Patient Story
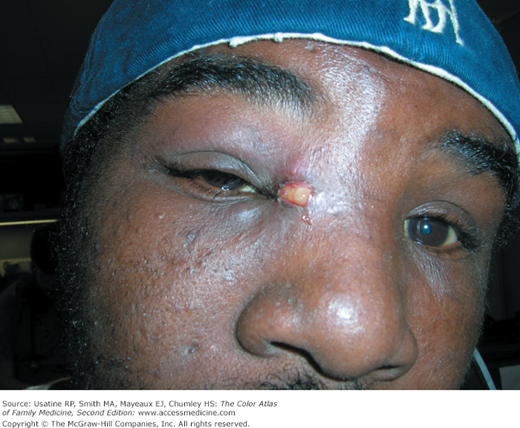
A young man is seen in a shelter in San Antonio after being evacuated from New Orleans after the devastating floods of Hurricane Katrina (Figure 121-1). He has facial pain and swelling and noticeable pus near the eye. His vision is normal. The area is anesthetized with lidocaine and epinephrine. The abscess is drained with a #11 blade. The patient is started on an oral antibiotic because of the proximity to the eye and the local swelling that could represent early cellulitis. A culture to look for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) was not available in the shelter, but close follow-up was set for the next day and the patient was doing much better.
Introduction
Epidemiology
- MRSA was the most common identifiable cause of skin and soft- tissue infections among patients presenting to emergency departments in 11 U.S. cities. S. aureus was isolated from 76% of these infections and 59% were community-acquired MRSA (CAMRSA).1
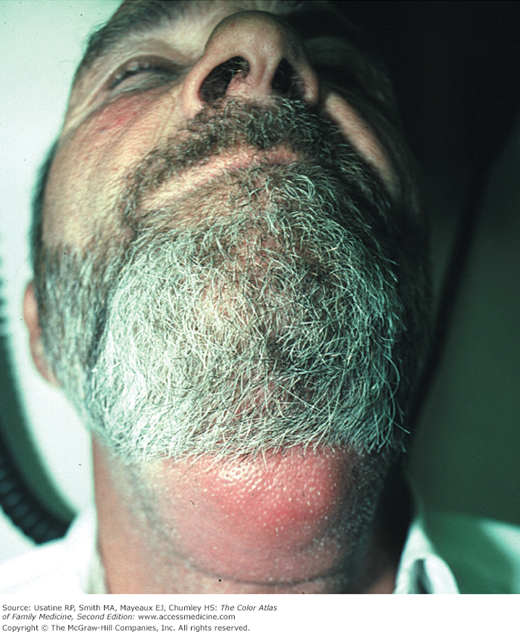
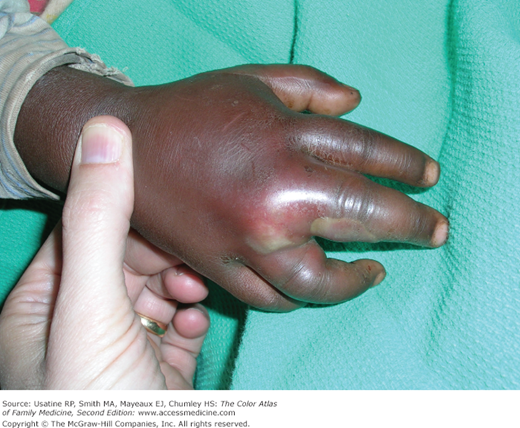
- Risk factors for MRSA infection and other abscesses—Intravenous drug abuse, homelessness, dental disease, contact sports, incarceration, and high prevalence in the community (Figure 121-2).
Etiology and Pathophysiology
- Most cutaneous abscesses are caused by S. aureus.
- Risk factors for developing an abscess with MRSA include patients who work or are exposed to a healthcare system, intravenous drug use, previous MRSA infection and colonization, recent hospitalization, being homeless, African American, and having used antibiotics within the last 6 months.2
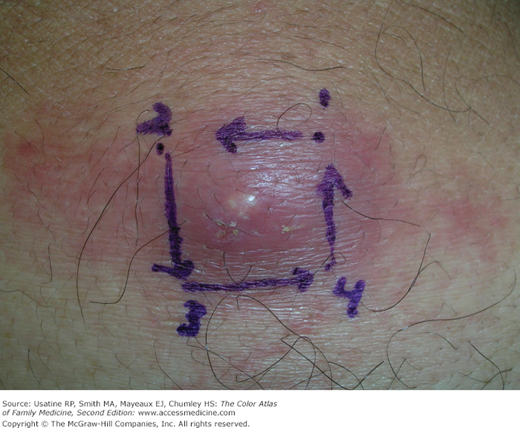
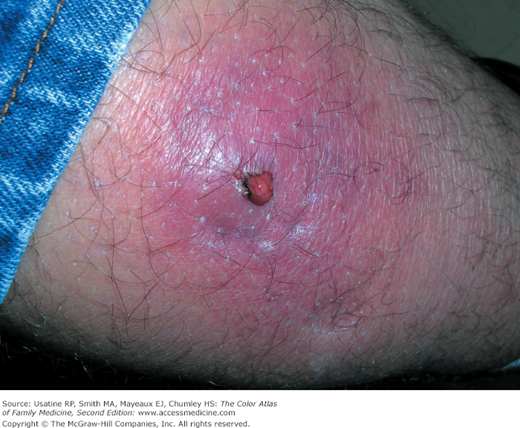
- CAMRSA has become so prevalent in our community that both the patients shown in Figures 121-3 and 121-4 had no special risk factors and both had abscesses that grew out MRSA. One study that evaluated management of skin abscesses drained in the emergency department showed that there was no significant association between amount of surrounding cellulitis or abscess size with the likelihood of MRSA-positive cultures.2
- A dental abscess can spread into tissue outside the mouth, as in the homeless person in Figure 121-2.
Diagnosis
Collection of pus in or below the skin. Patients often feel pain and have tenderness at the involved site. There is swelling, erythema, warmth, and fluctuance in most cases (Figures 121-1, 121-2, Figures 121-3, 121-4, 121-5). Determine if the patient is febrile and if there is surrounding cellulitis.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree