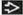Tuberous Sclerosis
Aleksandr Vasilyev, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Etiology/Pathogenesis
TSC1 gene, chromosome 9q34: Hamartin
TSC2 gene, chromosome 16p13: Tuberin
Chromosome 16p deletion may result in TSC2/PKD1 contiguous gene syndrome with early onset PKD
Clinical Issues
Major features
Facial angiofibromas, ungual or periungual fibromas
More than 3 hypomelanotic macules, shagreen patch
Retinal hamartomas, cortical tuber, subependymal nodule or astrocytoma
Cardiac rhabdomyoma, lymphangioleiomyomatosis, renal angiomyolipoma
Minor features
Multiple renal cysts, hamartomatous rectal polyps, retinal achromic patch, white matter radial migration tracts, bone cysts, gingival fibromas, “confetti” skin lesions, enamel pits
Microscopic Pathology
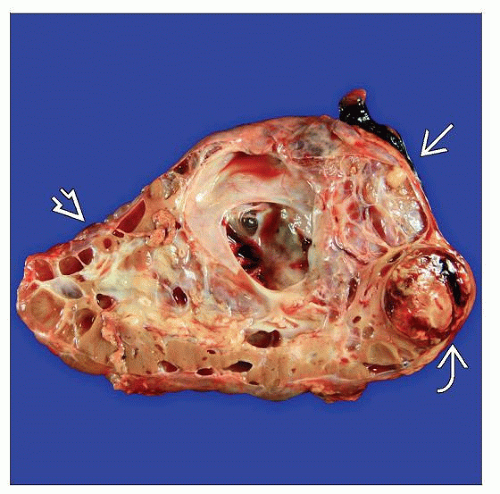
Angiomyolipomas and angiomyolipomatous change of renal parenchyma is most common finding
Cysts lined by large plump cells with deeply eosinophilic cytoplasm are characteristic of TSC
Renal cell carcinomas
Top Differential Diagnoses
ADPKD
VHL
Multicystic dysplasia
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Tuberous sclerosis (TSC)
Synonyms
Tuberous sclerosis complex
Definitions
Molecular disorder of hamartin of tuberin proteins resulting in hamartomatous lesions in skin, CNS, kidney, and other organs
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Molecular Pathology
TSC1 gene, chromosome 9q34: Hamartin
TSC2 gene, chromosome 16p13: Tuberin
Abnormal Pi3K: AKT, mTOR signaling
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree