Tuberculosis
Key Facts
Terminology
Lung infection caused by inhalation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Clinical Issues
Primary infection usually asymptomatic and leads to formation of the Ghon complex (apical nodule with calcification) and hilar lymphadenopathy
Progressive primary TB occurs when the primary foci do not involute and progress to disseminated, cavitary lesions
Most common mechanism of secondary TB is reactivation of a latent focus of infection
Often associated with chronic, debilitating diseases or immunosuppressive states (AIDS, transplant, cancer, diabetes, alcoholism)
Microscopic Pathology
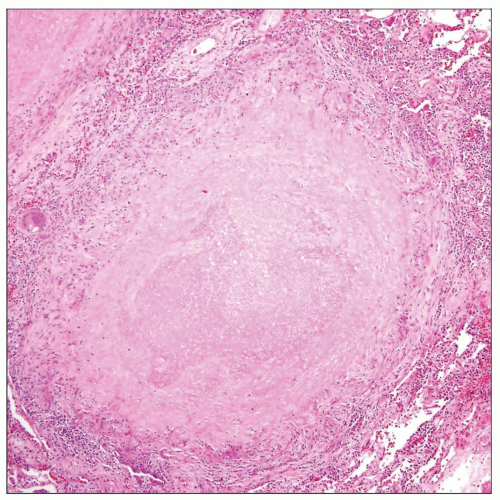
Basic pathologic manifestation of TB is granulomatous inflammation, with necrotizing, palisading epithelioid granulomas
Palisading granulomas can progress to complete fibrosis and calcification
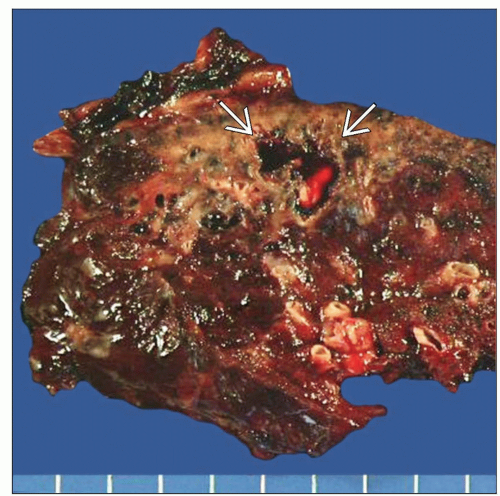
Necrotizing granulomas may enlarge to form cavities with central liquefaction that may range from 3-10 cm in diameter
Mycobacteria are slender rods measuring 4 µm in length; they cannot be visualized on routine histology and require special stains
Ancillary Tests
Best stain for M. tuberculosis is the Ziehl-Neelsen stain, which stains acid-fast bacilli (AFB)
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Tuberculosis (TB)
Definitions
Lung infection caused by inhalation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Infectious Agents
Tuberculosis transmitted through inhalation of airborne droplets contaminated with the bacillus
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
About 1/3 of the world’s population is infected with tuberculosis; more prevalent in underdeveloped countries
About 10% of HIV-infected patients will develop active disease annually
Presentation
Primary TB is defined as an infection occurring in a previously uninfected host
Primary infection is usually asymptomatic and leads to formation of the Ghon complex (apical nodule with calcification) and hilar lymphadenopathy
Progressive primary TB occurs when the primary foci do not involute and progress to disseminated, cavitary lesions
Fulminant infection with dissemination via the bloodstream can lead to miliary tuberculosis
Secondary or chronic TB is defined as active disease developing in a previously sensitized host
Most common mechanism of secondary TB is reactivation of a latent focus of infection
May also be the result of massive reinfection from external source
Symptoms include cough, weight loss, fatigue, and fever with cavitary lesions in the upper lobes
Often associated with chronic, debilitating diseases or immunosuppressive states (AIDS, transplant, cancer, diabetes, alcoholism)
Natural History
Symptomatic TB is a disease mainly of debilitated and immunosuppressed patients
TB is a major cause of death in individuals infected with HIV
Treatment