Class
- Skeletal muscle relaxant, centrally acting; alpha-2 agonist
Tizanidine
Commonly Prescribed for
(FDA approved in bold)
- Acute and intermittent management of increased muscle tone related to spasticity
- Spasticity can result from neurological conditions, such as multiple sclerosis (MS), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), primary lateral sclerosis, and spinal cord injury
- Migraine prophylaxis
- Neck pain/lower back pain
- Myofascial pain
Tizanidine
 How the Drug Works
How the Drug Works
- Alpha-2 adrenergic agonist (mostly at alpha-2A receptors) which also acts at imidazoline receptors. Reduces spasticity by increasing presynaptic inhibition of motor neurons
Tizanidine
How Long Until It Works
- Pain – hours-weeks
Tizanidine
If It Works
- Slowly titrate to most effective tolerated dose
Tizanidine
If It Doesn’t Work
- Increase to highest tolerated dose. If ineffective, gradually reduce dose and consider alternative medications
Tizanidine
 Best Augmenting Combos for Partial Response or Treatment-Resistance
Best Augmenting Combos for Partial Response or Treatment-Resistance
- Botulinum toxin is effective, especially as an adjunct for focal spasticity, i.e., post-stroke or head injury affecting the upper limbs. For conditions with multiple areas of spasticity, i.e., cerebral palsy, this combination can be very useful
- May be used carefully in combination with baclofen, although additive sedation can be problematic
- Use other centrally acting muscle relaxants with caution due to potential additive CNS depressant effect
Tizanidine
Tests
- Monitor liver and renal function at baseline and at 1, 2, and 3 months. Monitor hepatic enzymes at 6 months and periodically after that
Adverse Effects (AEs)
Tizanidine
How Drug Causes AEs
- Related to alpha-2 adrenergic agonist effect causing hypotension. Increased sedation may be due to actions at the imidazoline receptors
Tizanidine
Notable AEs
- Dry mouth, weakness, and somnolence are most common. Dizziness, hypotension, and elevation of hepatic transaminases
- Hallucinations (usually visual) occur in about 3% of patients
Tizanidine
 Life-Threatening or Dangerous AEs
Life-Threatening or Dangerous AEs
- Bradycardia and prolongation of QTc interval with higher doses. Tizanidine withdrawal can cause rebound hypertension
Tizanidine
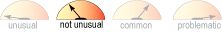
Weight Gain
- Not unusual
Tizanidine
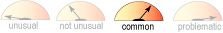
Sedation
- Common
Tizanidine
What to Do About AEs
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


