Hepatitis C accounts for ∼ 20% of cases of acute hepatitis
Clinical Issues
•
Symptoms generally mild or patients are asymptomatic

Fulminant hepatic failure is rare
•
Most patients with acute hepatitis A virus infection fully recover within 2 months of disease onset

No specific drug therapy available for acute hepatitis A virus infection
•
Laboratory values

Elevated transaminases at 5-10x normal values

Viral serologies often helpful
•
Supportive care is mainstay of treatment for patients with acute hepatitis A or acute hepatitis E

Drug therapy (antivirals or immune modulators) may be useful in acute hepatitis B and C
Microscopic
•
Lobular disarray characterized by diffuse lobular inflammation and hepatocyte swelling, necrosis, and regeneration
•
May see mild portal and periportal inflammation, particularly in acute hepatitis A virus infection
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
•
Hepatocyte necrosis and inflammation resulting from acute viral infection
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Hepatitis A Virus
•
Single-stranded RNA virus in Picornaviridae family
•
Usually spreads via oral or fecal-oral transmission

Community outbreaks related to contaminated food or water
•
Accounts for ∼ 1/2 of acute viral hepatitis cases in USA
•
At least 4 genotypes described, but only 1 serotype exists

Infection with one genotype confers immunity against all genotypes
•
Never results in chronic infection
Hepatitis B Virus
•
Partially double-stranded DNA virus in Hepadnaviridae family
•
Parenteral, perinatal, and sexual transmission
•
Up to 40% of acute hepatitis cases in USA attributable to hepatitis B
•
∼ 10% of infected patients develop chronic infection
Hepatitis C Virus
•
RNA virus of Flaviviridae family
•
Parenteral, perinatal, and sexual transmission
•
Accounts for ∼ 20% of cases of acute hepatitis
•
Only 10-15% of infected individuals develop symptomatic acute hepatitis
•
If untreated, ∼ 85% of infected patients develop chronic infection
Hepatitis D Virus (Delta Agent)
•
Parenteral and sexual transmission
•
Requires coinfection with hepatitis B virus or superinfection in patient with chronic hepatitis B virus infection
Hepatitis E Virus
•
Single-stranded, nonenveloped RNA virus in Caliciviridae family

Vertical transmission

Parenteral transmission

Consumption of raw or undercooked meat of infected animals

Contaminated water supply
•
Endemic in parts of Asia, Africa, and India
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
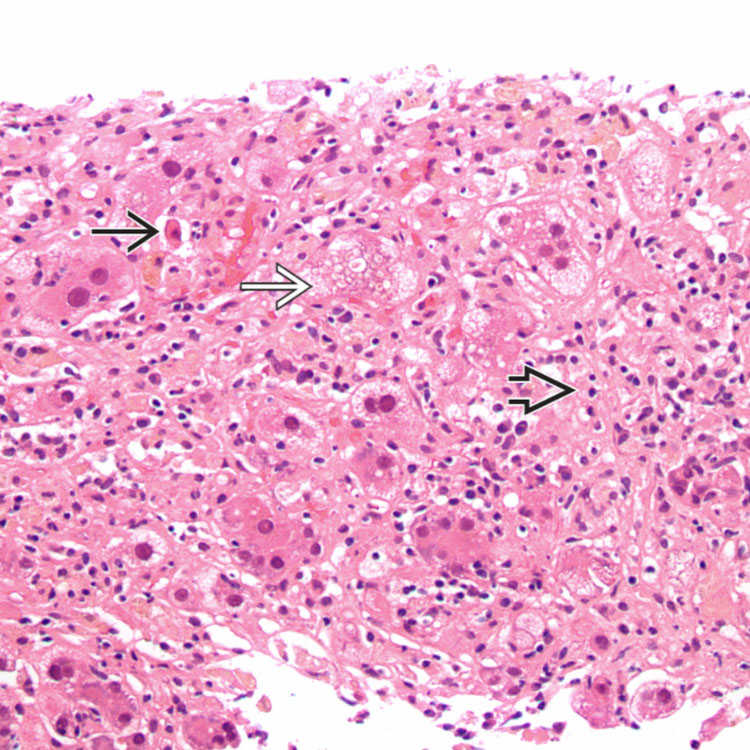
 , single-cell necrosis
, single-cell necrosis  , and areas of hepatocyte dropout
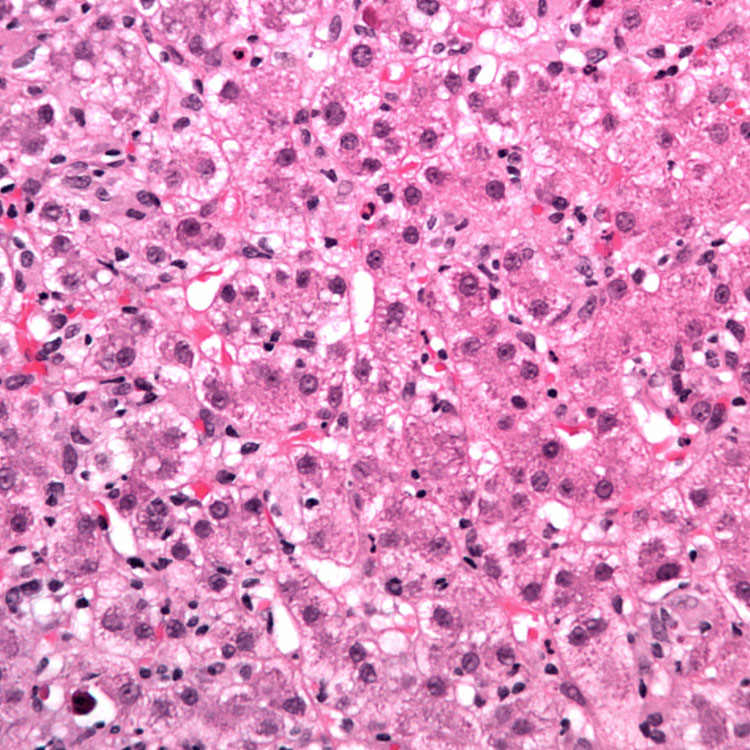
, and areas of hepatocyte dropout  in a background of lobular inflammation. The lobule looks disorganized at relatively low power, indicative of the injury to the hepatocytes.
in a background of lobular inflammation. The lobule looks disorganized at relatively low power, indicative of the injury to the hepatocytes.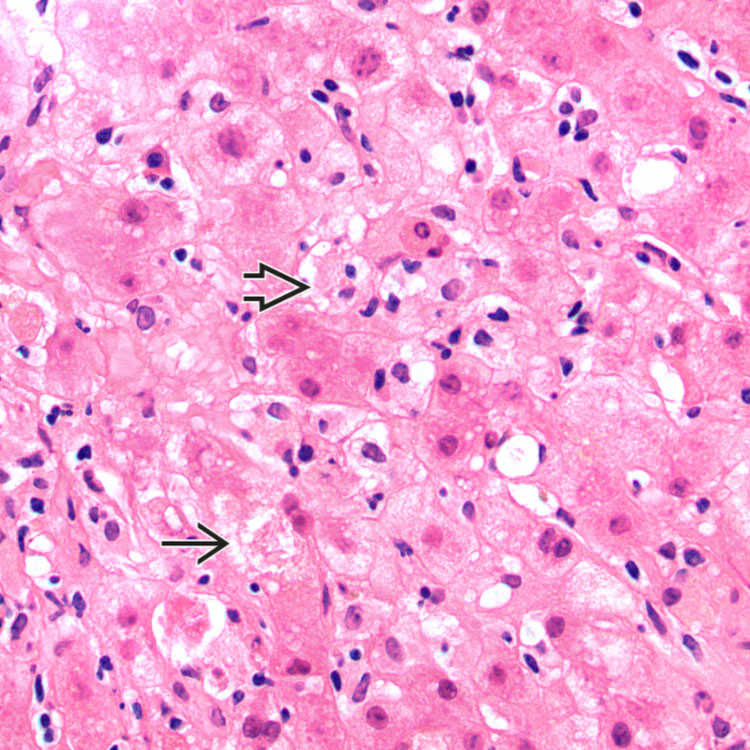
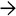 , Kupffer cell hyperplasia
, Kupffer cell hyperplasia  , and lobular inflammation in a case of acute viral hepatitis.
, and lobular inflammation in a case of acute viral hepatitis.
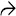 , Kupffer cell hyperplasia
, Kupffer cell hyperplasia 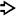 , and lobular inflammation in a case of acute viral hepatitis.
, and lobular inflammation in a case of acute viral hepatitis.