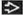Yersinia
Laura W. Lamps, MD
Key Facts
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Common food- and water-born gastrointestinal infection
Image Findings
May mimic acute appendicitis or Crohn disease
May show nonspecific features of enterocolic inflammation such as thickened bowel wall, adenopathy
Macroscopic Features
Preferentially involves ileum, right colon, and appendix
Yersinia is common cause of isolated granulomatous appendicitis
Mesenteric adenopathy frequently seen
Microscopic Pathology
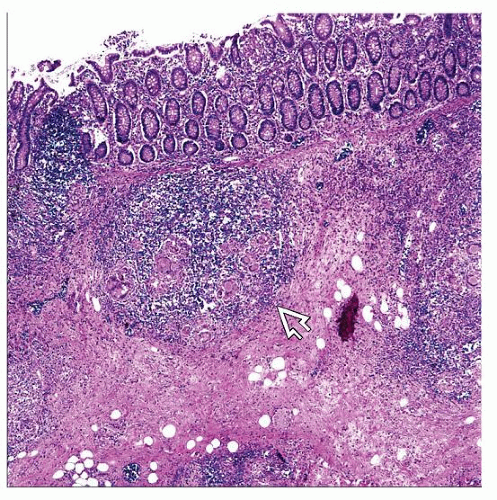
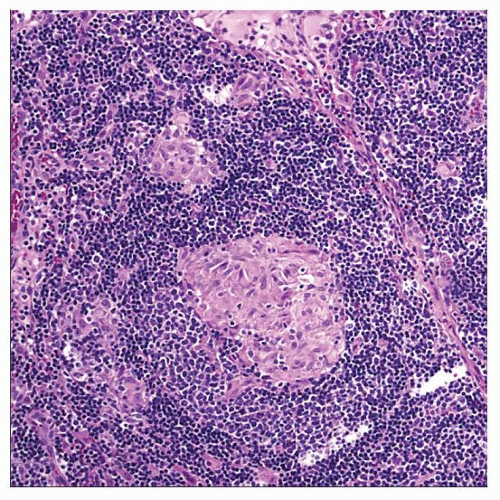
Epithelioid granulomas with prominent lymphoid cuffs
Transmural lymphoid aggregates
Mucosal ulceration
Mural fibrosis
Aphthoid, linear, or both
Diagnostic Checklist
Granulomatous inflammation with ulceration, mural fibrosis, and transmural lymphoid aggregates
Features closely mimic Crohn disease
Gram stain not helpful; consider culture, serologies, and molecular testing
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Yersinia enterocolitica (YE)
Yersinia pseudotuberculosis (YP)
Synonyms
Yersiniosis
Definitions
Gram-negative coccobacilliform enteric bacteria that cause appendicitis, enterocolitis, and mesenteric lymphadenitis
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Environmental Exposure
Common food- and water-borne gastrointestinal pathogen
Found in meat, water, and dairy products
1 of most common causes of bacterial enteritis in western and northern Europe
Incidence rising in Europe and USA
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
Diarrhea
Abdominal pain
Symptoms and signs of appendiceal Yersinia infection can mimic acute nonspecific suppurative appendicitis
Yersinia common cause of isolated granulomatous appendicitis
Patients with isolated granulomatous appendicitis rarely progress to generalized inflammatory bowel disease
Lymphoid hyperplasia may cause ileal obstruction
Treatment
Usually self-limited in immunocompetent patients; require no therapy or supportive care
Patients presenting with appendicitis or bowel obstruction may require surgery
Prognosis
Excellent in immunocompetent patients
Immunocompromised or debilitated patients and those with iron overload at risk for more serious &/or chronic disease