Intraampullary: Arise in ampulla (lined by pancreatobiliary epithelium)

Periampullary: Arise in duodenal surface of papilla (lined by intestinal epithelium)
Clinical Issues
•
5-year overall survival rate: 40%

Determined by histologic type, grade, stage, coexisting adenoma
Microscopic
•
2 main histologic types

Intestinal-type adenocarcinoma
–
Similar to adenocarcinoma of colon and small bowel

Pancreatobiliary-type adenocarcinoma
–
2nd most common (15-20%)
–
Similar to pancreatic ductal or bile duct adenocarcinoma
Ancillary Tests
•
Intestinal type

CK20, CDX-2, or MUC2 (+), MUC1(-)

CK20, CDX-2, and MUC2 (+), irrespective of MUC1
•
Pancreatobiliary type

MUC1(+), CDX-2 and MUC2 (-)
Top Differential Diagnoses
•
Adenocarcinomas of pancreas, distal common bile duct, and duodenum
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
•
Periampullary adenocarcinoma
Definitions
•
Malignant epithelial neoplasm originating in ampulla of Vater

Centered on, circumferentially surrounding, or completely replacing ampulla
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Histogenesis
•
Intraampullary: Arise in ampulla (lined by pancreatobiliary epithelium)
•
Periampullary: Arise in duodenal surface of papilla (lined by intestinal epithelium)
Predisposing Syndromes
•
Familial adenomatous polyposis, Lynch syndrome, type 1 neurofibromatosis
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
•
Incidence

0.7 and 0.4 cases per 100,000 males and females, respectively

0.5% of all gastrointestinal malignancies
•
Age

Mean: 62 years (range: 29-85 years)
–
Younger in patients with predisposing syndromes
Presentation
•
Jaundice, abdominal pain, pancreatitis, weight loss
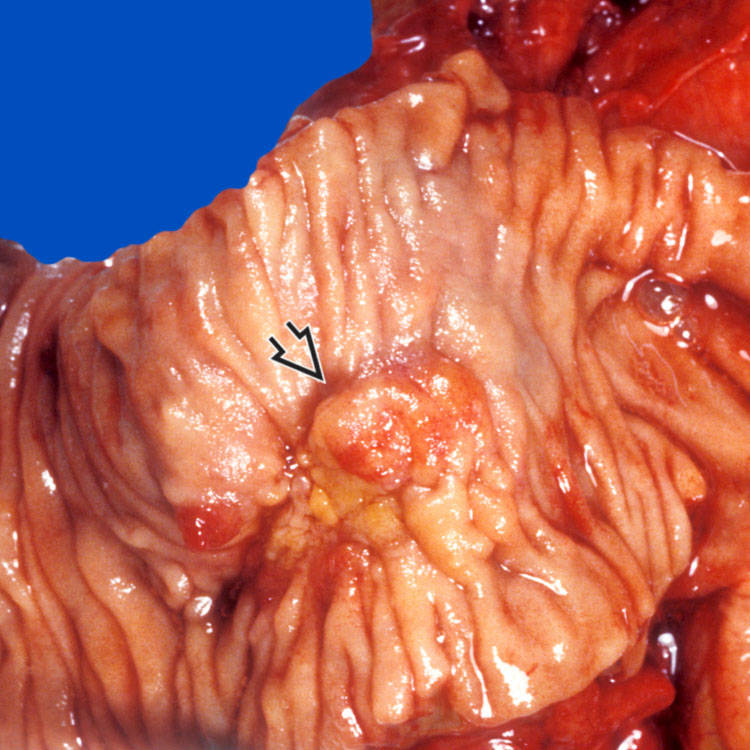
 involving the papilla and periampullary duodenal mucosa. Histologic examination confirms the diagnosis of ampullary adenocarcinoma.
involving the papilla and periampullary duodenal mucosa. Histologic examination confirms the diagnosis of ampullary adenocarcinoma.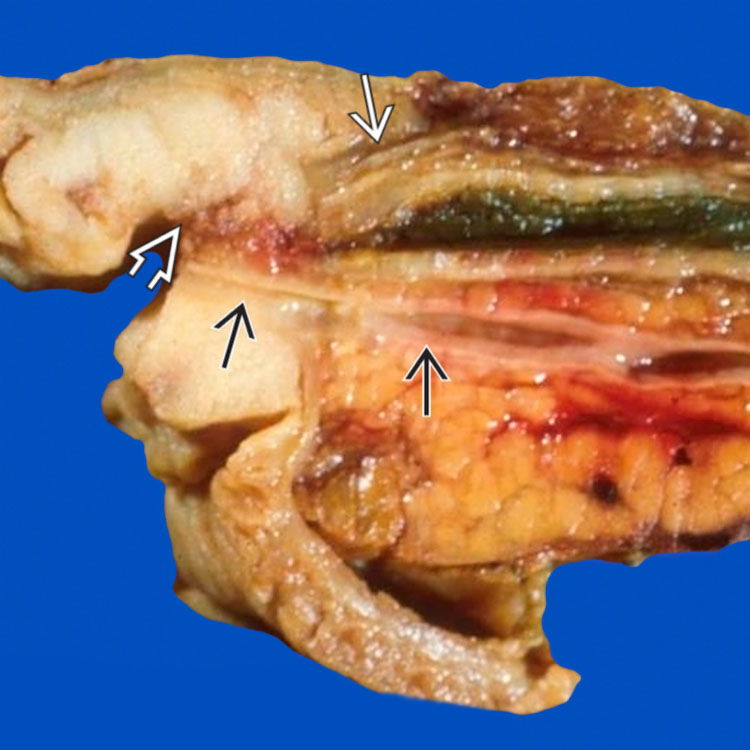
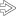 of the common bile duct
of the common bile duct  , which is dilated proximally. The pancreatic duct
, which is dilated proximally. The pancreatic duct 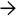 is not obstructed.
is not obstructed.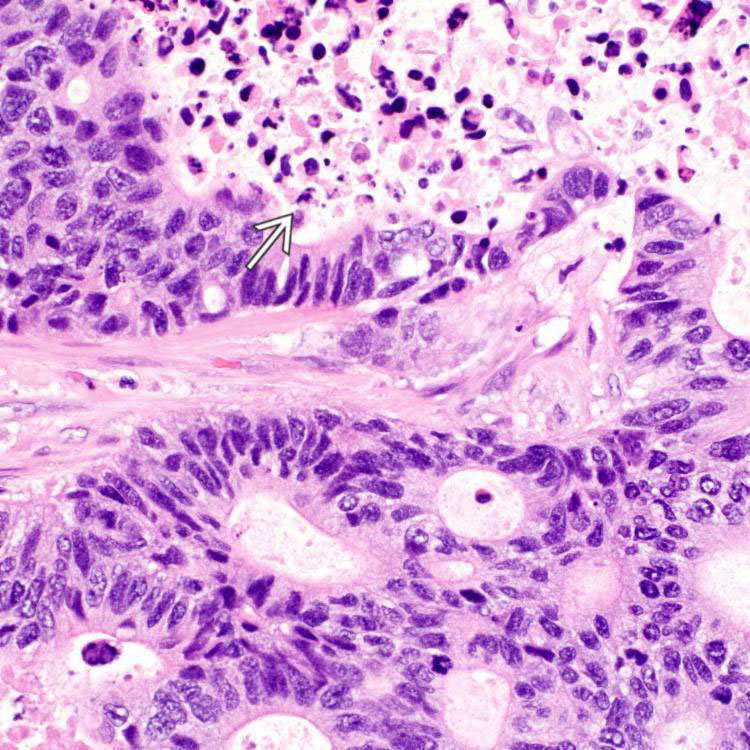
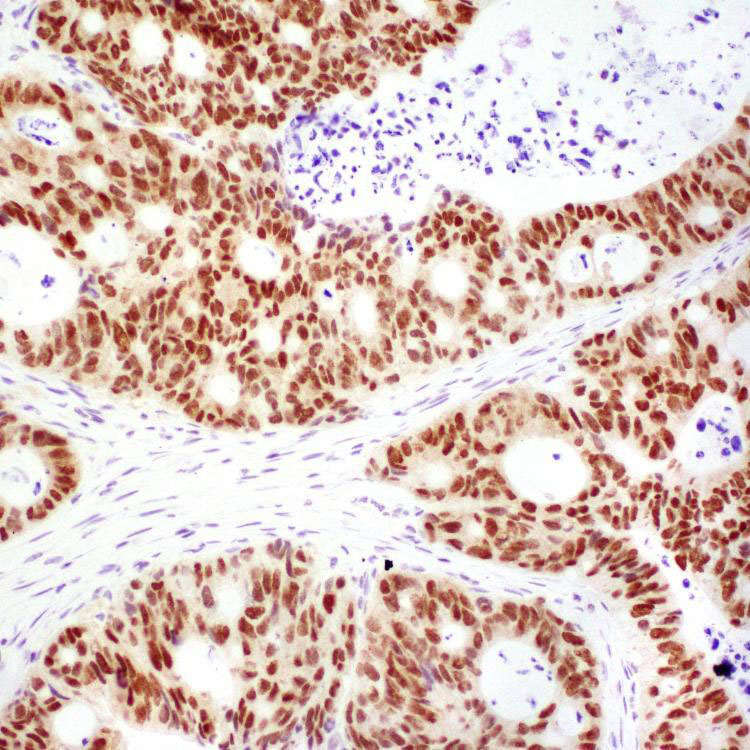
 . Tumor cells are columnar with stratified, elongated or oval nuclei, resembling adenocarcinoma of colon and small bowel.
. Tumor cells are columnar with stratified, elongated or oval nuclei, resembling adenocarcinoma of colon and small bowel.