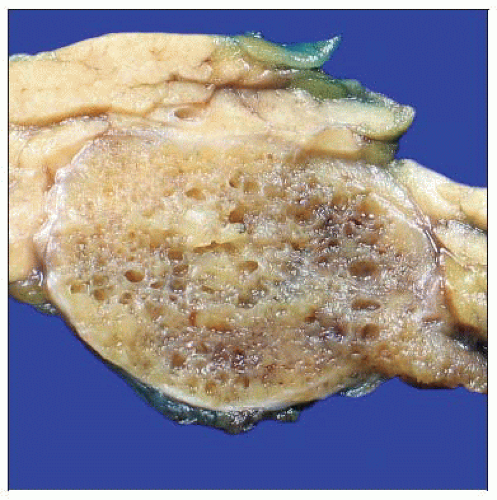
Well-differentiated Neuroendocrine Neoplasm, Pancreas
Vikram Deshpande, MD
Key Facts
Etiology/Pathogenesis
MEN1
von Hippel-Lindau syndrome
Tuberous sclerosis
Sporadic
Clinical Issues
Surgical resection remains mainstay of therapy for tumors confined to pancreas
Features associated with adverse outcome include
Mitosis > 2/10 HPF
Tumor necrosis
Vascular invasion
High Ki-67 labeling index
Microscopic Pathology
Monotonous population of round cells arranged in wide range of patterns including nested, trabecular, glandular, and solid
Ancillary Tests
Chromogranin and synaptophysin
Diffusely and strongly positive
Ki-67
Top Differential Diagnoses
Acinar cell carcinoma
Solid pseudopapillary neoplasm
Poorly differentiated endocrine carcinoma
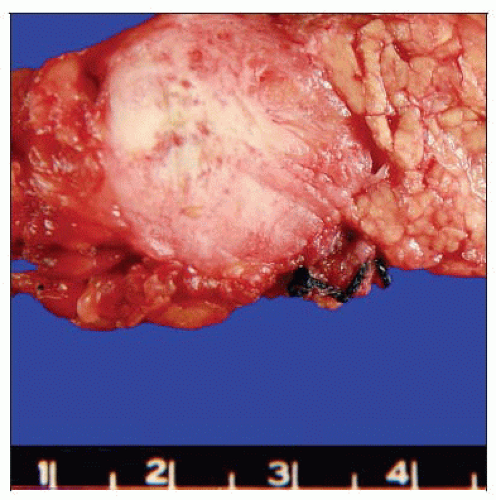 This well-circumscribed solid mass in the pancreas is typical of a well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumor. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Pancreatic endocrine neoplasm (PEN)
Synonyms
Pancreatic endocrine tumor
Islet cell tumor
Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor
Definitions
Low- to intermediate-grade neuroendocrine neoplasm of pancreas
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Syndromic
Multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome (MEN1)
von Hippel-Lindau syndrome
Tuberous sclerosis
Sporadic
Majority of cases are nonsyndromic and sporadic
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
Epidemiology
Peak incidence between 30-60 years
No significant gender predilection
Presenting symptoms
Abdominal pain
Jaundice
Asymptomatic, detected by imaging
Such incidentally detected pancreatic endocrine neoplasms are increasingly common
Endocrine function
Functioning tumors
Insulinoma
Glucagonoma
Somatostatinoma
Gastrinoma
Vipomas
Nonfunctional tumors
More common than functional tumors
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Surgical resection remains mainstay of therapy for tumors confined to pancreas
Enucleation is restricted to small tumors (typically < 2 cm)
Options for tumors metastatic to liver
Resection of primary and surgical debulking of metastatic tumor
Long-acting somatostatin analogs (octreotide and lanreotide)
Liver-directed therapy including embolization, chemoembolization, radiofrequency ablation
Novel agents such as inhibitor of VEGF, inhibitor of tyrosine kinase, and mTOR pathway
Prognosis
Outcome is variable
Histological and immunohistochemical features help estimate risk of aggressive behavior
Features associated with adverse outcome include
Mitosis > 2/10 HPF
Tumor necrosis
Vascular invasion
Perineural invasion
High Ki-67 labeling index
Cytokeratin 19 positive tumor
Size > 2 cm
IMAGE FINDINGS
CT Findings
Solid, or less commonly, solid and cystic, wellcircumscribed, enhancing lesion
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Solid, round to oval, well-circumscribed mass
Approximately 5% of tumors are cystic
Either multilocular or unicystic
Size
Tumors < 0.5 cm are termed microadenomas
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Monotonous population of round cells
Wide range of patterns including nested, trabecular, glandular, and solid
Nuclear chromatin is typically coarse with “salt and pepper” appearance
Less common cytoplasmic variations include oncocytic, vacuolated lipid-rich variant, and rhabdoid
Morphological appearance generally does not predict functional status
Exceptions to this rule
Amyloid deposits are indicative of insulinoma
Large nucleoli may be present
ANCILLARY TESTS
Immunohistochemistry
Chromogranin and synaptophysin
Diffusely and strongly positive
Recommended for confirmation of diagnosis
Other neuroendocrine markers, such as CD56, CD57, and NCAM are not specific for neuroendocrine differentiation
Cytokeratins
Positive for keratin 8 and 18
Ki-67
Along with mitotic counts, it is the only widely accepted predictive marker
Immunohistochemistry for peptide hormones
Rarely required for diagnosis
Nonfunctional tumors may stain for multiple peptides
Marker for PENs in metastatic setting
ISL1 positivity would support primary endocrine tumor in pancreas
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Acinar Cell Carcinoma
Acinar pattern suggests acinar cell carcinoma
Intracytoplasmic PAS-positive diastase-resistant granules are present
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree