Chapter 5 Adrenergic Drugs
1. Endogenous catecholamines (norepinephrine, epinephrine, and dopamine) are found in peripheral sympathetic nerve endings, the adrenal medulla, and the brain.
a. Potentiate the effects of catecholamines by decreasing their disappearance from the synaptic cleft
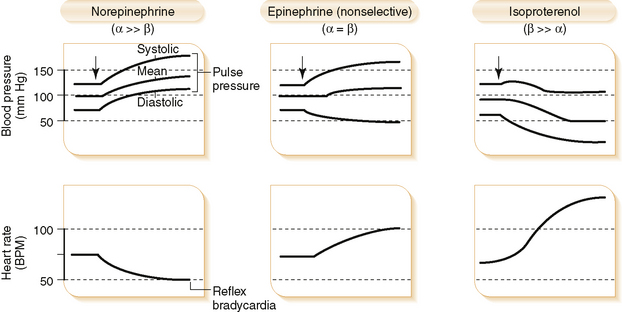
a. Stimulates β1– and α1-adrenergic receptors causing increased contractility and heart rate as well as vasoconstriction
TABLE 5-1 Pharmacologic Effects and Clinical Uses of Adrenoreceptor Agonists
| Drug | ||
|---|---|---|
| Direct-Acting Adrenoreceptor Agonists | Effect and Receptor Selectivity | Clinical Application |
| Catecholamines | ||
| Dobutamine | Shock, heart failure | |
| Dopamine | Shock, heart failure | |
| Epinephrine | Anaphylaxis, open-angle glaucoma, asthma, hypotension, cardiac arrest, ventricular fibrillation, reduction in bleeding in surgery, prolongation of local anesthetic action | |
| Isoproterenol | Atrioventricular block, bradycardia | |
| Norepinephrine | Hypotension, shock |
| Noncatecholamines | ||
|---|---|---|
| Albuterol | Asthma | |
| Clonidine | Decreased sympathetic outflow (α2) | Chronic hypertension |
| Oxymetazoline | Vasoconstriction (α1) | Decongestant |
| Phenylephrine | Pupil dilation, decongestion, mydriasis, neurogenic shock, blood pressure maintenance during surgery | |
| Ritodrine | Bronchodilation and uterine relaxation (β2) | Premature labor |
| Terbutaline | Bronchodilation and uterine relaxation (β2) β2 > β1 | Asthma, premature labor |
| Fenoldopam | Hypertensive emergency | |
| Indirect-Acting Adrenoreceptor Agonists | ||
|---|---|---|
| Amphetamine | Narcolepsy, obesity, attention deficit disorder | |
| Cocaine | Local anesthesia | |
| Mixed-Acting Adrenoreceptor Agonists | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ephedrine | Decongestant | |
| Pseudoephedrine | Vasoconstriction (α1) | Decongestant |
BOX 5-1 Adrenoreceptor Agonists
Direct-Acting Agonists and Receptor Selectivity
| Catecholamines | |
| Dobutamine | β1 (α1) |
| Dopamine (DA) D1 | (α1 and β1 at high doses) |
| Epinephrine (EPI) | α1, α2, β1, β2 |
| Isoproterenol (ISO) | β1, β2 |
| Norepinephrine (NE) | α1, α2, β1 |
| Noncatecholamines | |
| Albuterol | β2 |
| Clonidine | α2 |
| Methyldopa (prodrug) | α2 |
| Oxymetazoline | α1 |
| Naphazoline | α1 |
| Phenylephrine | α1 |
| Ritodrine | β2 |
| Salmeterol | β2 |
| Terbutaline | β2 |
(1) Alpha effects (vasoconstriction) are greater than beta effects (inotropic and chronotropic effects)
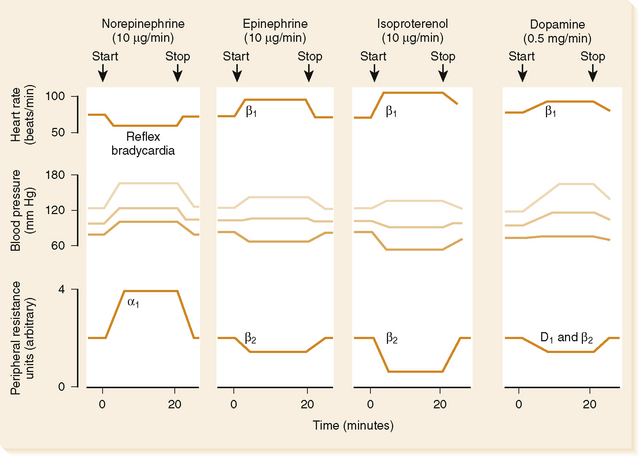
• Stimulates D1 specific dopamine receptors on renal vasculature, and at higher doses it also stimulates β1– and α1-adrenergic receptors
(1) Low doses stimulate primarily renal dopamine receptors (0.5−2 µg/kg/min) causing vasodilation in the kidney.
(2) Moderate doses also stimulate β1-adrenergic receptors (2−10 µg/kg/min) increasing cardiac contractility.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree