Synovial Sarcoma
Satish K. Tickoo, MD
Victor E. Reuter, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Synovial sarcoma (SS)
Mesenchymal spindle cell tumor with rare epithelial differentiation characterized by specific chromosomal translocation t(X;18)(p11;q11)
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Primary renal synovial sarcoma shares characteristic SYT-SSX gene fusion with its more common soft tissue counterpart
Clinical Issues
Rare primary mesenchymal tumor; not more than 50 cases described
Concurrent or subsequent metastases very frequent
Lung is most commonly reported site of metastasis
Macroscopic Features
Most of these tumors are large, necrotic, and cystic
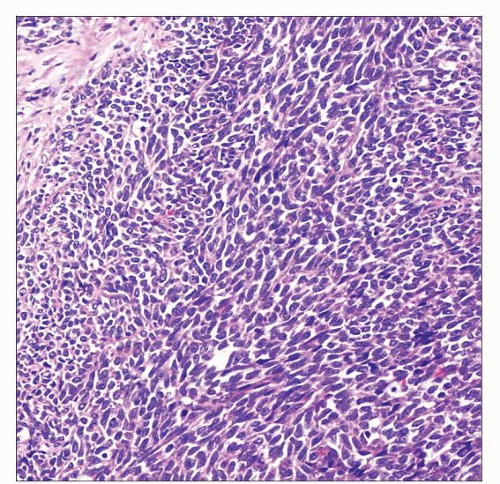
Microscopic Pathology
Most renal synovial sarcomas show monophasic spindle cell histology
Intratumoral cysts common (> 80% with cysts on microscopy)
Ancillary Tests
Frequently positive for bcl-2, CD99, and vimentin
In some, focal or rare cell positivity for EMA/MUC1 and cytokeratins (EMA more often than cytokeratins)
Top Differential Diagnoses
Primitive neuroectodermal tumor
Blastemal Wilms tumor
Cellular mesoblastic nephroma
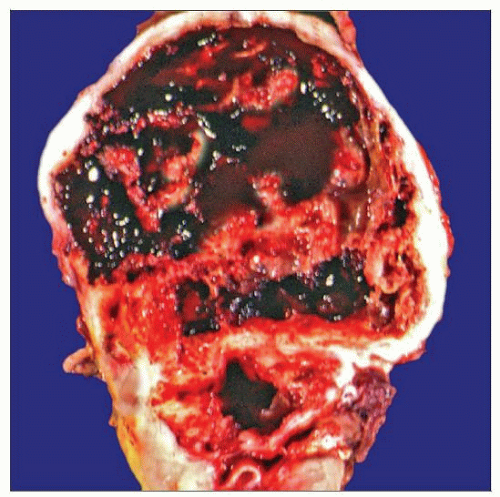 Primary renal synovial sarcoma shows the typical features of the tumor: Large size, extensive necrosis, cystic change, and hemorrhage. Cysts are grossly observed in 2/3 of the cases. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Synovial sarcoma (SS)
Definitions
Mesenchymal spindle cell tumor with rare epithelial differentiation characterized by specific chromosomal translocation t(X;18)(p11;q11)
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Molecular Features
Primary renal synovial sarcoma shares characteristic SYT-SSX gene fusion with its more common soft tissue counterpart
Unlike predominance of SYT-SSX1 fusion in soft tissue SS, most reported renal SS have shown SYT-SSX2 gene fusion
SYT-SSX2 fusion correlates with monophasic histology in soft tissue
This may explain predominance of monophasic spindle cell morphology of SS in kidney
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Rare primary mesenchymal tumor; not more than 50 cases described
Age
Range: 20-61 years (median: 35 years)
Gender
Almost equal M:F incidence
Presentation
Presentation is similar to that of other mass lesions
Cases may present with symptoms related to metastases
Treatment
Managed with combination of surgery and adjuvant chemotherapy
Response rates to ifosphamide and doxorubicinbased chemotherapy ˜ 24%
Prognosis
Aggressive tumors
Concurrent or subsequent metastases very frequent
Lung is most commonly reported site of metastasis
Other sites of metastasis include regional lymph nodes, liver, bones, and abdominal cavity soft tissues
1 of few sarcomas with metastases to lymph nodes
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Most tumors are large, necrotic, and grossly cystic
Approximately 2/3 show cysts on gross evaluation