ALK+ Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma
Francisco Vega, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Terminology
CD30(+) lymphoma of T- or null cell lineage having chromosomal abnormalities involving 2p23 (ALK locus)
Clinical Issues
Children and adults
Most patients present with clinical stage III/IV
Extranodal involvement common (60%)
5-year survival: 80-90%
Microscopic Pathology
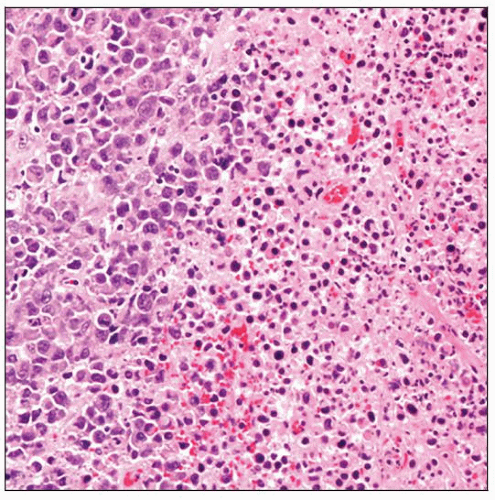
Cytological spectrum of neoplastic cells from small to large
“Hallmark cells” characteristic
Ancillary Tests
Immunophenotypic studies needed to confirm diagnosis
ALK positive
CD30 strongly and uniformly positive
Lymphoma characterized by chromosomal translocations involving ALK gene
Most frequent is t(2;5)(p23;q35), detected in 75%
Top Differential Diagnoses
Classical Hodgkin lymphoma (CHL)
ALK(−) ALCL
Peripheral T-cell lymphoma, NOS
DLBCL expressing CD30
Cutaneous ALCL
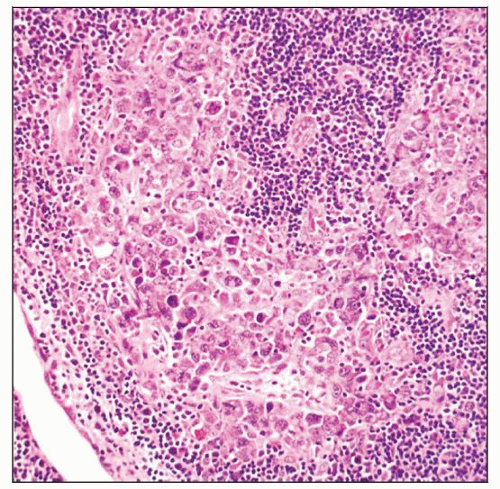 ALK(+) ALCL, classical variant, involving lymph node. The neoplastic cells grow cohesively and preferentially involve sinuses. (Courtesy M. Lim, MD, PhD.) |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) positive, anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL)
Definitions
CD30-positive systemic lymphoma of T- or null cell lineage with chromosomal abnormalities involving 2p23 and ALK
Current WHO classification distinguishes 2 types of systemic ALCL
ALK(+) and ALK(−)
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
Children and young adults
Male predominance
B symptoms, especially fever
Most patients present with clinical stage III/IV disease
Extranodal involvement common (60%)
Particularly skin, soft tissue, and lungs
Bone marrow (5-30%)
Involvement of central nervous system is rare
Treatment
Intensive chemotherapy, doxorubicin-based regimens
Prognosis
5-year survival 90%
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Neoplastic cells: Large, irregular, and bizarre
Often with polylobated nuclei
Cytological spectrum of neoplastic cells from small to large
Cell size variability helpful in distinguishing ALCL from classical Hodgkin lymphoma
“Hallmark” cells characteristic
Large cells with eccentric horseshoe- or kidney-shaped nuclei
Prominent paranuclear eosinophilic Golgi region
Histologic variants
Common or classical (80%)
Lymphohistiocytic (5-10%)
Small cell (5-10%)
Sarcomatoid (1%)
ANCILLARY TESTS
Immunohistochemistry
Strongly and uniformly positive for CD30 and ALK
ALCL can be of T- or null cell lineage
In cases of T-cell lineage, aberrant T-cell immunophenotype is common
Most tumors do not express CD3, CD5, or T-cell receptors (suggests defective T-cell signaling)
Cytotoxic molecules(+)
Clusterin(+)
EMA(+/−), CD45/LCA(+/−)
Bcl-2(−), EBV(−)
B-cell antigens(−)
Type of ALK staining correlates with type of underlying genetic abnormality
Cytoplasmic and nuclear: t(2;5)
Cytoplasmic, not coarsely granular: Variant translocations
Except t(2;X) and t(2;17)
Cytoplasmic, coarsely granular: t(2;17)
Membranous: t(2;X)
Cytogenetics
ALK(+) ALCL characterized by chromosomal translocations involving ALK gene at 2p23
Methods used for demonstrating ALK abnormalities
Conventional cytogenetics
Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)
Reverse-transcriptase (RT) PCR
Long-range PCR
Immunohistochemistry
Chromosomal translocations
75-80% of cases t(2;5)(p23;q35)
t(2;5) juxtaposes nucleophosmin (NPM) gene at 5q35 with ALK gene at 2p23
t(2;5) drives expression of novel fusion protein NPM-ALK
Variant chromosomal abnormalities (25% of cases)
ALK gene rearranged with other genes
Tropomyosin 3 (TPM3), t(1;2)(p25;p23)
TRK-fused gene (TFG), t(2;3)(p23;q21)
ATIC, inv(2)(p23;q35)
Moesin (MSN), t(2;X)(p23; q11-12)
Clathrin heavy chain (CLTCL), t(2;17)(p23;q23)
Tropomyosin 4 (TPM4), t(2;19)(p23;q13.1)
ALO17, t(2;17)(p23;q25)
MYH9, t(2;22)(p23;q11.2)
Additional translocations involving ALK will be recognized in future
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma (CHL)
Immunophenotype very helpful to confirm diagnosis of CHL
HRS cells are positive for
pax-5 (nuclear and characteristically weak)
CD20 or CD79a in 20% of cases; variable
Negative for
EMA
CD45/LCA
ALK
In contrast, ALK(+) ALCL tumor cells are ALK(+) and pax-5(−)
ALK(−) ALCL
Currently defined as lymphoma morphologically within spectrum of ALK(+) ALCL
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree