Class
- Antiadrenergic, antidopaminergic, synaptic vesicle blocker, antimonoaminergic
Tetrabenazine
Commonly Prescribed for
(FDA approved in bold)
- Chorea in Huntington’s disease (HD)
- Dyskinesias in HD
- Psychosis
- Hemiballism
- Dystonia (especially tardive)
- Myoclonus
- Gilles de la Tourette syndrome (GTS) or tics
- Hypertension
Tetrabenazine
 How the Drug Works
How the Drug Works
- Depleting agent that reversibly depletes stores of monoamines (dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin, and histamine) from nerve terminals and blocks post-synaptic dopamine receptors. Effectiveness is likely related to dopamine depletion
Tetrabenazine
How Long Until It Works
- Usually less than 1 week
Tetrabenazine
If It Works
- In neurologic conditions, continue to assess effect of the medication, determine if still needed and adjust to optimal dose
Tetrabenazine
If It Doesn’t Work
- Chorea: Consider benzodiazepines and anticonvulsants (valproate). Neuroleptics are usually effective. Reserpine is an alternative depleting agent
- Generalized dystonia: Anticholinergics, baclofen, or benzodiazepines may be effective. Surgical treatments (including pallidotomy, thalamotomy, deep brain stimulation, myotomy, rhizotomy, or peripheral denervation) are reserved for refractory cases
- GTS/tics – Neuroleptics and alpha-2 adrenergic agonists are often effective
Tetrabenazine
 Best Augmenting Combos for Partial Response or Treatment-Resistance
Best Augmenting Combos for Partial Response or Treatment-Resistance
- Chorea – combine with anticonvulsants, neuroleptics, or benzodiazepines
- Dystonia – combine with anticholinergics or benzodiazepines
- GTS/tics – Combine with neuroleptics for refractory cases
Tetrabenazine
Tests
- At doses of 50 mg or greater, test patients for the CYP-450 2D6 gene to determine if they are poor, intermediate, or extensive metabolizers
Adverse Effects (AEs)
Tetrabenazine
How Drug Causes AEs
- Related to monoamine depletion
Tetrabenazine
Notable AEs
- Drowsiness, fatigue, dizziness, depression, anxiety, insomnia
- Parkinsonism, akathisia, orthostatic hypotension, nausea
- Upper respiratory tract infection, dyspnea, dysuria
Tetrabenazine
 Life-Threatening or Dangerous AEs
Life-Threatening or Dangerous AEs
- Falls and resulting trauma
- Neuroleptic malignant syndrome
- Parkinsonism and extrapyramidal tract dysfunction (less common than neuroleptics)
- QTc prolongation (usually mild)
- Dysphagia
Tetrabenazine
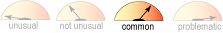
Weight Gain
- Common
Tetrabenazine
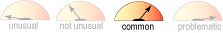
Sedation
- Common
Tetrabenazine
What to Do About AEs
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


