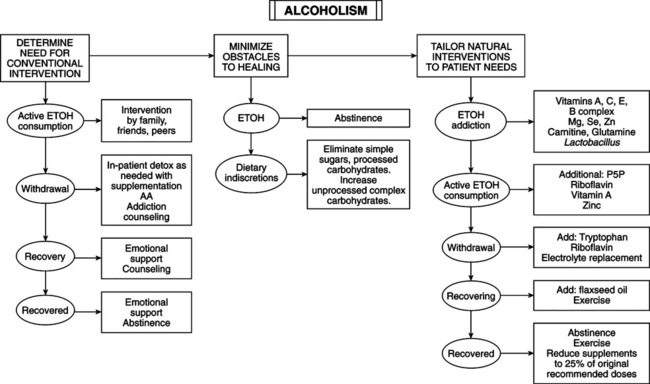
• Alcohol dependence manifested when alcohol is withdrawn: tremulousness, convulsions, hallucinations, delirium • Alcoholic binges, benders (48 hours or more of drinking associated with failure to meet usual obligations), or blackouts • Evidence of alcohol-induced illnesses: cirrhosis, gastritis, pancreatitis, myopathy, polyneuropathy, cerebellar degeneration • Physical signs of excess alcohol consumption: alcohol odor on breath, flushed face, tremor, ecchymoses • Psychological/social signs of excess alcohol consumption: depression, loss of friends, arrest for driving while intoxicated, surreptitious drinking, drinking before breakfast, frequent accidents, unexplained work absences. • Consequences: increased mortality: 10-12 years lower life expectancy; twice death rate in men, three times in women; six times the suicide rate; major factor in four leading causes of death in men aged 25-44 (accidents, homicides, suicides, cirrhosis); economic toll; health effects: metabolic damage to every cell; intoxication; abstinence and withdrawal syndromes; nutritional deficiency diseases; cerebellar degeneration; cerebral atrophy; psychiatric disorders; esophagitis, gastritis, ulcer; increased risk of cancer of mouth, pharynx, larynx, esophagus; pancreatitis; liver fatty degeneration and cirrhosis; arrhythmias; myocardial degeneration; hypertension; angina; hypoglycemia; decreased protein synthesis; increased serum and liver triglycerides; decreased serum testosterone; myopathy; osteoporosis; rosacea, spider veins; coagulation disorders. • Effects on fetus: growth retardation; mental retardation; fetal alcohol syndrome; teratogenicity. • 18 million alcoholics in United States; often a “hidden” disease disguised by sympathetic family and friends. • Etiology: obscure; multifactorial: genetic, physiologic, psychological, and social factors equally important; 35% of alcoholics start between ages 15 and 19 years, 80% before age 30; most common in men; female/male ratio is rising to 1:2. Women become addicted at lower intake than men. • Intoxication signs: central nervous system depression: drowsiness, errors of commission, disinhibition, dysarthria, ataxia, and nystagmus; 15 mL pure ETOH (1 oz whiskey, 4 oz wine, or 10 oz beer) raises blood ETOH level by 25 mg/dL in 70-kg person; effects of varying levels of blood ETOH are as follows: • Withdrawal symptoms: 1-3 days after last drink; anxiety, tremulousness, mental confusion, tremor, sensory hyperactivity, visual hallucinations, autonomic hyperactivity, diaphoresis, dehydration, electrolyte disturbances, seizures, and cardiovascular abnor-malities.
Alcoholism
DIAGNOSTIC SUMMARY
GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS
Yes (0)
No (2)
Yes (0)
No (2)
Yes (5)
No (0)
Yes (2)
No (0)
Yes (2)
No (0)
Yes (2)
No (0)
Yes (2)
No (0)
Yes (5)
No (0)
Yes (5)
No (0)
Yes (2)
No (0)

Intoxication and withdrawal
Blood Level (mg/dl)
Effect
<50
No significant motor dysfunction
100
Mild intoxication: decreased inhibitions, slight visual impairment, slight muscular incoordination, slowing of reaction time; legally intoxicated in most jurisdictions
150
Ataxia, dysarthria, slurring of speech, nausea and vomiting
350
Marked muscular incoordination, blurred vision, approaching stupor
500
Coma and death ![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Alcoholism
