CHAPTER 2. PEAK EXPIRATORY FLOW RATE MEASUREMENT AND SPIROMETRY
Indications15
Contraindications16
Equipment17
Practical procedure – PEFR 17
Practical procedure – spirometry 19
Interpreting the spirometry results20
The spirometer was invented by physician John Hutchison (1811–1861) in 1846. The peak flow meter was introduced into clinical use around 1960.
INTRODUCTION
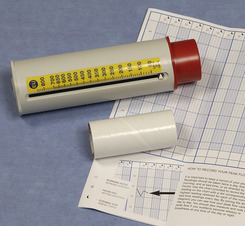
Peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR) and bedside spirometry are simple and cheap non-invasive measures of ventilatory function. A peak flow meter (Fig. 2.1) measures the fastest rate of expiratory airflow in litres per minute. Peak flow meters come in various guises, but they all serve the same function.
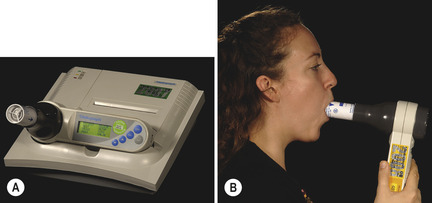
Spirometry (Fig. 2.2) also measures expiratory airflow, but provides extra information including the forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1), the forced vital capacity (FVC) and the FEV1/FVC ratio. The value of this ratio can be indicative of obstructive or restrictive ventilatory deficits.
 |
| Fig. 2.2 |
INDICATIONS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Spirometry is a safe and non-invasive test. However, performing PEFR measurement or spirometry does increase intra-thoracic, intra-abdominal and intra-ocular pressures. Therefore, spirometry does carry a small risk to individuals with certain co-morbidities, and so these can be regarded as relative contraindications:
EQUIPMENT
• Peak flow meter and clean mouthpiece.
• Peak flow chart.
• Bedside spirometer (with attached graph paper if a manual tracing).
• Bronchodilator inhaler (with spacer if required) for reversibility testing.
PRACTICAL PROCEDURE – PEFR
 Tip Box
Tip BoxPatients who are taking inhaled bronchodilators may give unreliable measurements if testing is not synchronized with their dosing regime. If the patient is taking inhaled bronchodilators, the scheduled regular dose prior to performing PEFR measurement or spirometry should be omitted in order to give valid pre- and post-bronchodilator measurements.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree