Cells characteristically cluster around thin-walled capillaries
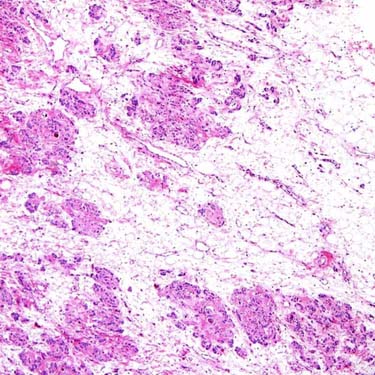
Angiomyofibroblastoma (AMFB) is a distinctive, benign neoplasm of the lower female genital tract. At low magnification, the classic morphologic pattern is that of irregular zones of cellularity within a myxoid or fibrous stroma.
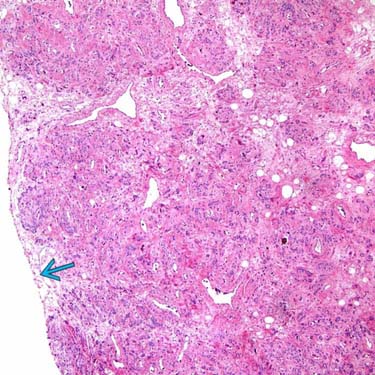
Some areas of AMFB are less myxoid and more fibrous, as seen here. Note the sharp circumscription
 , a feature seen in most examples.
, a feature seen in most examples.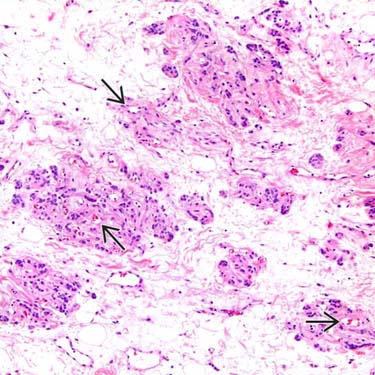
The neoplastic cells of AMFB are characteristically clustered around small, thin-walled capillary channels
 , which can often be recognized by the presence of intraluminal erythrocytes. The intervening myxoid stroma is hypocellular.
, which can often be recognized by the presence of intraluminal erythrocytes. The intervening myxoid stroma is hypocellular.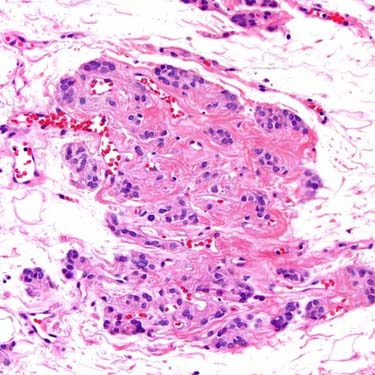
In classic cases of AMFB, the tumor cells are epithelioid, ovoid, or plasmacytoid-appearing, and form small nests or clusters around capillary channels. This perivascular orientation is characteristic of this tumor.
MICROSCOPIC
Histologic Features
• Plump epithelioid, ovoid, or plasmacytoid tumor cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm




Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








