60 CASE 60
A 56-year-old man comes to his family physician complaining of fecal incontinence.
LABORATORY STUDIES
Anal manometry: Decreased tone in the internal anal sphincter but normal tone in the external anal sphincter
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF KEY SYMPTOMS
The defecation reflex requires intact enteric nerves, afferent sensory signals transmitted to the spinal cord, efferent parasympathetic nerves from the spinal cord, and a functional pudendal nerve (Fig. 60-1). These nerves can be disrupted by surgery, such as the surgery to repair hemorrhoids.
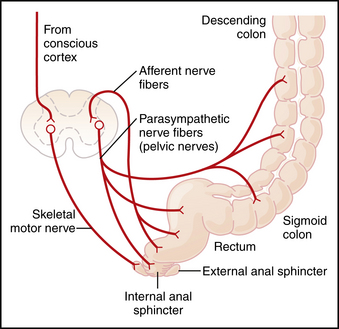
FIGURE 60–1 Afferent and efferent pathways of the parasympathetic mechanism for enhancing the defecation reflex.
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


