ALK+ Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma
Tariq Muzzafar, MBBS
Key Facts
Etiology/Pathogenesis
ALK gene abnormalities at chromosome 2p23 appear to be key transforming event
Result in formation of fusion genes and ALK overexpression
Clinical Issues
Rare; ˜ 80 cases reported
Lymph nodes are most commonly involved and biopsied (˜ 75%)
60-70% of patients have stage III or IV disease
Aggressive clinical course and poor survival
Microscopic Pathology
Partial or diffuse effacement of lymph node architecture
Lymphoma cells infiltrate sinusoids in many cases
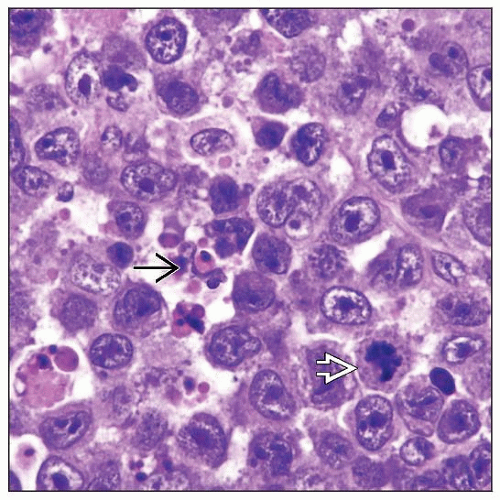
Monomorphic, large immunoblast-like cells; ± plasmacytoid differentiation
Ancillary Tests
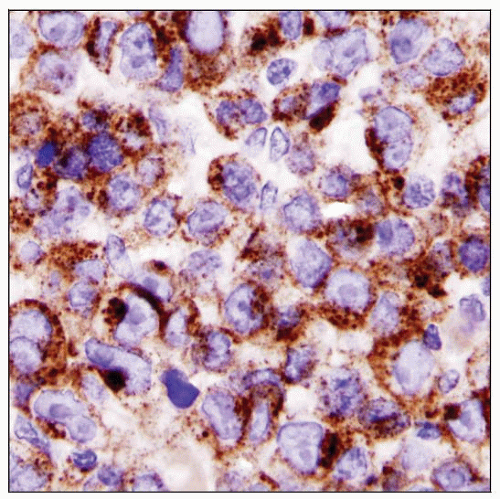
ALK strongly positive
EMA(+), CD138(+), VS38c(+)
Cytoplasmic IgA(+) in > 95% of cases
CD30 usually (-), EBER(-)
Pan-B- and pan-T-cell markers negative
ALK gene abnormalities in all cases
Most common: CLTC-ALK
Top Differential Diagnoses
Plasmablastic lymphoma
DLBCL immunoblastic variant
Plasmacytoma/plasma cell myeloma
ALK(+) anaplastic large cell lymphoma
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)
Definitions
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma expressing ALK protein and associated with ALK gene abnormalities
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Etiology
No known association with infectious or environmental factors
Genetics
ALK gene abnormalities at chromosome 2p23 appear to be key transforming event
Result in formation of fusion genes
Clathrin heavy-chain gene (CLTC)-ALK
Nucleophosmin (NPM)-ALK
SEC31A-ALK
Overexpression of ALK protein
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
< 1% of all cases of DLBCL
Approximately 80 cases reported to date
Age
Range: 9-85 years
Median: ˜ 40 years
Gender
Male to female ratio: ˜ 5 to 1
Ethnicity
No apparent ethnic predisposition
Site
Lymph nodes are most commonly involved and biopsied (˜ 75%)
Extranodal sites of involvement include
Bone marrow in ˜ 25% of patients
Nasal cavity, nasopharynx, oral cavity
Stomach, small intestine
Spleen, ovary
Bones, soft tissues
Epidural mass, brain
Enlarged mediastinal lymph nodes can present as mediastinal mass
Patients can present with leukemic involvement
Presentation
Systemic (B-type) symptoms common
60-70% of patients have stage III or IV disease
Widespread lymphadenopathy
Aggressive clinical course
Laboratory Tests
Serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels elevated in ˜ 50% of patients
HIV serology is (-)
Treatment
Drugs
Most patients have been treated with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP) regimen
Based on survival data, this therapeutic approach is not optimal
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Lymph node
Partial or diffuse effacement of lymph node architecture
Lymphoma cells infiltrate sinusoids in many cases
± focal necrosis
± binucleated HRS-like cells
± multinucleated giant lymphoma cells
Mitotic figures easily identified
Extranodal sites
Similar morphologic features
Sinusoidal infiltration usually not appreciated at extranodal sites
Bone marrow
Variable degree of involvement
Sinusoidal involvement is uncommon in bone marrow