61 CASE 61
A 6-year-old boy is brought to the pediatrician by his mother, who indicates the child is not well.
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF KEY SYMPTOMS
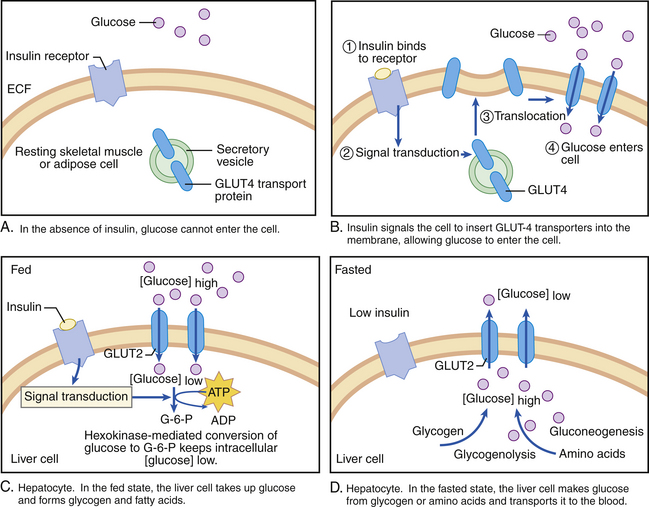
Insulin decreases blood glucose by stimulating glucose uptake, utilization, and storage. Insulin enhances glucose uptake by skeletal muscle and adipose tissue by increasing the number of functional GLUT-4 transport proteins on the cell membrane (Fig. 61-1). Combined elevations in insulin and growth hormone stimulate amino acid uptake and protein synthesis in a variety of tissues. The hepatic and brain glucose transport proteins (GLUT-2 and GLUT-3, respectively) are not directly impacted by insulin. Insulin, however, increases hepatic glucose uptake and glycogen formation by increasing the activity of hexokinase and the cellular metabolic conversion of glucose. The combined actions of insulin result in a marked decrease in plasma glucose concentration.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree