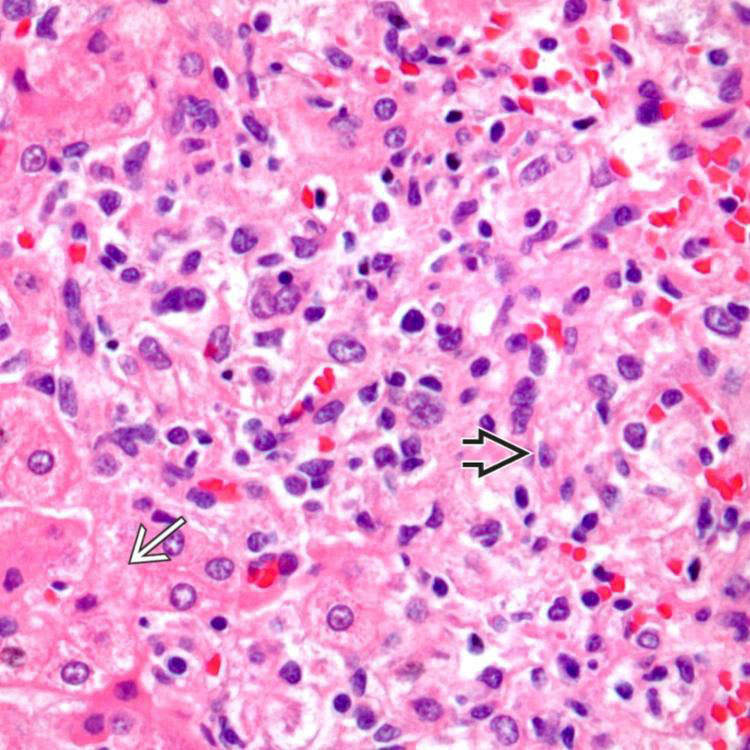
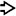 of an angiomyolipoma contrasts with the more eosinophilic and granular hepatocyte cytoplasm
of an angiomyolipoma contrasts with the more eosinophilic and granular hepatocyte cytoplasm  .
.







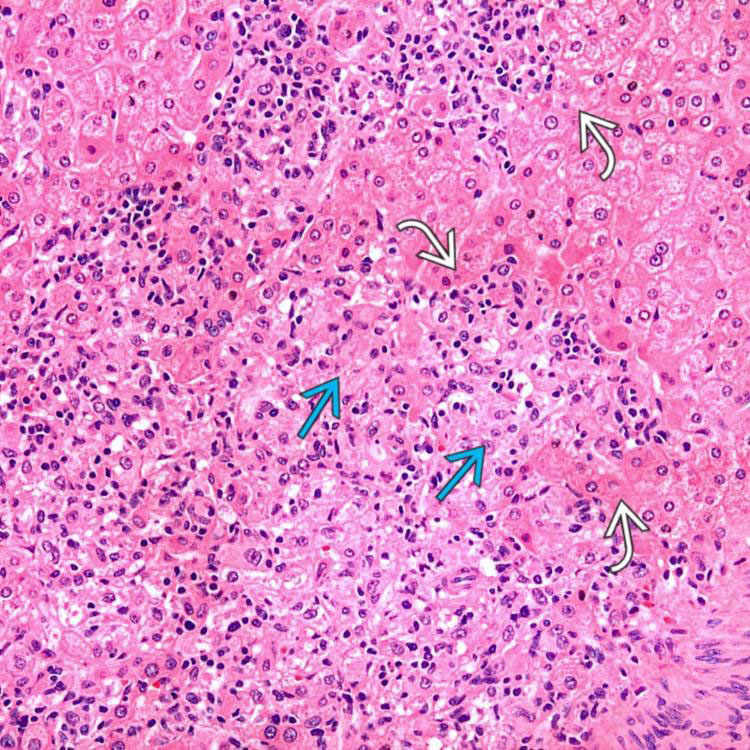
 at the interface with background liver
at the interface with background liver  is not an indication of malignancy.
is not an indication of malignancy.









