81 CASE 81
LABORATORY STUDIES
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF KEY SYMPTOMS
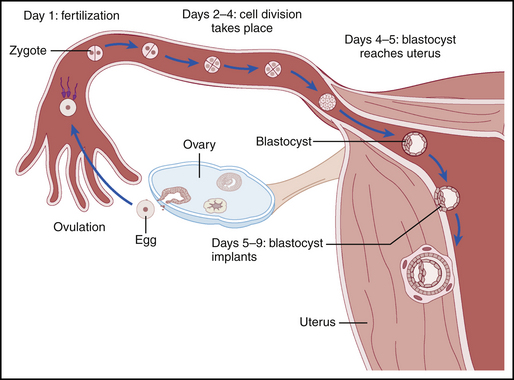
Female reproductive fertility is limited to the brief period of time (around 24 hours) after ovulation. After ovulation, the ovum enters the fimbriae of the fallopian tube and is transported to the uterus during the next 6 days. Pregnancy requires the fertilization of the egg shortly after it enters the fallopian tube. During the remaining time while passing through the fallopian tube the fertilized egg matures into a blastocyst and successfully implants onto the uterine endometrium (Fig. 81-1). One region of the blastocyst becomes the embryo, and a different region of the blastocyst digests the uterine endometrium and matures into a placenta. The placenta and the embryo have the same genetic composition and, consequently, chorionic villous sampling can be used to genotype the embryo. A blastocyst that implants in a region of the body other than the uterus is termed an “ectopic pregnancy.”
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree