Chapter 6 The heart and cardiovascular system
CLINICAL HISTORY
Breathlessness
Patients with heart disease that causes breathlessness experience it during physical exertion (exertional dyspnoea) and sometimes when they lie flat in bed (positional dyspnoea or orthopnoea). Sometimes, the patient awakes from sleep extremely breathless and has to sit up gasping for breath (paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnoea).
Chest pain
CHEST PAIN CAUSED BY MYOCARDIAL ISCHAEMIA
more coronary arteries. Less often, angina is a symptom of aortic stenosis or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Rarely, syndrome X describes angina with normal coronary arteries. Prinzmetal’s angina is due to coronary spasm.
PALPITATION
Palpitation is defined as abnormal awareness of the heart beat. It is often helpful to ask the patient to tap out the heart rhythm on the table.
SYNCOPE (FAINTING, BLACKOUTS)
In fainting, loss of consciousness is seldom abrupt; the patient looks pale both before and immediately afterwards. In contrast, syncope caused by heart block is often sudden, unheralded and complete. The patient looks pale while collapsed; recovery (which is often equally sudden) may be heralded by a pink flush. Vertebrobasilar insufficiency is common in elderly patients: there may be restricted neck movement and active or passive movements of the neck may precipitate symptoms.
A FRAMEWORK FOR ROUTINE PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
Hands in heart disease
The fingernails may show splinter haemorrhages (Fig. 6.1) in subacute infective endocarditis and finger clubbing in endocarditis or cyanotic congenital heart disease.
Feeling the peripheral pulses
BRACHIAL PULSE
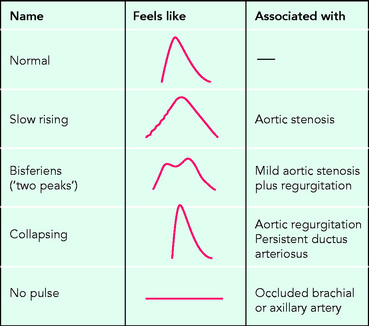
Use the thumb of the right hand, applied to the front of the elbow just medial to the biceps tendon with the fingers cupped round the back of the elbow. Figure 6.2 illustrates the different pulse waveforms.
CAROTID PULSE
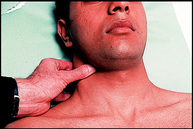
The best way to feel the patient’s right carotid artery is to locate the tip of the examiner’s left thumb against the patient’s larynx (Fig. 6.3). In severe aortic stenosis, there is characteristically a slow rising carotid pulse. Another sign best appreciated at the carotid is the jerky pulse of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Measuring blood pressure
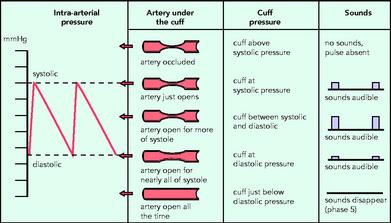
The generation of the Korotkoff sounds is shown diagrammatically in Figure 6.4.
 Emergency: Severe hypotension (shock)
Emergency: Severe hypotension (shock)
Emergency medical assessment of the patient with severe hypotension (shock)

 Differential diagnosis: Dyspnoea
Differential diagnosis: Dyspnoea Questions to ask: Breathlessness
Questions to ask: Breathlessness Symptoms and signs: New York Heart Association classification of heart failure
Symptoms and signs: New York Heart Association classification of heart failure Questions to ask: Angina
Questions to ask: Angina Symptoms and signs: Anginal pain
Symptoms and signs: Anginal pain Differential diagnosis: Chest pain at rest
Differential diagnosis: Chest pain at rest Questions to ask: Palpitation
Questions to ask: Palpitation Differential diagnosis: Palpitation
Differential diagnosis: Palpitation Differential diagnosis: Stokes–Adams versus epilepsy
Differential diagnosis: Stokes–Adams versus epilepsy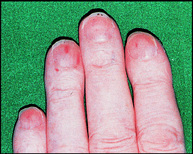
 Differential diagnosis: Systemic hypertension
Differential diagnosis: Systemic hypertension Differential diagnosis: Hypotension
Differential diagnosis: Hypotension

