Thrombotic Microangiopathy, Drugs
Neeraja Kambham, MD
Key Facts
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Direct endothelial injury or immune mediated
> 60 drugs reportedly associated with TMA, but often difficult to establish causative role
Chemotherapeutic agents
Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) therapy
Immunomodulators (CNi, mTORi)
Antiplatelet drugs of thienopyridine family
Quinine
Clinical Issues
Proteinuria ranges from mild to nephrotic
Mild renal insufficiency or acute renal failure
Worsening hypertension
Treatment
Withdrawal of offending drug
Plasma exchange helpful in some settings
Better prognosis if TMA is limited to kidney
Diagnosis
Thrombocytopenia
Schistocytes on peripheral smear
Serum lactate dehydrogenase may be elevated
ADAMTS13 levels may be low in TMA due to thienopyridines
Microscopic Pathology
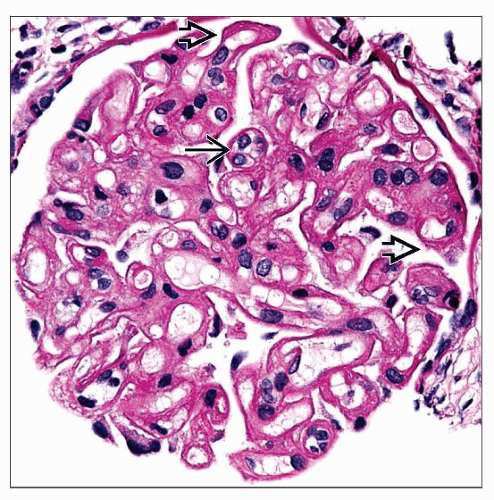
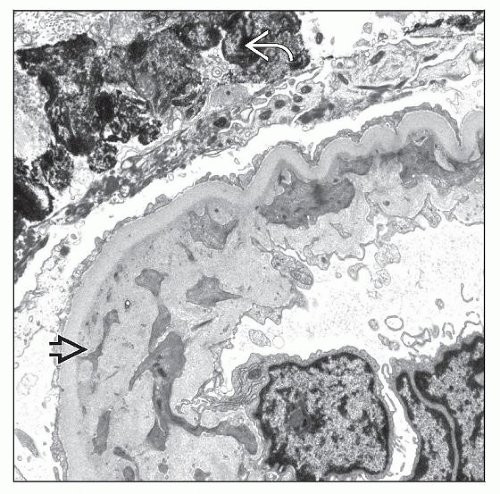
Fibrin thrombi and endothelial swelling in glomeruli and arterioles
Reduplicated GBM in chronic phase
Top Differential Diagnoses
TMA due to other causes
Antibody-mediated rejection in renal allografts
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA)
Definitions
Atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) caused by drugs
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Mechanism of TMA Induction
Direct endothelial injury due to dose-related toxicity
Immune-mediated with induction of autoantibodies
Implicated Drugs
> 60 drugs reportedly associated with TMA, but often difficult to establish causative role
Chemotherapeutic agents
Mitomycin-C
Dose-dependent endothelial toxicity
Median time from last dose to development of TMA is 75 days
Gemcitabine
Endothelial damage causes TMA
Median time from initiation of therapy to development of TMA is 6-8 months
Other agents include bleomycin, cisplatin, daunorubicin, vinblastine, deoxycoformycin
Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) therapy
VEGF receptor blockers (bevacizumab, VEGF trap)
VEGF synthesis by podocytes is needed for survival of glomerular endothelial cells that express VEGF receptors
TMA due to endothelial damage can occur from 1 week to 9 months after initiation of therapy
Symptoms can occur after discontinuation of drug
Sunitinib
Inhibits receptor tyrosine kinases such as VEGF
Endothelial damage causes TMA
Immunomodulators
Calcineurin inhibitors (CNi)
Cyclosporine and tacrolimus are associated with TMA
Direct endothelial toxicity due to reduced prostacyclin synthesis or reduced formation of activated protein C
Toxicity often seen in 1st 6 months after transplantation
Sirolimus
Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) regulates production of VEGF in addition to its effects on cell cycle
Inhibition of VEGF results in endothelial damage
Toxicity is exacerbated by concomitant calcineurin inhibitors
Antiplatelet drugs of thienopyridine family
Ticlopidine and clopidogrel
TMA occurs within 1st month (or even within 1st week) of exposure
Cause direct endothelial toxicity
ADAMTS13 levels can be severely deficient (< 5%) in some cases, and inhibitor to ADAMTS13 has been detected
Miscellaneous drugs
Quinine
Used for treatment of malaria and nocturnal leg cramps; found in herbal supplements and tonic water
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree