Wegener Granulomatosis
Key Facts
Etiology/Pathogenesis
No definitive etiology is known for WG
Clinical Issues
Incidence
More common in adults, usually in 5th decade of life
Since WG is systemic and can affect any particular system; these sites may include
Upper and lower respiratory system
Genitourinary system, mainly kidney
Ocular system
Breast
Laboratory findings
c-ANCA is positive in nearly all cases of WG
p-ANCA is not as specific as c-ANCA, as it may be positive in other conditions
Leukocytosis
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate is usually elevated
Treatment
Cyclophosphamide and prednisone
Trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole
Prognosis
Untreated WG is fatal
Treated patients do relatively well, but remissions are common
Top Differential Diagnoses
Lymphomatoid granulomatosis
Usually shows atypical lymphoid proliferation
Churg-Strauss syndrome
Commonly associated with asthma
Infectious process
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Wegener granulomatosis (WG)
Definitions
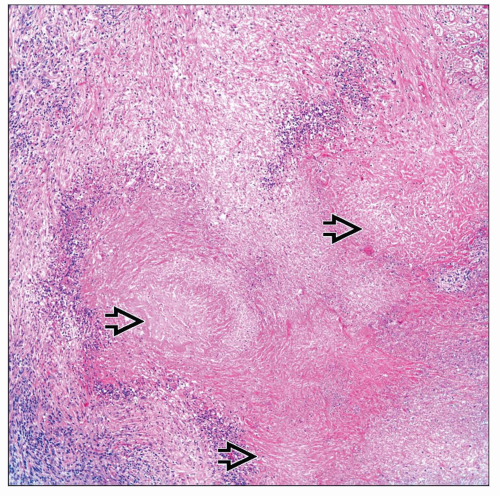
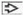
Systemic inflammatory process characterized by vasculitis and granulomatous reaction
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Etiology
No definitive etiology is known for WG
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Incidence of this condition varies and can be up to 8 per 1,000,000 people
Age
More common in adults, usually in 5th decade of life
Rarely occurs in young people or children
Gender
No apparent predilection
Ethnicity
No ethnic predilection
Site
Since WG process is systemic, it can affect any particular system
Sites may include
Upper and lower respiratory system
Genitourinary system, mainly kidney
Ocular system
Breast
Presentation
Rhinorrea
Oral and nasal ulcers
Cough
Dyspnea
Pleuritic pain
Hemoptysis
Laboratory Tests
Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies
Cytoplasmic antineutrophilic antibody (c-ANCA) is positive in nearly all cases of WG
Perinuclear antineutrophilic antibody (p-ANCA) not as specific as c-ANCA, as it may be seen positive in other conditions
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate is usually elevated
Leukocytosis
Thrombocytopenia
Anemia (normochromic-normocytic)
Treatment
Drugs
Cyclophosphamide and prednisone
Trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole
Prognosis
Untreated WG is fatal
Treated patients do relatively well, and remissions are common
Younger patients appear to fare better than older patients
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Multiple bilateral cavitary and solid pulmonary nodules
Areas of necrosis are usually present
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree