Angiokeratoma
Steven D. Billings, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
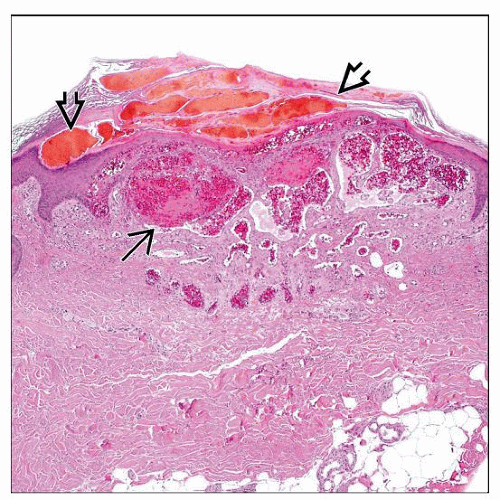
Ectatic superficial dermal blood vessels associated with reactive epidermal hyperplasia
Clinical Issues
Solitary and multiple angiokeratomas
Angiokeratoma of Fordyce
Angiokeratoma of Mibelli
Angiokeratoma corporis diffusum
Associated with Anderson-Fabry disease
Angiokeratoma circumscriptum
Microscopic Pathology
Marked ectasia of papillary dermal blood vessels, which may appear to extend into epidermis
May have evidence of thrombosis and intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia
Reactive epidermal changes: Acanthosis, hyperkeratosis, and elongation of rete ridges around ectatic vessels
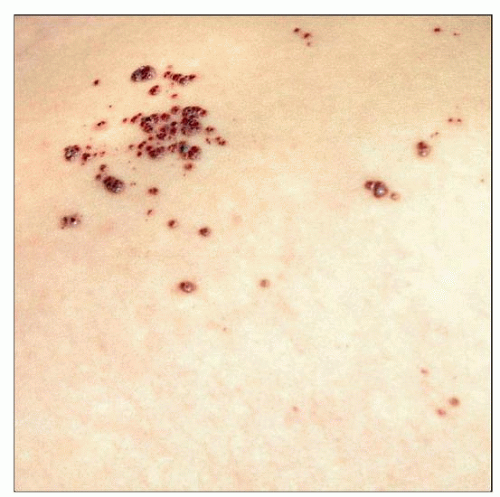 This clinical image demonstrates numerous grouped angiokeratomas in a patient with Anderson-Fabry disease. |
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Ectatic superficial dermal blood vessels associated with reactive epidermal hyperplasia
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
5 clinical variants
Solitary and multiple angiokeratoma
Usually solitary
Multiple lesions may have zosteriform presentation
Wide age range
Usually on extremities
Angiokeratoma of Fordyce
Elderly men
Solitary or multiple papules on scrotum
Angiokeratoma of Mibelli
Presents in childhood and adolescence
Warty lesions over bony prominences of acral locations
Angiokeratoma corporis diffusum
Multiple, often clustered papules
Bathing suit distribution
Associated with Anderson-Fabry disease: X-linked recessive disorder of α-galactosidase A
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree