Class
- Antiepileptic drug (AED)
Topiramate
Commonly Prescribed for
(FDA approved in bold)
- Partial-onset seizures (adjunctive; adults and pediatric patients age 2–16)
- Primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures (adjunctive; adults and pediatric patients age 2–16)
- Migraine prophylaxis
- Drop attacks associated with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome
- Obesity
- Bipolar disorder
- Binge-eating disorder/bulimia
- Cluster headache prophylaxis
- Idiopathic intracranial hypertension
- Alcohol dependence
- Essential tremor
Topiramate
 How the Drug Works
How the Drug Works
There are multiple mechanisms of action, and it is uncertain which of these give the drug its effectiveness
- Augmentation of the GABA-A receptor
- Sodium channel blocker
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, isoenzymes II and IV
- Glutamate receptor (specifically the AMPA/kainate subtype) antagonist
- May work by inhibiting protein kinase activity
- Possible serotonin activity on 5-HT2C receptors
Topiramate
How Long Until It Works
- Seizures – may decrease by 2 weeks
- Migraines – may decrease in as little as 2 weeks, but can take up to 3 months on a stable dose to see full effect
Topiramate
If It Works
- Seizures – goal is the remission of seizures. Continue as long as effective and well-tolerated. Consider tapering slowly, stopping after 2 years without seizures, depending on the type of epilepsy
- Migraine – goal is a 50% or greater reduction in migraine frequency or severity. Consider tapering or stopping if headaches remit for more than 6 months or if considering pregnancy
Topiramate
If It Doesn’t Work
- Increase to highest tolerated dose
- Epilepsy: consider changing to another agent, adding a second agent or referral for epilepsy surgery evaluation
- Migraine: address other issues, such as medication-overuse, other coexisting medical disorders, such as anxiety, and consider changing to another agent or adding a second agent
Topiramate
 Best Augmenting Combos for Partial Response or Treatment-Resistance
Best Augmenting Combos for Partial Response or Treatment-Resistance
- For some patients with epilepsy or migraine, low-dose polytherapy with 2 or more drugs may be better tolerated and more effective than high-dose monotherapy
- Epilepsy: keep in mind drug interactions and their effect on levels
- Migraine: consider beta-blockers, antidepressants, natural products, other AEDs, and non-medication treatments such as biofeedback to improve headache control
Topiramate
Tests
- Mild to moderate decreases in bicarbonate can occur with topiramate, but are uncommon reasons for discontinuation. Routine screening for metabolic acidosis is not recommended
Adverse Effects (AEs)
Topiramate
How Drug Causes AEs
- CNS AEs may be caused by sodium channel blockade or GABA-A receptor augmentation
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibition causes paresthesias, metabolic acidosis; may lead to kidney stones
Topiramate
Notable AEs
Topiramate
 Life-Threatening or Dangerous AEs
Life-Threatening or Dangerous AEs
- Metabolic acidosis
- Kidney stones (calcium phosphate)
- Narrow angle-closure glaucoma (rare)
- Fever, dehydration and lack of sweating (more common in children)
Topiramate
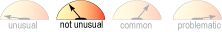
Weight Gain
- Unusual
Topiramate
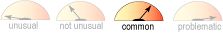
Sedation
- Common
Topiramate
What to Do About AEs
- AEs often decrease or remit after a longer time on a stable dose
- Paresthesias may respond to high potassium diets or potassium tablets
- Cognitive AEs tend to improve with small decreases in dose
- For patients with kidney stones, check the type of stone. Topiramate usually causes calcium phosphate stones
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


