Adenocarcinoma In Situ
Jesse K. McKenney, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Noninvasive glandular lesion characterized by atypical columnar epithelium
Also called “noninvasive urothelial carcinoma with glandular differentiation” and “urothelial carcinoma with villoglandular differentiation”
Clinical Issues
Hematuria
Similar to high-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma
Many progress to invasive urothelial carcinoma (50%)
Subsequent invasion may have variant morphology (small cell and micropapillary)
Macroscopic Features
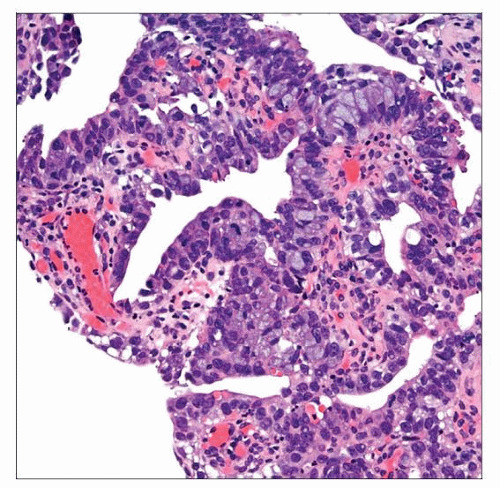
Varies from exophytic papillary lesions to flat lesions
Microscopic Pathology
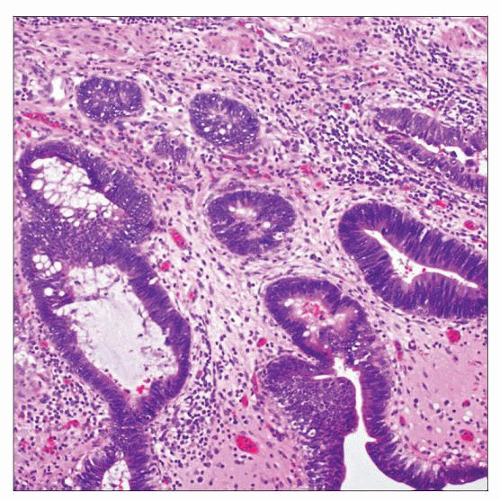
Lining neoplastic cells are columnar with luminal cytoplasm
Frequently associated with other urothelial neoplasia
Intracytoplasmic mucin occasionally present
May have multiple growth patterns (flat, papillary, and cribriform)
Top Differential Diagnoses
Urothelial carcinoma in situ
Urothelial carcinoma with gland-like spaces
Cystitis glandularis ± intestinal metaplasia
Villous adenoma
Noninvasive micropapillary carcinoma
Clear cell adenocarcinoma
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Noninvasive urothelial carcinoma with glandular differentiation
Urothelial carcinoma with villoglandular differentiation
Papillary adenocarcinoma in situ
Definitions
Noninvasive glandular neoplasm of urinary bladder
Characterized by atypical columnar epithelium
Often admixed with urothelial carcinoma
Recent proposal to rename this lesion noninvasive urothelial carcinoma with glandular differentiation
To distinguish from glandular carcinoma in situ arising in cystitis glandularis, which may be precursor of adenocarcinoma
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
Hematuria
Gross or microscopic
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Transurethral excision
Similar to high-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma
Adjuvant therapy
Intravesical chemotherapy
Intravesical BCG therapy
Prognosis
Many progress to invasive urothelial carcinoma (50%)
Subsequent invasion may have aggressive variant morphology
Not typically associated with invasive adenocarcinoma
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Varies from exophytic papillary lesions to flat lesions
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
May have multiple growth patterns
Flat
Papillary
Cribriform
Lining neoplastic cells are columnar with luminal cytoplasm
Intracytoplasmic mucin occasionally present
Apoptotic debris and mitotic activity common
Necrosis is rare
Frequently associated with other morphologic patterns of urothelial neoplasia
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree