The two upper limbs are attached to the trunk by the shoulder girdle. This is formed by the collar bones (clavicle) and shoulder blades (scapula). Each upper limb can be divided into four main regions: the shoulder, arm, forearm, and hand.
Movements of the shoulder and elbow joints position the hand precisely in space, so that it can carry out a wide range of functions. These vary from the delicate, coordinated actions required to tie shoe laces, through to gripping, lifting, moving, and throwing objects. The hand also has numerous sensory receptors, which allow us to tell the difference between objects just on the basis of touch.


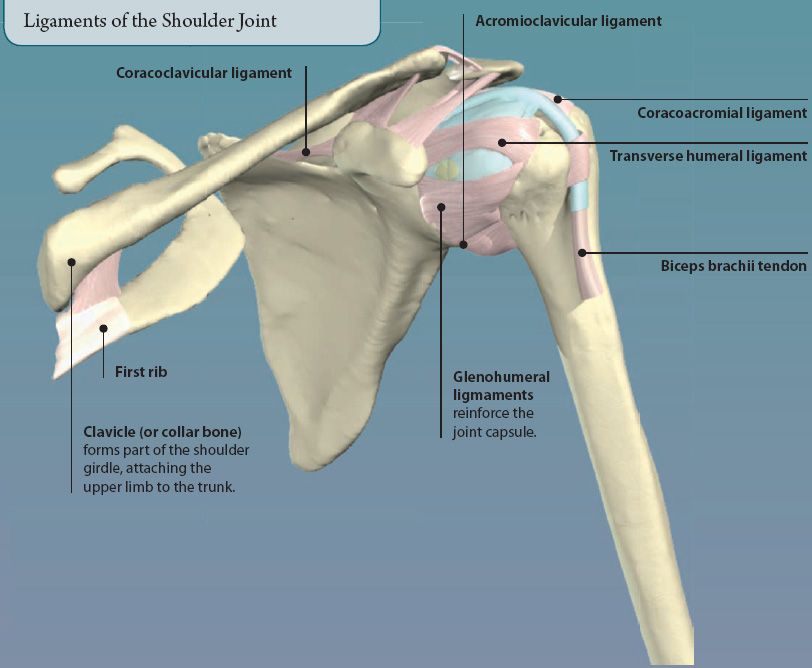
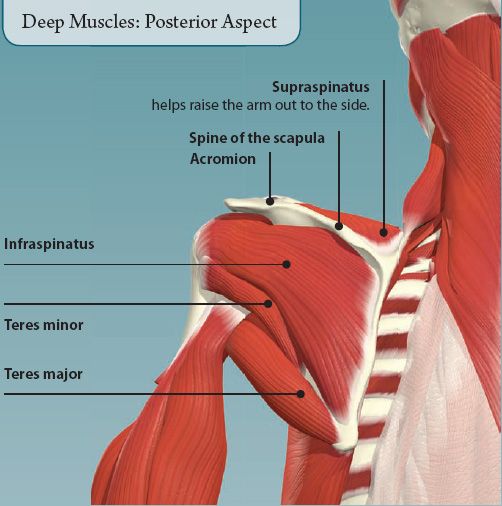
SHOULDER JOINT
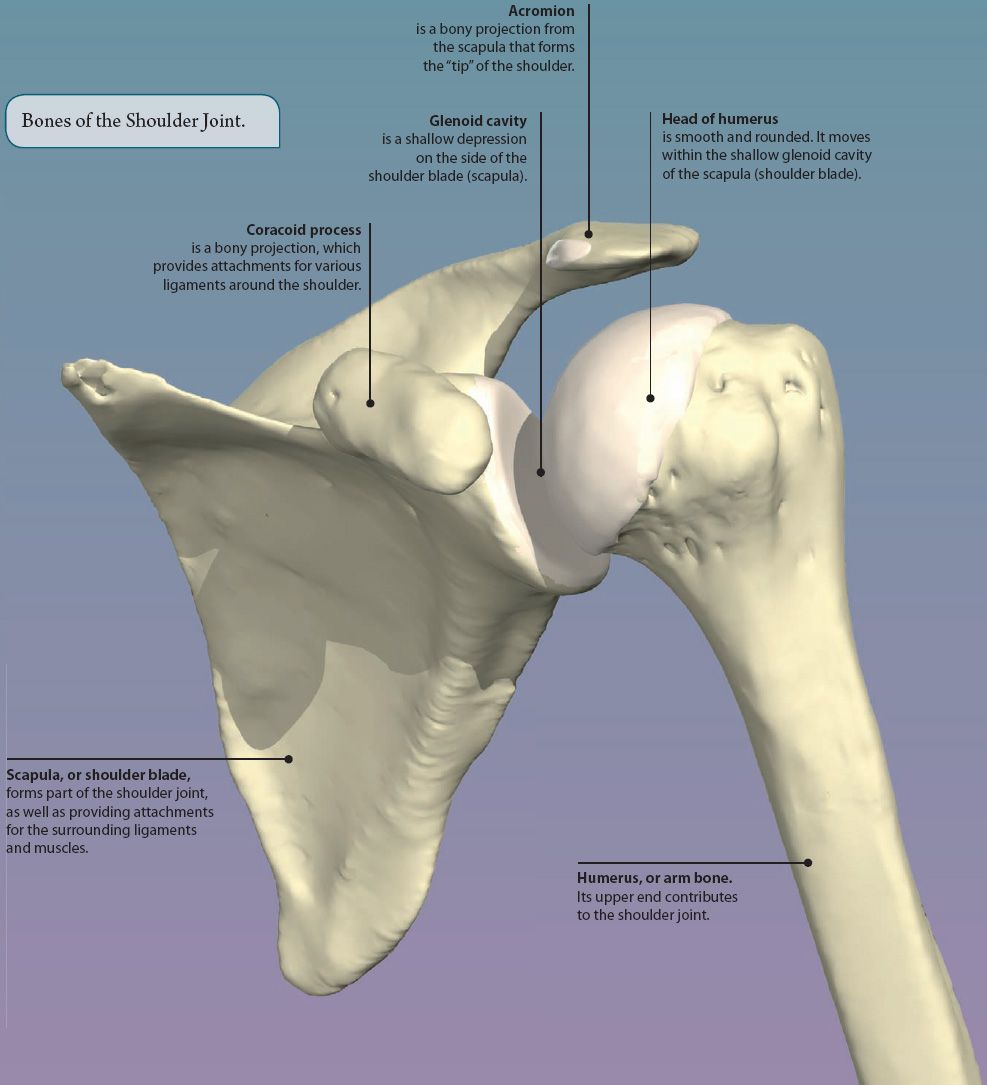
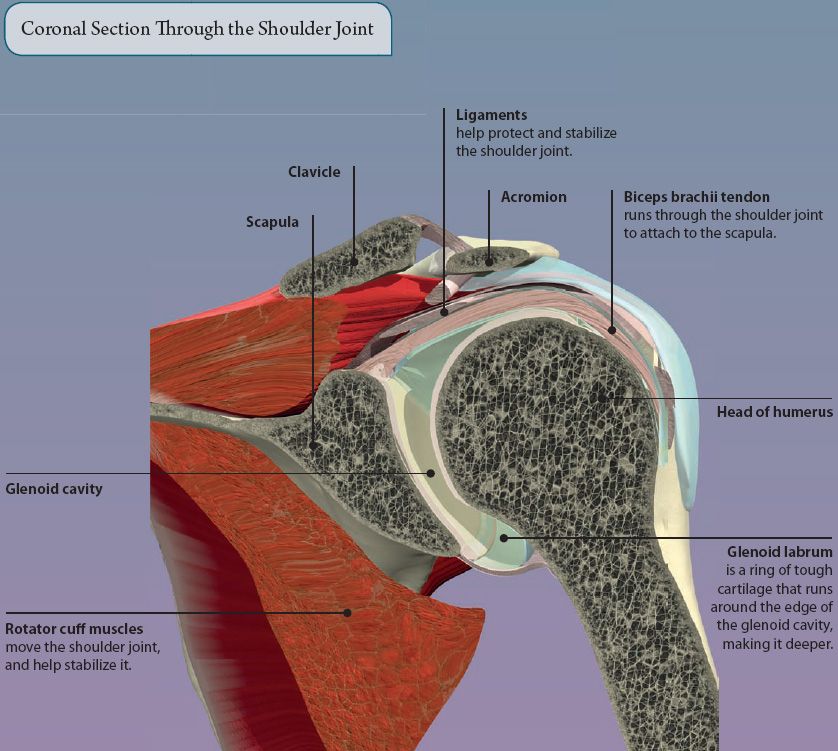
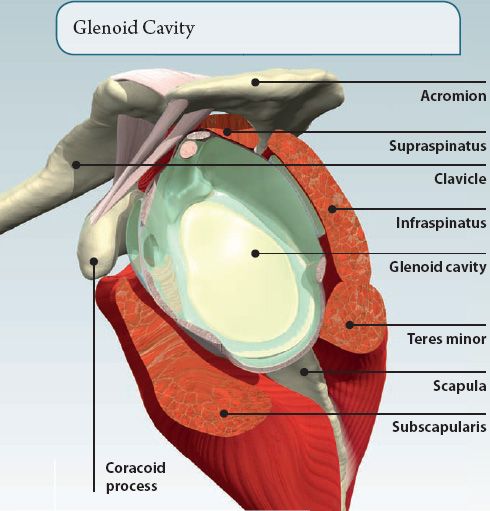
The shoulder is an example of a ball and socket joint. It is formed by the rounded head of the humerus (arm bone) moving within the glenoid cavity of the scapula (shoulder blade). It is the most mobile joint in the body, capable of a wide range of movements. Strong ligaments and muscles help to make the joint stable.
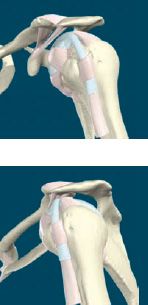
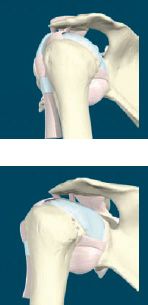
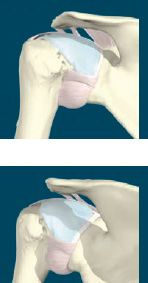
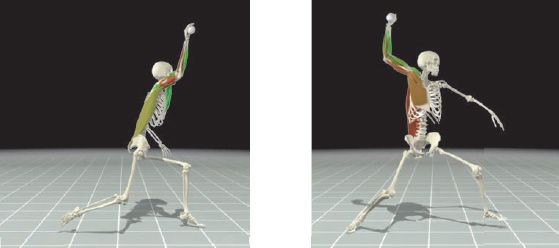
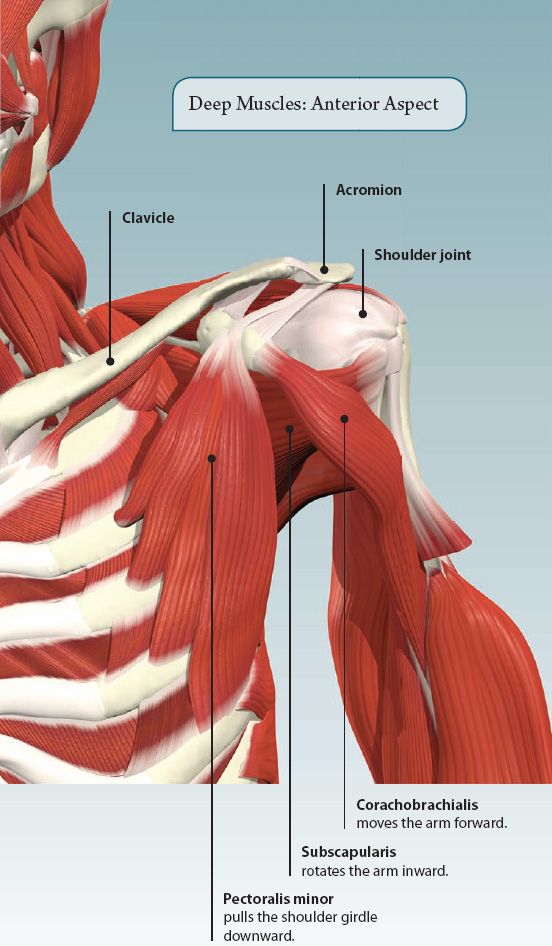
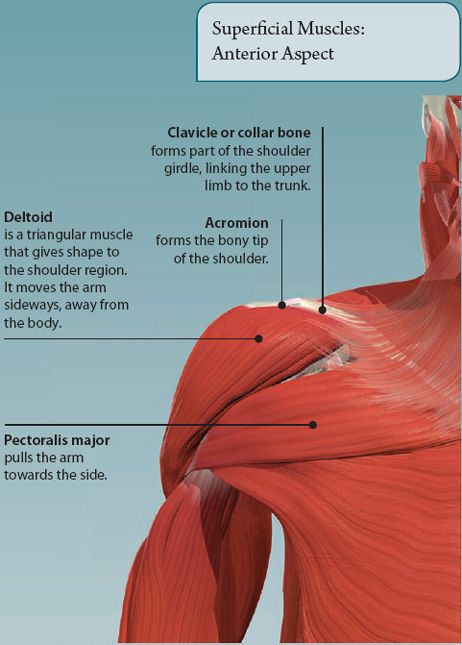
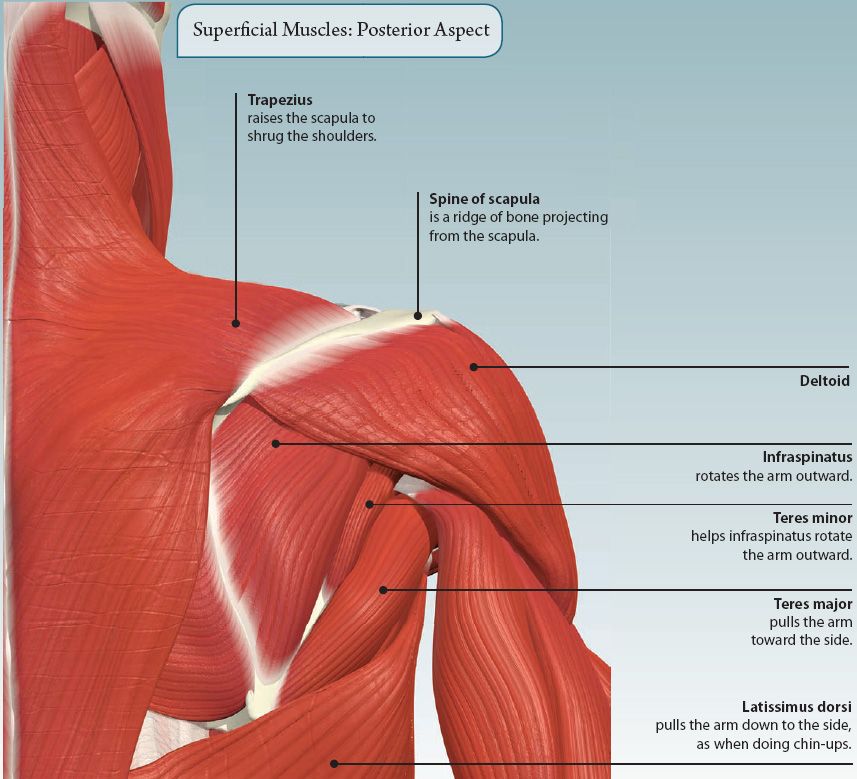
MUSCLES OF THE SHOULDER
The shoulder is the region of the upper limb that attaches it to the trunk. It contains the highly mobile shoulder joint. Muscles acting at this joint move the upper limb forward and backward, out to the side, and back across the body, as well as turning it inwards and outwards.
The rotator cuff is formed by four muscles that are attached to the scapula, and humerus. As well as producing movements at the shoulder, they also stabilize the shoulder joint, and prevent it from dislocating (popping out). The rotator cuff muscles are: supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis.
Tendonitis
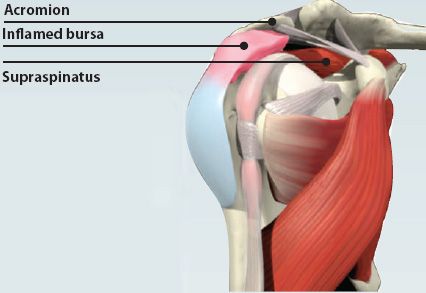
The tendon of the supraspinatus muscle passes beneath the acromion, through the narrow subacromial space. A fluid-lined sac, called the subacromial bursa, helps prevent friction from repetitive movements of the tendon. However, sometimes the bursa and tendon can get irritated and inflamed. This leads to pain when moving the arm out to the side, and is known as subacromial bursitis or supraspinatus tendonitis.
Did you know?
The deltoid muscle is a common site for giving intramuscular injections, due to its large size and easy accessibility.
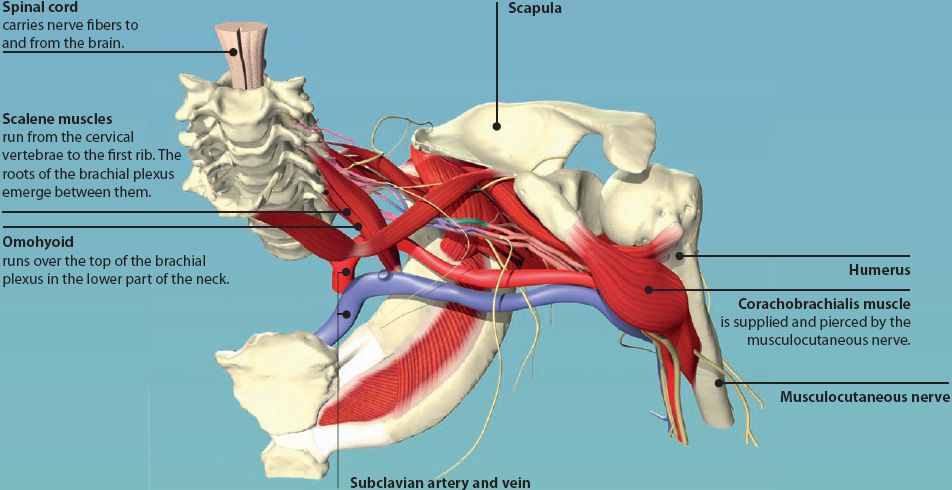
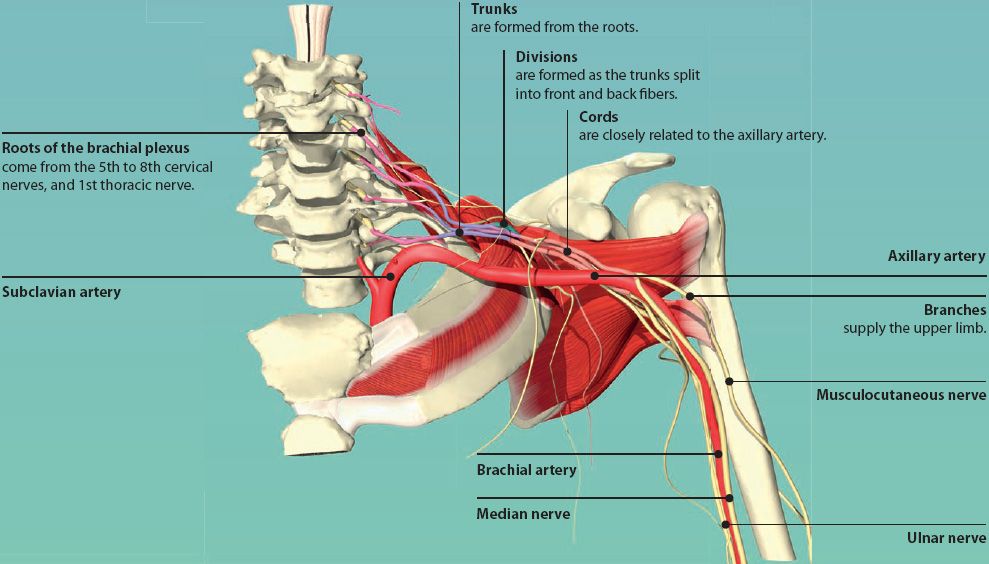
BRACHIAL PLEXUS
The brachial plexus is a network of nerves formed in the lower part of the neck. It is made up of roots, trunks, divisions, cords, and branches. The branches of the brachial plexus supply sensation and motor function to the entire upper limb. The five main branches of the brachial plexus are the axillary, median, musculocutaneous, radial, and ulnar nerves.
Median nerve
innervates muscles of the forearm that bend the fingers and wrist. It also supplies sensation to the thumb, index, and middle finger.
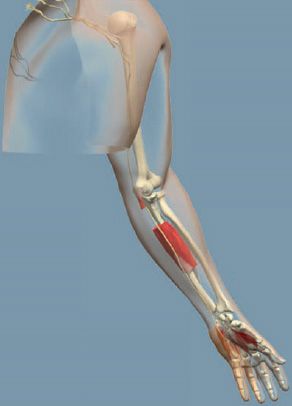
Ulnar nerve
innervates the small muscles of the hand along with a few muscles of the forearm. It supplies sensation to the skin over the ring and little finger.
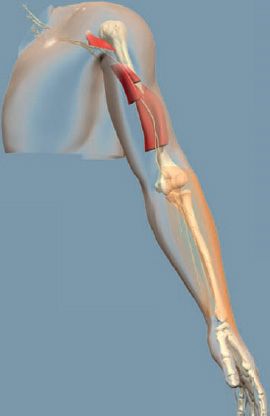
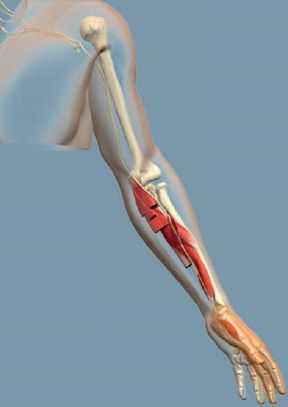
Musculocutaneous nerve
innervates muscles of the arm that bend the elbow. It also supplies sensation to part of the forearm.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree