CHAPTER 3. PLEURAL ASPIRATION (OF FLUID OR AIR)
Indications23
Contraindications23
British Thoracic Society (BTS) guidelines for managing pneumothoraces24
Tension pneumothorax – emergency management24
Equipment25
Location of site of aspiration26
Practical procedure27
Post-procedure investigations31
Complications31
Suggested reading32
INTRODUCTION
Pleural aspiration of fluid or air is a bedside technique that can be performed for diagnostic and/or therapeutic purposes.
INDICATIONS
• Diagnostic aspiration of pleural fluid.
• Therapeutic aspiration of pleural effusion (better done by placing a drain; see Chapter 4).
• Therapeutic aspiration of simple pneumothorax.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
BRITISH THORACIC SOCIETY (BTS) GUIDELINES FOR MANAGING PNEUMOTHORACES
Pleural aspiration has a role in the management of pneumothoraces if certain criteria are met:
• Primary pneumothorax (no evidence of underlying lung disease):
— if patient is not breathless or there is <2 cm rim of air on chest X-ray, observe and do not proceed to aspiration/drainage
— if patient breathless or >2 cm rim of air on chest X-ray, then aspirate. If unsuccessful, consider repeat aspiration up to a total of 2.5 L. If an air leak persists, insert a chest drain (see Chapter 4).
• Secondary pneumothorax (known underlying lung disease):
— if patient is not breathless, or there is <2 cm rim of air on chest X-ray, or patient is less than 50 years old, consider aspiration
— if patient breathless or > 2 cm rim of air on chest X-ray, then insert a chest drain (see Chapter 4).
TENSION PNEUMOTHORAX – EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT
• This is a medical emergency requiring immediate recognition and treatment. If left untreated the increasing size of the tension pneumothorax compresses the mediastinum, ultimately obstructing venous return to the right heart and causing subsequent haemodynamic collapse and death.
 Tip Box
Tip BoxTension pneumothorax is a clinical diagnosis that does not require radiological confirmation – this wastes valuable time.
 Tip Box
Tip BoxDo not waste time with local anaesthetic – warn the patient of the procedure and the importance of performing it quickly.
PROCEDURE
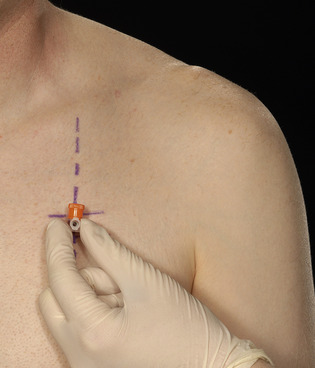
• Upon diagnosing a tension pneumothorax, immediately insert a large-bore cannula over the upper border of the third rib in the second anterior intercostal space, mid-clavicular line (Fig. 3.1).
• Upon removing the trocar a ‘hiss’ of air should be heard, signifying decompression of the tension and reversion to a simple pneumothorax.
• The purpose of needle thoracocentesis is to convert a tension pneumothorax into a simple pneumothorax. Inserting the cannula allows air to escape to atmosphere during expiration rather than accumulating and placing the intrathoracic structures under tension. Therefore formal drainage of the residual simple pneumothorax will still be required with an intercostal drain (see Chapter 4).
EQUIPMENT
• Dressing pack.
• Sterile gown, gloves and drapes.
• Chlorhexidine cleaning solution.
• Lidocaine.
• 2 × 10mL syringes.
• Orange needle.