Adenomatoid Tumor
Cyril Fisher, MD, DSc, FRCPath
Key Facts
Terminology
Benign mesothelial tumor
Clinical Issues
Usually solitary, rarely multiple
Most common in 4th-7th decades
Most common in male and female genital organs
Epididymis, spermatic cord
Uterus, fallopian tube
Adrenal gland
Painless mass
Malignant change does not occur
Macroscopic Features
Rarely larger than 2 cm in diameter
Occasionally cystic
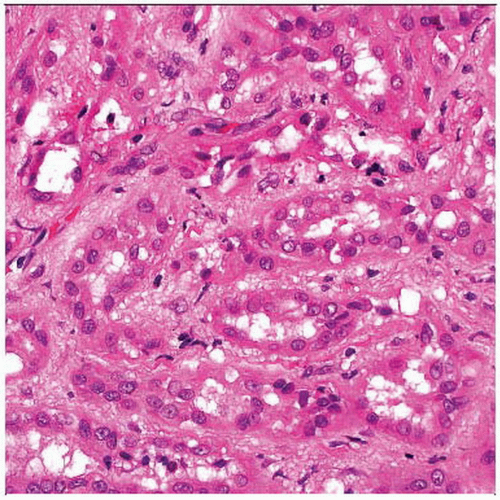
Microscopic Pathology
Gland-like tubules
Thin-walled spaces
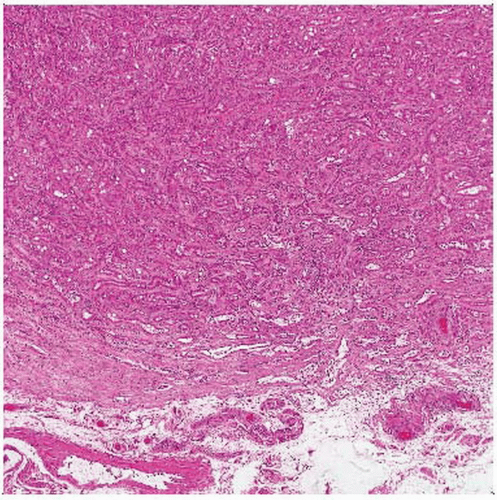 Hematoxylin & eosin shows a well-marginated lesion without a capsule. The cellular component is evenly distributed within a collagenous stroma. |
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Benign mesothelial tumor
Most common in male and female genital organs
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Benign Neoplasm
No causal factors known
Antecedent or Associated Conditions
Can coexist with multicystic peritoneal mesothelioma
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Relatively uncommon
Usually solitary, rarely multiple
Age
Most common in 4th-7th decades
Rare in 1st 2 decades
Gender
Occurs in both males and females
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree