Rare to absent in early lesions, prominent and confluent in late lesions
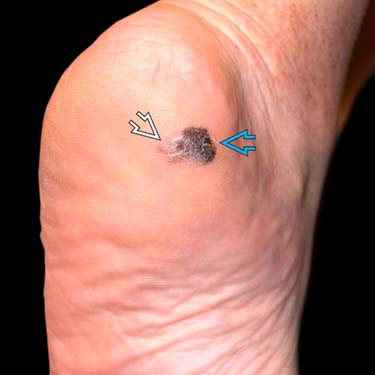
The heel of this patient shows a dark brown plaque with early depigmentation and an erythematous rim
 . The lesion has a sharp border on the medial aspect
. The lesion has a sharp border on the medial aspect  . (Courtesy J. Finch, MD.)
. (Courtesy J. Finch, MD.)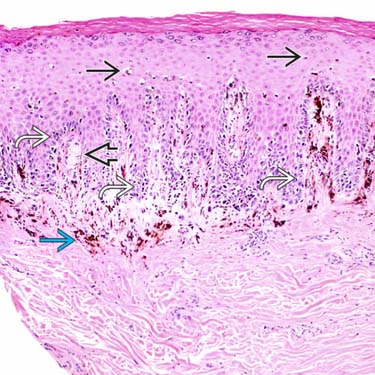
Lentiginous growth of atypical melanocytes
 is seen in this early in situ lesion. Only rare upward scatter
is seen in this early in situ lesion. Only rare upward scatter  of atypical melanocytes is identified. A Meissner corpuscle
of atypical melanocytes is identified. A Meissner corpuscle  is seen in the dermis. There is marked uneven melanin incontinence
is seen in the dermis. There is marked uneven melanin incontinence  .
.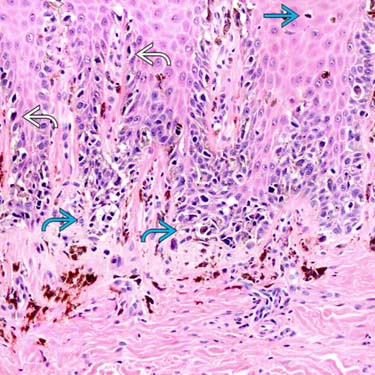
There is a lentiginous growth
 and poorly nested growth pattern
and poorly nested growth pattern  identified at the dermal-epidermal junction. There is only limited pagetoid upward scatter
identified at the dermal-epidermal junction. There is only limited pagetoid upward scatter  , unlike cutaneous melanoma. The finding of lentiginous growth with cytological atypia is sufficient for the diagnosis of melanoma in situ, acrolentiginous type.
, unlike cutaneous melanoma. The finding of lentiginous growth with cytological atypia is sufficient for the diagnosis of melanoma in situ, acrolentiginous type.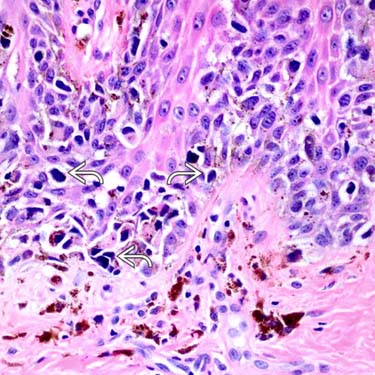
Higher magnification of same lesion shows angulated, hyperchromatic nuclei with scant amounts of cytoplasm
 . Note the melanocytic hyperplasia has replaced most of the basal keratinocytes.
. Note the melanocytic hyperplasia has replaced most of the basal keratinocytes.CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
• < 5% of all malignant melanomas
• Most frequently reported symptoms are change in size, bleeding, change in color, and becoming raised or nodular
Prognosis
• Compared to other cutaneous melanomas, disease-specific survival rates are lower




Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree














