64 CASE 64
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF KEY SYMPTOMS
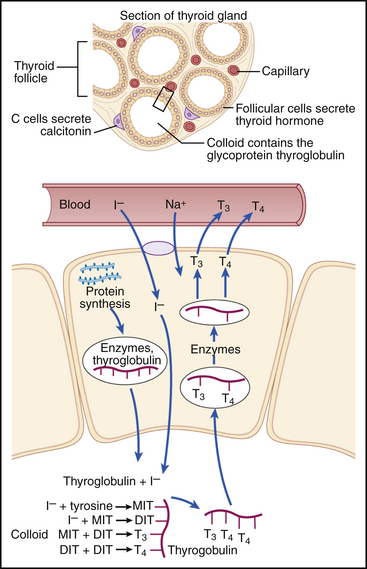
Thyroid hormone is an amino acid derivative synthesized in the thyroid gland (Fig. 64-1). The thyroid gland consists of numerous follicles containing colloid surrounded by follicular cells. Follicular cells absorb iodide by sodium-coupled transport and accumulate the iodide within the colloid. The follicular cells also synthesize the large protein thyroglobulin and the enzymes necessary to attach the iodide to the tyrosine. Tyrosine residues bind to the thyroglobulin and are iodinated sequentially within the colloid. Each tyrosine can bind up to two iodides and, after iodination, two tyrosine residues join to form the mature thyroid hormones T3 and T4. The thyroglobulin bound to thyroid hormone is absorbed back into the follicular cell. The T3 and T4 are separated from the thyroglobulin and secreted into the blood.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree